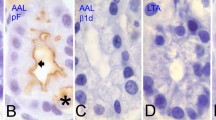
Summary
We employed sialidase procedures followed by lectin stainings combined with oxidizing and deacetylating agents to visualize the distribution and sequentiate sialoglycoconjugates in the bovine submandibular gland. In particular we evidenced in acinar and ductal cells the dishomogeneous presence of sialic acids acetylated in the polyhydroxy side chain (C7, C8, C9), whereas O-acetyl substituents at position C1 and/or C4 were not found. Sialoglycoderivatives were also differentiated by the occurrence of penultimate sugars; indeed the dimers sialic acid-(α2→3,6)-β-galactose and sialic acid-(α2→6)-α-N-acetylgalactosamine were identified. Using such technique we supported further the possibility to develop methods for the identification of the positions of Oacetyl groups and the reconstruction of terminal disaccharides within surface and cytoplasm glycoconjugates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accili D, Menghi G, Scocco P, Bondi AM (1990) Lectin histochemistry for differentiating glycoconjugates secreted by the bovine submandibular gland. 53° Congr. Unione Zoologica italiana. ed. U.Z.I. Palermo, p 416
Bertolini M, Pigman W (1970) The existence of oligosaccharides in bovine and ovine submaxillary mucins. Carbohydr Res 14:53–63
Corfield AP, Schauer R (1982) Metabolism of sialic acids. In: Schauer R (ed) Sialic acids. Chemistry, metabolism and function. Cell Biology Monographs, vol. 10. Springer, Wien, pp 194–261
Culling CFA, Reid PE (1982) Histochemistry of sialic acids. In: Schauer R (ed) Sialic acids. Chemistry, metabolism and function. Cell Biology Monographs, vol. 10, Springer, Wien, pp 173–193
D'Arcy SM, Donoghue CM, Koeleman CAM, Van Den Eijnden DH, Savage AV (1989) Determination of structure of a novel acidic oligosaccharide with blood-group activity isolated from bovine submaxillary-gland mucin. Biochem J 260:389–393
Goldstein IJ, Poretz RD (1986) Isolation and chemical properties of lectins. In: Liener IE, Sharon N, Goldstein IJ (eds) The lectins Academic Press, New York, pp 33–247
Gottschalk A (1957) The structure of the prosthetic group of bovine submaxillary gland mucoprotein. Biochem Biophys Acta 24:649–650
Ledeen RW, Yu RK (1976) Sialic acid chemistry. In: Rosemberg A, Schengrund CL (eds) Biological roles of sialic acids. Plenum Press, New York, pp 1–48
Leppi TJ, Spicer SS (1967) The histochemistry of carbohydrate-rich substances in certain ungulate salivary glands. Anat Rec 159:179–192
Menghi G, Bondi AM, Materazzi G (1985) Distribution of lectin binding sites in rabbit oviduct. Anat Rec 211:279–284
Menghi G, Accili D, Bondi AM, Gabrielli G (1989) Enzymatic degradation and quantitative lectin labeling for characterizing glycoconjugates which act as lectin acceptors in cat submandibular gland. Histochemistry 90:331–338
Menghi G, Ottaviani E, Accili D, Bolognani Fantin AM (1991) Identification of muramyl derivatives in Mollusca Gastropoda tissue. Histochemistry 96:209–216
Montreuil J (1980) Primary structure of glycoprotein glycans: basis for the molecular biology of glycoproteins. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem 37:157–213
Nisizawa K, Pigman W (1959) The composition and properties of the mucin clot from cattle submaxillary glands. Arch Oral Biol 1:161–170
Pigman W (1977) Submandibular and sublingual glycoproteins. In: Horowitz MI, Pigman W (eds) The glycoconjugates, vol 1. Academic Press, New York, pp 137–152
Pigman W, Hashimoto Y (1963) Composition of bovine submaxillary mucins. Biochim Biophys Acta 69:579–580
Quintarelli G, Tsuiki S, Hashimoto Y, Pigman W (1960) Histochemical studies of bovine salivary gland mucins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2:423–426
Quintarelli G, Tsuiki S, Hashimoto Y, Pigman W (1961) Studies of sialic acid-containing mucins in bovine submaxillary and rat sublingual glands. J Histochem Cytochem 9:176–183
Ravetto C, Galluzzo F, Siervo R (1964) On the presence of a ganglioside in bovine submaxillary gland. J Histochem Cytochem 12:791–792
Reid PE, Culling CFA, Dunn WL (1978) A histochemical method for the identification of 9-O-acyl sialic acids. An investigation of bovine submaxillary gland and intestinal mucins. J Histochem Cytochem 26:187–192
Reid PE, Needham J, Owen DA (1991) Histochemical identification of 9-O-acyl sialic acids: studies of bovine submandibular and rat sublingual gland and human colon. Histochem J 23:149–154
Reuter G, Pfeil L, Schauer R, Kamerling JP, Versluis C, Vliegenthart JFG (1983) Identification of new sialic acids derived from glycoprotein of bovine submandiblar gland. Eur J Biochem 134:139–143
Schauer R (1978) Characterization of sialic acids. In: Ginsburg V (ed) Methods in enzymology, vol 50. Academic Press, New York, pp 65–89
Schauer R (1982) Chemistry, metabolism and biological functions of sialic acids. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem 40:131–234
Schauer R (1987) Analysis of sialic acids. In: Ginsburg V (ed) Methods in enzymology, vol 138. Academic Press, New York, pp 132–161
Schulte BA, Spicer SS (1985) Histochemical methods for characterizing secretory and cell surface sialoglycoconjugates. J Histochem Cytochem 33:427–438
Schulte BA, Spicer SS, Miller RL (1984) Histochemical localization of sialoglycoconjugates with a sialic acid-specific lectin from the slug Limax flavus. Histochem J 16:1125–1132
Schulte BA, Spicer SS, Miller RL (1985) Lectin histochemistry of secretory and cell-surface glycoconjugates in the ovine submandibular gland. Cell Tissue Res 240:57–66
Shackleford JM, Klapper CE (1962) Structure and carbohydrate histochemistry of mammalian salivary glands. Am J Anat 111:25–47
Shackleford JM, Wilborn WH (1968) Structural and histochemical diversity in mammalian salivary glands. Ala J Med Sci 5:180–204
Svennerholm L (1962) Quantitative estimation of sialic acid. III. An anion exchange resin method. Acta Chem Scand 37:105–107
Taatjes DJ, Roth J, Peumans W, Goldstein IJ (1988) Elderberry bark lectin-gold techniques for the detection of Neu5Ac (α2,6) Gal/GalNAc sequences: applications and limitations. Histochem J 20:478–490
Tettamanti G, Pigman W (1968) Purification and characterization of bovine and ovine submaxillary mucins. Arch Biochem Biophys 124:41–50
Tsuji T, Osawa T (1986) Carbohydrate structures of bovine submaxillary mucin. Carbohydr Res 151:391–402
Warren L (1959) The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acid. J Biol Chem 234:1971–1975
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menghi, G., Accili, D., Scocco, P. et al. Sialoglycoderivatives of bovine submandibular gland identified in situ by histochemical techniques combined with lectins. Histochemistry 97, 397–403 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00270386
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00270386