Summary
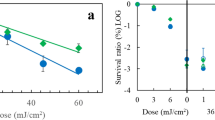
Photodynamically induced DNA damage in Serratiaphase ϰ may be repaired by the host cell. The extent of this host cell reactivation (HCR) depends on the photosensitizing dye used: HCR of proflavine+visible light induced DNA damage appears to be more efficient than the one of DNA damage induced by methylene blue+visible light. This significant difference in HCR is not due to a preferential inhibition of the enzymes of DNA dark repair by either one of the dyes injected into the host cell along with the phage's genome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, M. H.: Bacteriophages, p. 443–522. New York: Interscience Publ. 1959.
Alper, T., Hodgkins, B.: “Excision repair” and dose-modification: Questions raised by radiobiological experiments with acriflavine. Mutation Res. 8, 15–23 (1969).
Bellin, J. S., Yankus, C. A.: Effects of photodynamic degradation on the viscosity of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 112, 363–371 (1966).
Böhme, H.: Absence of repair of photodynamically induced damage in two mutants of Proteus mirabilis with increased sensitivity to monofunctional alkylating agents. Mutation Res. 6, 166–168 (1968).
— Geissler, E.: Repair of lesions induced by photodynamic action and by ethyl methanesulfonate in E. coli. Molec. Gen. Genetics 103, 228–232 (1968).
Brendel, M.: Induction of mutation in phage T4 by extracellular treatment with methylene blue and visible light. Molec. Gen. Genetics 101, 111–115 (1968).
— Kaplan, R. W.: Photodynamische Mutationsauslösung und Inaktivierung beim Serratia-phagen ϰ durch Methylenblau und Licht. Molec. Gen. Genetics 99, 181–190 (1967).
—: Photodynamische Inaktivierung des E. coliphagen T4: Untersuchung der Kreuzungsreaktivierung und des Schutzeffektes von Spermin. Z. Vererbungsl. 98, 41–48 (1966).
Calberg-Bacq, C. M., Delmelle, M., Duchesne, J.: Inactivation and mutagenesis due to the photodynamic action of acridines and related dyes on extracellular bacteriophage T4B. Mutation Res. 6, 15–24 (1968).
Cramer, W. A., Uretz, R. B.: Acridine orange-sensitized photoinactivation of T4 bacteriophage I. Parameter affecting phage sensitivity to visible light. Virology 29, 462–468 (1966a).
—: Acridine orange-sensitized photoinactivation of T4 bacteriophage II. Genetic studies with photoinactivated phage. Virology 29, 469–479 (1966b).
Cummings, D. J., Kozloff, L. M.: Various properties of the head protein of T2 bacteriophage. J. molec. Biol 5, 50–62 (1962).
Feiner, R. R., Hill, R. F.: Effect of basic dyes on host-cell reactivation of ultra-violet-irradiated phage. Nature (Lond.) 200, 291–293 (1963).
Fraser, D., Mahler, H. R.: Studies in partially resolved bacteriophage-host systems VII. Diamines, dyes, empty phage heads, and protoplast infecting agent. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 53, 199–213 (1961).
Freifelder, D., Uretz, R. B.: Mechanism of photoinactivation of coliphage T7 sensitized by acridine orange. Virology 30, 97–103 (1966).
Geissler, E.: Untersuchungen über die Irreparabilität photodynamischer Schäden. Studia biophysica 2, 95–102 (1967a).
—: Zur Irreparabilität photodynamischer Schäden. Studia biophysica 3, 165–174 (1967b).
—: Reactivation of photodynamically inactivated lambda phages. Molec. Gen. Genetics 103, 233–237 (1968).
Harm, W.: Differential effects of acriflavine and caffeine on various ultra-violet-irradiated Escherichia coli strains and T1 phage. Mutation Res. 4, 93–110 (1967).
—: Dark repair of acridine dye-sensitized photoeffects in E. coli cells and bacteriophages. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 32, 350–358 (1968).
Hatchard, C. G., Parker, C. A.: A new sensitive chemical actinometer. II. Potassium ferrioxalate as a standard chemical actinometer. Proc. roy. Soc. A 235, 518–536 (1956).
Haynes, R. H.: Role of DNA repair mechanisms in microbial inactivation and recovery phenomena. Photochem. Photobiol. 3, 429–450 (1964).
Helprin, J. J., Hiatt, C. W.: Photosensitization of T2 coliphage with toluidine blue. J. Bact. 77, 502–505 (1959).
Howard-Flanders, P., Boyce, R. P.: DNA repair and genetic recombination: Studies on mutants of Escherichia coli defective in these processes. Radiat. Res., Suppl. 6, 156–184 (1966).
Ito, T., Hieda, K.: Absence of apparent dark recovery from the photodynamically induced mutational damages in yeast cells. Mutation Res. 5, 184–186 (1968).
Ito, T., Hieda, K.: Absence of apparent dark recovery from the photodynamically induced mutational damages in yeast cells. Mutation Res. 5, 184–186 (1968).
Kadish, L. J., Fisher, D. B., Pardee, A. B.: Photodynamic inactivation of free and vegetative bacteriophage T4. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 138, 57–65 (1967).
Kaplan, R. W., Brendel, M.: Formation of phototrophs in mixtures of two auxotrophic mutants of Serratia marcescens HY by a transducing bacteriophage produced by some auxotrophs. Molec. Gen. Genetics 104, 27–39 (1969).
Lotz, W., Kaplan, R. W., Mennigmann, H. D.: Wirkung von Aminoacridinen auf die intrazelluläre. Vermehrung und die Auslösung von Mutationen beim Phagen ϰ von Serratia marcescens. Mutation Res. 6, 329–343 (1968).
Patrick, M. H., Haynes, R. H., Uretz, R. B.: Dark recovery phenomena in yeast I. Comparative effects with various inactivating agents. Radiat. Res. 21, 144–163 (1964).
Ritchie, D. A.: Mutagenesis with light and proflavine in phage T4. Genet. Res. Camb. 5, 168–169 (1964).
—: The photodynamic action of proflavine on phage T4. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 20, 720–726 (1965).
Sastry, K. S., Gordon, M. P.: The photosensitized degradation of guanosine by acridine orange. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 129, 42–48 (1966).
Setlow, R. B.: Physical changes in mutagenesis. J. cell. comp. Physiol. 64, Suppl. 1, 51–68 (1964).
Simon, M. I., Van Vunakis, H.: The photodynamic reaction of methylene blue with deoxy-ribonucleic acid. J. molec. Biol. 4, 488–499 (1962).
—: The dye-sensitized photooxydation of purine and pyrimidine derivatives. Arch. Biochem. 105, 197–206 (1964).
Uretz, R. B.: Sensitivity to acridine sensitized photoinactivation in E. coli B, B/r, and Bs-1. Radiat. Res. 22, 245 (1964).
Wacker, A., Türck, G., Gerstenberger, A.: Zum Wirkungsmechanismus photodynamischer Farbstoffe. Naturwissenschaften 50, 377 (1963).
Waskell, L. A., Sastry, K. S., Gordon, M. P.: Studies on the photosensitized breakdown of guanosine by methylene blue. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 129, 49–53 (1966).
Welsch, J. M., Adams, M. H.: Photodynamic inactivation of bacteriophage. J. Bact. 68, 122–127 (1954)
Winkler, U.: Host-cell reactivation of lethal damage induced by ultraviolet light and X-rays in Serratia marcescens HY and its phage kappa. Virology 24, 518–520 (1964).
—: Wirtsreaktivierung von extrazellulär strahleninduzierten Prämutationen im Serratia-phagen kappa I. Erhöhung der Mutabilität von kappa durch Behinderung der Wirtsreaktivierung. Z. Vererbungsl. 97, 18–28 (1965).
Winkler, U., Johns, H. E., Kellenberger, E.: Comparative study of some properties of bacteriophage T4D irradiated with monochromatic ultraviolet light. Virology 18, 343–358 (1962).
Wolf-Ellmauer, H.: Quantitative Untersuchungen zur Induzierbarkeit der Phagenproduktion zweier lysogener Stämme mit identischen Prophagen. Z. allg. Mikrobiol. 1, 150–171 (1961).
Yamamoto, N.: Photodynamic inactivation of bacteriophage and its inhibition. J. Bact. 75, 443–448 (1958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by F. Kaudewitz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brendel, M. Different photodynamic action of proflavine and methylene blue on bacteriophage. Molec. Gen. Genet. 108, 303–311 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00267767
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00267767