Summary
The effects of single dose (20 mg) and short-term (20 mg/day for 8 days) oral treatment with omeprazole on the pharmacokinetics and effects of oral nifedipine (10 mg capsule) and on gastric pH have been investigated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled cross-over study in 10 non-smoking healthy male subjects.
The single dose of omeprazole had no significant effect on any pharmacokinetic parameter of nifedipine, nor on gastric pH, or blood pressure or heart rate.
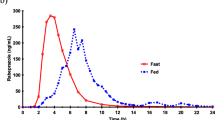
Short-term omeprazole treatment increased the AUC of nifedipine by 26% (95% confidence interval 9–46%), but all other pharmacokinetic parameters of nifedipine, including elimination half-life, Cmax, tmax, and recovery of the main urinary metabolite, were not significantly changed. The median gastric pH during the absorption phase of nifedipine was increased by short-term omeprazole (pH 4.2) compared to placebo treatment (pH 1.4). Blood pressure and heart rate did not differ between treatments.
The interaction between nifedipine and omeprazole is not likely to be of major clinical relevance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reg»rdh CG, Gabrielsson M, Hoffman KJ, Löfberg I, Sk»nberg I (1985) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of omeprazole in animals and man — an overview. Scand J Gastroenterol 20 (Suppl 108): 79–94
Reg»rdh CG, Andersson T, Lagerström PO, Lundborg P, Sk»nberg I (1990) The pharmacokinetics of omeprazole in humans. A study of single intravenous and oral doses. Ther Drug Monit 12: 163–172
Dickins M, Bridges JW (1982) The relationship between the binding of 2-n-alkylbenzimidazoles to rat hepatic microsomal cytochrome P-450 and the inhibition of monooxygenation. Biochem Pharmacol 31: 1315–1320
Murray M, Ryan AJ, Little PJ (1982) Inhibition of hepatic microsomal aminopyrine N-demethylase activity by benzimidazole derivatives. Quantitative structure-activity relationships. J Med Chem 25: 887–892
Andersson T, Cederberg C, Edvardsson G, Heggelund A, Lundborg P (1990) Effect of omeprazole treatment on diazepam plasma levels in slow versus normal rapid metabolizers of omeprazole. Clin Pharmacol Ther 47: 79–85
Andersson T, Andrén K, Cederberg C, Edvardsson G, Heggelund A, Lundborg P (1990) Effect of omeprazole and cimetidine on plasma diazepam levels. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 39: 51–54
Gugler R, Jensen JC (1985) Omeprazole inhibits oxidative drug metabolism. Studies with diazepam and phenytoin in vivo and 7-ethoxycoumarin in vitro. Gastroenterology 89: 1235–1241
Gugler R, Jensen JC (1987) Drugs other than H2-receptor antagonists as clinically important inhibitors of drug metabolism in vivo. Pharmacol Ther 33: 133–137
Henry DA, Somerville KW, Kitchingman G, Langman MJS (1984) Omeprazole: effects on oxidative drug metabolism. Br J Clin Pharmacol 18: 195–200
Prichard PJ, Walt RP, Kitchingman GK, Somerville KW, Langman MJS, Williams J, Richens A (1987) Oral phenytoin pharmacokinetics during omeprazole therapy. Br J Clin Pharmacol 24: 543–545
Sutfin T, Balmer K, Boström H, Eriksson S, Höglund P, Paulsen O (1989) Stereoselective interaction of omeprazole with warfarin in healthy men. Ther Drug Monit 11: 176–184
Guengerich FP, Böcker RH (1988) Cytochrome P-450-catalyzed dehydrogenation of 1,4-dihydropyridines. J Biol Chem 263: 8168–8175
Guengerich FP, Martin MV, Beaune PH, Kremers P, Wolff T, Waxman DJ (1986) Characterization of rat and human liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 involved in nifedipine oxidation, a prototype for genetic polymorphism in oxidative drug metabolism. J Biol Chem 261: 5051–5060
Guengerich FP, Brian WR, Iwasaki M, Sari MA, Bäärnhielm C, Berntsson P (1991) Oxidation of dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers and analogues by human liver cytochrome P-450 IIIA4. J Med Chem 34: 1838–1844
Funaki T, Soons PA, Guengerich FP, Breimer DD (1989) In vivo oxidative cleavage of a pyridine-carboxylic acid ester metabolite of nifedipine. Biochem Pharmacol 38: 4213–4216
Guengerich FP, Peterson LA, Böcker RH (1988) Cytochrome P-450-catalyzed hydroxylation and carboxylic acid ester cleavage of Hantzsch pyridine esters. J Biol Chem 263: 8176–8183
Soons PA, Schellens JHM, Breimer DD (1991) Variability in pharmacokinetics and metabolism of nifedipine and other dihydropyridine calcium entry blockers. In: Kalow W, ed. Genetic Factors Influencing the Metabolism of Foreign Compounds. Pergamon Press, Oxford (in press)
Adams LJ, Antonow DR, McClain CJ, McAllister R (1986) Effect of ranitidine on bioavailability of nifedipine. Gastroenterology 90: 1320
Majeed IA, Murray WJ, Newton DW, Othman S, All-Turk WA (1987) Spectrophotometric study of the photodecomposition kinetics of nifedipine. J Pharm Pharmacol 39: 1044–1046
Soons PA, Schellens JHM, Roosemalen MCM, Breimer DD (1991) Analysis of nifedipine and its pyridine metabolite dehydronifedipine in blood and plasma: review and improved HPLC methodology. J Pharm Biomed Anal 9: 475–484
Kleinbloesem CH, van Brummelen P, Breimer DD (1987) Nifedipine: relationship between pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Clin Pharmacokinet 12: 12–29
Kleinbloesem CH, van Brummelen P, Danhof M, Faber H, Urquhart J, Breimer DD (1987) Rate of increase in the plasma concentration of nifedipine as a major determinant of its hemodynamic effects in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 41: 26–30
Roosemalen MCM, Soons PA, Funaki T, Breimer DD (1991) High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of the polar metabolites of nifedipine in plasma, blood and urine. J Chromatogr 565: 516–522
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1982) Pharmacokinetics, 2nd ed. New York: Marcel Dekker
Henry DA, Gerkens JF, Brent PJ, Dosen PJ (1986) Omeprazole: effects on oxidative drug metabolism in the rat. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 13: 377–381
Kromer W, Postius S, Riedel R, Simon WA, Hanauer G, Brand U, Gönne S, Parsons ME (1990) BY 1023/SK&F 96022 INN pantoprazole, a novel gastric proton pump inhibitor, potently inhibits acid secretion but lacks relevant cytochrome P-450 interactions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 254: 129–135
Andersson T, Lundborg P, Reg»rdh CG (1991) Lack of effect of omeprazole treatment on steady-state plasma levels of metoprolol. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 40: 61–65
Andersson T, Bergstrand R, Cederberg C, Eriksson S, Lagerström PO, Sk»nberg I (1991) Omeprazole treatment does not affect the metabolism of caffeine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 49: 172
Henry D, Brent P, Whyte I, Mihaly G, Devenish-Meares S (1987) Propranolol steady-state pharmacokinetics are unaltered by omeprazole. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 33: 369–373
Oosterhuis B, Jonkman JHG (1989) Omeprazole: pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and interactions. Digestion 44 [Suppl 1]: 9–17
Andersson T, Lagerström PO, Unge P (1990) A study of the interaction between omeprazole and phenytoin in epileptic patients. Ther Drug Monit 12: 329–333
Li G, Klotz U (1990) Inhibitory effect of omeprazole on the metabolism of midazolam in vitro. Arzneim Forsch 40: 1105–1107
Kronbach T, Fischer V, Meyer UA (1988) Cyclosporin metabolism in human liver: identification of a cytochrome P-450III gene family as the major cyclosporin-metabolizing enzyme explains interactions of cyclosporin with other drugs. Clin Pharmacol Ther 43: 630–635
Kronbach T, Mathys D, Umeno M, Gonzalez FJ, Meyer UA (1989) Oxidation of midazolam and triazolam by human liver cytochrome P450IIIA4. Molec Pharmacol 36: 89–96
Andersson T, Andrén K, Cederberg C, Lagerström PO, Lundborg P, Sk»nberg I (1990) Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of omeprazole after single and repeated oral administration in heathy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 29: 557–563
Howden CW, Meredith PA, Forrest JAH, Reid JL (1984) Oral pharmacokinetics of omeprazole. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 26: 641–643
Müller P, Dammann HG, Seitz H, Simon B, Kommerell B (1984) Repeated omeprazole administration and human gastric acid secretion. Ital J Gastroenterol 16: 6–8
Lind T, Andersson T, Sk»nberg I, Olbe L (1987) Biliary excretion of intravenous [14C] omeprazole in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 42: 504–508
Soons PA, Schoemaker HC, Cohen AF, Breimer DD Intra-individual variability in nifedipine pharmacokinetics and effects in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soons, P.A., van den Berg, G., Danhof, M. et al. Influence of single- and multiple-dose omeprazole treatment on nifedipine pharmacokinetics and effects in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 42, 319–324 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00266355
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00266355