Summary
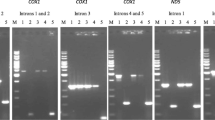
The linear mitochondrial DNAs of the two infertile algal species Chlamydomonas smithii and C. reinhardtii are co-linear with the exception of a 1 kb intron (α intron) located in the cytochrome b gene of C. smithii. C. smithii also possesses an additional HpaI restriction site (H marker) located in the COXI gene, about 5 kb from the intron. In reciprocal crosses, C. smithii (H +α+) × C. reinhardtii (H −α−), the α intron is transmitted to all diploid progeny, whereas the H marker is frequently transmitted either biparentally or paternally depending on whether the C. smithii parent is maternal (mt +) or paternal (mt −). In diploids resulting from artificial fusion between vegetative cells, the absolute transmission of a is accompanied by the frequent transmission of the H + marker, irrespective of the mating type of the parental strains. Finally, in reciprocal crosses between C. smithii (H +α+) and recombinant H −α+ clones, the transmission of the H marker is predominantly paternal or biparental. These results allow us to conclude that (1) the a intron behaves as a group I intron whose unidirectional conversion influences the transmission of the H marker; and (2) the mt − paternal mitochondrial genome is transmitted more often than the mt +. The mating type has no effect in diploids obtained by artificial fusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blank R, Hauptmann E, Arnold CG (1980) Variability of mitochondrial population in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Planta 150:236–241
Bolotin M, Coen D, Deutsch J, Dujon B, Netter P, Petrochilo E, Slonimski PP (1971) La recombinaison des mitochondrias chez Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bull Inst Pasteur 69:215–239
Boynton JE, Palmer JD, Harris EH, Gillham NW (1984) Inheritance and molecular divergence of chloroplast and mitochondrial genomes in crosses between the interfertile algal species Chlamydomonas smithii and C. reinhardtii. Genetics 107: Suppl s13
Boynton JE, Harris EH, Burkhart BD, Lamerson PM, Gillham NW (1987) Transmission of mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes in crosses of Chlamydomonas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:2391–2395
Colleaux L, Michel-Wolwertz M-R, Matagne RF, Dujon B (1990) The apocytochrome b gene of Chlamydomonas smithii contains a mobile intron related to both Saccharomyces and Neurospora introns. Mol Gen Genet, in press
Dujon B (1989) Group I introns as mobile genetic elements: Facts and mechanistic speculations — A review. Gene 82:91–114
Dutcher SK (1988) Nuclear fusion — defective phenocopies in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: Mating-type functions for meiosis can act through the cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:3946–3950
Gillham NW (1978) Organelle heredity. Raven Press, New York, pp 1–602
Gorman DS, Levine RP (1965) Cytochrome F and plastocyanin: Their sequence in the photosynthetic electron transport chain of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 54:1665–1669
Grant DM, Gillham NW, Boynton JE (1980) Inheritance of chloroplast DNA in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:6067–6071
Jacquier A, Dujon B (1985) An intron-encoded protein is active in a gene conversion process that spreads an intron into a mitochondrial gene. Cell 41:383–394
Matagne RF (1981) Transmission of chloroplast alleles in somatic fusion products obtained from vegetative and/or “gametes” of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Curr Genet 3:31–36
Matagne RF (1987) Chloroplast gene transmission in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: A model for its control by the mating-type locus. Curr Genet 12:251–256
Matagne RF, Beckers MC (1987) Isolation and characterization of biochemical and morphological mutants in Chlamydomonas smithii. Plant Sci Lett 49:85–88
Matagne RF, Rongvaux D, Loppes R (1988) Transmission of mitochondrial DNA in crosses involving diploid gametes homozygous or heterozygous for the mating-type locus in Chlamydomonas. Mol Gen Genet 214:257–262
Matagne RF, Michel-Wolwertz M-R, Munaut C, Duyckaerts C, Sluse F (1989) Induction and characterization of mitochondrial DNA mutants in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol 108:1221–1226
Netter P, Petrochilo E, Slonimski PP, Bolotin-Fukuhara M, Coen D, Deutsch J, Dujon B (1974) Mitochondrial genetics VII: Allelism and mapping of ribosomal mutants resistant to chloramphenicol, erythromycin, and spiramycin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 78:1063–1100
Osafune T, Mihara S, Hase E, Ohkuro I (1972) Electron microscope studies on the vegetative cellular life cycle of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Dangeard in synchronous culture I. Some characteristics of changes in subcellular structures during the cell cycle, especially in formation of giant mitochondria. Plant and Cell Physiol 13:211–227
Pratje E, Vahrenholz C, Bühler S, Michaelis G (1989) Mitochondrial DNA of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: The ND4 gene encoding a subunit of NADH dehydrogenase. Curr Genet 16:61–64
Ryan R, Grant D, Chiang KS, Swift H (1978) Isolation and characterization of mitochondrial DNA from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:3268–3272
Surzycki S (1971) Synchronously grown cultures of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Methods Enzymol 23A:67–73
Zinn A, Butow R (1985) Non reciprocal exchange between alleles of the yeast mitochondrial 21 S rRNA gene: Kinetics and the involvement of a double strand-break. Cell 40:887–895
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by D. M. Lonsdale
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Remacle, C., Bovie, C., Michel-Wolwertz, MR. et al. Mitochondrial genome transmission in Chlamydomonas diploids obtained by sexual crosses and artificial fusions: Role of the mating type and of a 1 kb intron. Molec. Gen. Genet. 223, 180–184 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265051
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265051