Summary
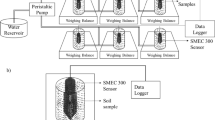
The stability of 22 commercially available soil salinity sensors was studied: 23% were considered to be stable under the imposed experimental conditions during a period of 14 months. During the same time period, accuracy of sensors decreased from ±0.32 to ±0.98 mmho cm−1. Time response is adequate under saturated conditions (Fig. 3) but it may be extremely long for unsaturated soils (Fig. 4 and Table 2). Measurements of the soil solution electrical conductivity with salinity sensors and by the suction probe extraction technique demonstrated that the soil matrix affects the salt distribution near soil surfaces and within the pore space. Time response (63% of total change) of sensor thermistor is 0.9 min, with an estimated accuracy of ±0.3 °C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Enfield CG, Evans DD (1969) Conductivity instrumentation for in-situ measurement of soil salinity. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc, 33:787
Hoffman GJ, Dirksen C, Ingvalson RD, Maas EV, Oster JD, Rawlins SL, Rhoades JD, Van Schilfgaarde I (1978) Minimizing salt in drain water by irrigation management. Agric Water Mgmt 1:233
Ingvalson RD, Oster JD, Rawlins SL, Hoffman GJ (1970) Measurement of water potential and osmotic potential in soil with a combined thermocouple psychrometer and salinity sensor. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc, 34:570
Kemper WD (1959) Estimation of osmotic stress in soil water from the electrical resistance of finely porous ceramic units. Soil Sci 87:345
Oster JD, Ingvalson RD (1967) In-situ measurement of soil salinity with a sensor. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 31:572
Oster JD, Willardson LS (1971) Reliability of salinity sensors for the management of soil salinity. Agron J 63:695
Oster JD, McNeal BL (1971) Computation of soil solution composition variation with water content for desaturated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 35:436
Reicosky DC, Millington RJ, Peters DB (1970) A salt sensor for use in saturated and unsaturated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 34:214
Richards LA (1966) A soil salinity sensor of improved design. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 30:333
Todd RM, Kemper WD (1972) Salt dispersion coefficients near an evaporating surface. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 36:539
Wesseling J, Oster JD (1973) Response of salinity sensors to rapidly changing salinity. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 37:553
Wood JD (1978) Calibration stability and response time for salinity sensors. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:248
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aragüés, R. Factors affecting the behaviour of soil salinity sensors. Irrig Sci 3, 133–147 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00264856
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00264856