Summary
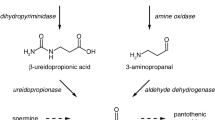
Three unlinked genes where mutation can lead to D(+)-pantothenic acid auxotrophy in Aspergillus nidulans have been identified. pantoA is probably the structural gene for pantothenate synthetase (EC 6.3.2.1) whilst pantoB and pantoC are involved in the syntheses of D-pantoic acid and β-alanine, respectively. A pantoC− mutant is tentatively considered to be bloaked in conversion of 5,6-dihydrouracil to β-ureidopropionate. An alternative route of β-alanine biosynthesis occurs by the transamination of malonic semialdehyde, catalysed by GABA transaminase. The possibility that β-alanine can be replaced by certain structurally related compounds and yet nevertheless yield biologically active coenzyme A analogues is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arst, H.N., Jr.: Integrator gene in Aspergillus nidulans. Nature (Lond.) 262, 231–234 (1976)
Arst, H.N., Jr.: Some genetical aspects of ornithine, metabolism in Aspergillus nidulans. Molec. gen. Genet. 151, 105–110 (1977a)
Arst, H.N., Jr.: The basis for an apparent auxotrophy for reduced sulphur metabolites in sF− mutants of Aspergillus nidulans. Genet. Res. 30, 207–210 (1977b)
Arst, H.N., Jr., Bailey, C.R.: The regulation of carbon metabolism in Aspergillus nidulans. In: Genetics and physiology, of Aspergillus (J.E. Smith and J.A. Pateman, eds.), pp. 131–146. London: Academic Press 1977
Arst, H.N., Jr., Cove, D.J.: Methylammonium resistance in Aspergillus nidulans. J. Bact. 98, 1284–1293 (1969)
Arst, H.N., Jr., Cove, D.J.: Nitrogen metabolite repression in Aspergillus nidulans. Molec. gen. Genet. 126, 111–141 (1973)
Arst, H.N., Jr., MacDonald, D.W.: A gene cluster in Aspergillus nidulans with an internally located cis-acting regulatory region. Nature (Lond.) 254, 26–31 (1975)
Asen, S., Thompson, J.F., Morris, C.J., Irreverre, F.: Isolation of β-aminoisobutyric acid from bulbs of Iris tingitana var. Wedgewood. J. biol. Chem. 234, 343–346 (1959)
Bal, J., Kajtaniak, E.M., Pieniazek, N.J.: 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide: a good mutagen for Aspergillus nidulans. Mutation Res. 56, 153–156 (1977)
Britten, R.J., Davidson, E.H.: Gene regulation for higher cells: a theory. Science 165, 349–357 (1969)
Clutterbuck, A.J.: Aspergillus nidulans. In: Handbook of genetics, Vol. I, pp. 447–510. (R.C. King, ed.). New York: Plenum Press 1974
Cove, D.J.: The induction and repression of nitrate reductase in the fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 113, 51–56 (1966)
Hynes, M.J.: A cis-dominant regulatory mutation affecting enzyme induction in the eukaryote Aspergillus nidulans. Nature (Lond.) 253, 210–212 (1975)
Käfer, E.: An 8-chromosome map of Aspergillus nidulans. Advanc. Genet. 9, 105–145 (1958)
Käfer, E.: Origins of translocations in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics 52, 217–232 (1965)
Käfer, E.: Meiotic and mitotic recombination in Aspergillus and its chromosomal aberrations. Advanc. Genet. 19, 33–131 (1977)
Kakimoto, Y., Armstrong, M.D.: The preparation and isolation of D-(-)-β-aminoisobutyric acid. J. biol. Chem. 236, 3282–3286 (1961)
Maas, W.K., Davis, B.D.: Pantothenate studies. I. Interference by D-serine and L-aspartic acid with pantothenate synthesis in Escherichia coli. J. Bact. 60, 733–745 (1950)
McCully, K.S., Forbes, E.: The use of p-fluorephenylalanine with “master strains” of Aspergillus nidulans for assigning genes to linkage groups. Genet. Res. 6, 352–359 (1965)
Ortega, M.V., Cardenas, A., Ubiera, D.: panD, a new chromosomal locus of Salmonella typhimurium for the biosynthesis of β-alanine. Molec. gen. Genet. 140, 159–164 (1975)
Penfold, H.A., Bailey, C.R., Arst, H.N., Jr.: An integrator gene in Aspergillus nidulans: regulatory and metabolic roles of ω-amino acids. Heredity 39, 433 (1977)
Pontecorvo, G., Roper, J.A., Hemmons, L.A., Macdonald, K.D., Bufton, A.W.J.: The genetics of Aspergillus nidulans. Advanc. Genet. 5, 141–238 (1953)
Rever, B.M.: Biochemical and genetical studies of inorganic nitrogen metabolism in Aspergillus nidulans. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Cambridge (1965)
Slotnick, I.J.: Dihydrouracil as a growth factor for a mutant strain of Escherichia coli. J. Bact. 72, 276–277 (1956)
Slotnick, I.J., Weinfeld, H.: Dihydrouracil as a growth factor for mutant strains of Escherichia coli. J. Bact. 74, 122–125 (1957)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by W. Gajewski
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arst, H.N. GABA transminase provides an alternative route of β-alanine synthesis in Aspergillus nidulans . Molec. Gen. Genet. 163, 23–27 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00268960
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00268960