Abstract
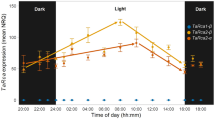
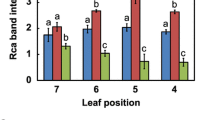
Transgenic tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L. cv. W38) plants with an antisense gene directed against the mRNA of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/ oxygenase (Rubisco) activase were used to examine the relationship between CO2-assimilation rate, Rubisco carbamylation and activase content. Plants used were those members of the r1 progeny of a primary transformant with two independent T-DNA inserts that could be grown without CO2 supplementation. These plants had from < 1% to 20% of the activase content of control plants. Severe suppression of activase to amounts below 5% of those present in the controls was required before reductions in CO2-assimilation rate and Rubisco carbamylation were observed, indicating that one activase tetramer is able to service as many as 200 Rubisco hexadecamers and maintain wild-type carbamylation levels in vivo. The reduction in CO2-assimilation rate was correlated with the reduction in Rubisco carbamylation. The anti-activase plants had similar ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate pool sizes but reduced 3-phosphoglycerate pool sizes compared to those of control plants. Stomatal conductance was not affected by reduced activase content or CO2-assimilation rate. A mathematical model of activase action is used to explain the observed hyperbolic dependence of Rubisco carbamylation on activase content.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA1P:
-
2′-carboxyarabinitol-1-phosphate
- Pipa :
-
intercellular, ambient partial pressure of CO2
- PGA:
-
3-phospho-glycerate
- Rubisco:
-
ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase
- RuBP:
-
ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate
- SSU:
-
small subunit of Rubisco
References
Andrews TJ, Lorimer GH (1987) Rubisco: Structure, mechanisms and prospects for improvement. In: Hatch MD, Boardman NK, (eds) The Biochemistry of plants. Academic Press, New York, pp 132–219
Andrews TJ, Hudson GS, Mate CJ, von Caemmerer S, Evans JR, Arvidsson YBC (1995) Rubisco: The consequences of altering its expression and activation in transgenic plants. J Exp Bot, in press
Badger MR, Sharkey TD, von Caemmerer S (1984) The relationship between steady-state gas exchange of leaves and the levels of carbon reduction cycle intermediates. Planta 160: 305–313
Brugnoli E, Hubick KT, von Caemmerer S, Wong SC, Farquhar GD (1988) Correlation between the carbon isotope discrimination in leaf starch and sugars of C3 plants and the ratio of intercellular and atmospheric partial pressure of carbon dioxide. Plant Physiol 88: 1418–1424
Butz ND, Sharkey TD (1989) Activity ratios of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase accurately reflect carbamylation ratios. Plant Physiol 89: 735–739
Edmondson DL, Badger MR, Andrews TJ (1990) Slow inactivation of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase during catalysis is caused by accumulation of a slow, tight-binding inhibitor at the catalytic site. Plant Physiol 93: 1390–1397
Evans JR, von Caemmerer S, Setchell BA, Hudson GS (1994) The relationship between CO2 transfer conductance and leaf anatomy in transgenic tobacco with reduced content of Rubisco. Aust J Plant Physiol 21: 475–495
Farquhar GD (1979) Models describing the kinetics of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. Arch Biochem Biophys 193: 456–468
Farquhar GD, von Caemmerer S (1982) Modelling of photosynthetic responses to environmental conditions. In: Lange OL, Nobel PS, Osmond CB, Ziegler H (eds) Encylopedia of plant physiol NS, vol 12B: Physiological plant ecology II. Water relations and carbon assimilation. Springer, Berlin, pp 549–587
Hewitt EJ, Smith TA, (1975) Plant mineral nutrition. English University Press
Hudson GS, Evans JR, von Caemmerer S, Arvidsson YBC, Andrews TJ (1992) Reduction of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase content by antisense RNA reduces photosynthesis in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Physiol 98: 294–302
Jiang CZ, Quick WP, Alred R, Kleibenstein D, Rodermel RS (1994) Antisense-RNA inhibition of rubisco activase expression. Plant J 5: 787–789
Jordan DB, Chollet R (1983) Inhibition of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase by substrate ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem 258: 13752–13758
Laing WA, Christeller JT (1976) A model for the kinetics of activation and catalysis of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Biochem J 159: 563–570
Lan Y, Mott KA (1991) Determination of apparent Km values for RuBP carboxylase/oxygenase activase using the spectrophotometric assay of Rubisco activity. Plant Physiol 95: 604–609
Lorimer GH, Badger MR, Andrews TJ (1976) The activation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by carbon dioxide and magnesium ions. Equilibria, kinetics, a suggested mechanism, and physiological implications. Biochemistry 15: 529–536
Mate CJ, Hudson GS, von Caemmerer S, Evans JR, Andrews TJ (1993) Reduction of ribulose carboxylase activase levels in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) by antisense RNA reduces ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase carbamylation and impairs photosynthesis. Plant Physiol 102: 1119–1128
Mott KA, Jensen RG, O'Leary JW, Berry JA (1984) Photosynthesis and ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate concentrations in intact leaves of Xanthium strumarium L. Plant Physiol 76: 968–971
Price GD, von Caemmerer S, Evans JR, Yu J-W, Kell P, Harrison K, Gallagher A, Badger MR (1995) The effect of a specific reduction of chloroplast glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase activity by antisense RNA in transgenic tobacco plants on photosynthetic CO2 assimilation. Planta 195: 369–378
Portis AR, Jr. (1990) Rubisco activase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1015: 15–28
Portis AR, Jr., Salvucci ME, Ogren WL (1986) Activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase at physiological CO2 and ribulosebisphosphate concentrations by rubisco activase. Plant Physiol 82: 967–971
Quick WP, Schurr U, Scheibe R, Schulze E-D, Rodermel SR, Bogorad L, Stitt M (1991) Decreased ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase in transgenic tobacco transformed with “antisense” rbcs. I Impact on photosynthesis in ambient growth conditions. Planta 183: 542–554
Robinson SP, Portis AR, Jr. (1988) Release of the nocturnal inhibitor, carboxyarabinitol-1-phosphate, from ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase by rubisco activase. FEBS Lett 233: 313–416
Salvucci ME (1992) Subunit interactions of Rubisco activase: Polyethylene glycol promotes self-association, stimulates ATPase and activation activities and enhances interactions with Rubisco. Arch Biochem Biophys 298: 688–696
Salvucci ME, Portis AR, Jr., Ogren WL (1985) A soluble chloroplast protein catalyzes ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activation in vivo. Photosynth Res 7: 193–201
Salvucci ME, Portis AR, Jr., Ogren WL (1986) Light and CO2 response of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activation in Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Physiol 80: 655–659
Seemann JR, Berry JA, Freas SM, Krump MA (1985) Regulation of ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity in vivo by a light-modulated inhibitor of catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 8024–8028
Servaites JC (1990) Inhibition of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase by 2-carboxyarabinitol-1-phosphate. Plant Physiol 92: 867–870
Somerville CR, Portis AR, Jr., Ogren WL (1982) A mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana which lacks activation of RuBP carboxylase in vivo. Plant Physiol 70: 381–387
Streusand VJ, Portis AR, Jr. (1987) Rubisco activase mediates ATP-dependent activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase. Plant Physiol 85: 152–154
von Caemmerer S, Edmondson DL (1986) Relationship between steady-state gas exchange, in vivo ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity and some carbon reduction cycle intermediates in Raphanus sativus. Aust J Plant Physiol 13: 669–688
von Caemmerer S, Evans JR, Hudson GS, Andrews TJ (1994) The kinetics of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in vivo inferred from measurements of photosynthesis in leaves of transgenic tobacco. Planta 195: 88–97
Vu CV, Allen LH, Bowes G (1984) Dark/Light modulation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity in plants from different photosynthetic categories. Plant Physiol 76: 843–845
Wang Z, Portis AR, Jr. (1992) Dissociation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate bound to ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase and its enhancement by ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase-mediated hydrolysis of ATP. Plant Physiol 99: 1348–1353
Wang Z, Snyder GW, Esau BD, Portis AR, Jr., Ogren WL (1992) Species-dependent variation in the interaction of substratebound ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) and Rubisco activase. Plant Physiol 100: 1858–1862
Wong SC, Cowan IR, Farquhar GD (1979) Stomatal coductance correlates with photosynthetic capacity. Nature 282: 424–426
Zhu G, Jensen RG (1991) Fallover of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activity. Decarbamylation of catalytic sites depends on pH. Plant Physiol 97: 1354–1358
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mate, C.J., von Caemmerer, S., Evans, J.R. et al. The relationship between CO2-assimilation rate, Rubisco carbamylation and Rubisco activase content in activase-deficient transgenic tobacco suggests a simple model of activase action. Planta 198, 604–613 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00262648
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00262648