Summary
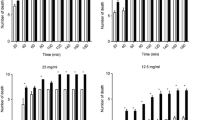
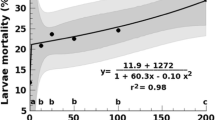
Liver flukes were incubated in vitro in solutions containing hexachlorophene (HCP) or its synthesized dimethylether (HCPD). Only HCP of the two lipophilic substances killed the flukes, which occurred within a short period of time. From these results it is suggested, that the phenolic groups in the HCP molecule are of importance for its fasciolicidal effect. Ultrastructural studies on the liver flukes after incubation in HCP or HCPD revealed that only HCP caused damage. This damage was observed on the cuticle but not on the adjacent tissue or the intestine. The alterations mainly comprised vacuolization of the cuticular cytoplasm depending upon dilatations of the cisterns of the endoplasmic reticulum. Further bleb formations on the surface were observed. It is concluded that the damage caused by HCP on the cuticle may be fatal for the fluke.
Zusammenfassung
Leberegel wurden in vitro in Lösungen gehalten, denen Hexachlorophen (HCP) oder synthetisierter Hexachlorophendimethyläther (HCPD) zugesetzt worden war. Von diesen 2lipophilen Substanzen tötete nur HCP die Egel, und zwar innerhalb kurzer Zeit. Aus diesen Ergebnissen wird geschlossen, daß die Phenol-Gruppen im HCP Molekül für diesen fascioliciden Effekt von Bedeutung sind. Ultrastrukturstudien an den Leberegeln nach der Haltung in HCP oder HCPD zeigten, daß nur HCP Schädigungen verursachte. Diese Schäden wurden nur an der Cuticula, nicht im benachbarten Gewebe oder am Darm beobachtet. Die Veränderungen bestanden hauptsächlich aus einer Vakuolisierung des cuticularen Cytoplasmas, die auf einer Erweiterung der Zisternen des endoplasmatischen Reticulum beruht. Weiterhin wurde Bläschenbildung an der Oberfläche beobachtet. Es wird die Schlußfolgerung gezogen, daß sich die durch HCP an der Cuticula verursachten Schädigungen für den Egel tödlich auswirken.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Björkman, N., and W. Thorsell: On the fine structure and resorptive function of the cuticle of the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica, L. Exp. Cell Res. 33, 319–329 (1964).
—, and E. Lienert: Studies on the action of some enzymes on the cuticle of Fasciola hepatica, L. Experientia (Basel) 19, 1–5 (1963).
Dawes, B.: Maintenance in vitro of Fasciola hepatica L. Nature (Lond.) 174, 654–655 (1954).
— Some apparent effects of bithionol (“Actamer”) on Fasciola hepatica. Nature (Lond.) 209, 424–425 (1966).
Gibson, T. E.: Veterinary anthelmintic medication, 2 ed., p. 41–48. Reading: Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux 1963.
Larson, H. L.: Determination of hexachlorophene content of soaps using ferric chloride reagent. J. Amer. Oil Chem. Soc. 28, 301–304 (1951).
Lienert, E.: Private communication 1965.
Luft, J. H.: Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 9, 409–414 (1961).
Mahler, W.: The ionization of certain bisphenols. J. Amer. chem. Soc. 76, 3920–3921 (1954).
Merck Index of Chemicals and Drugs, 7 ed., p. 675. Rahway: Merck & Co. 1960.
Millonig, G.: Advantages of a phosphate buffer for OsO4 solutions in fixation. J. appl. Phys. 39, 1637 (1961).
Pearse, A. G. E.: Histochemistry, 2 ed., p. 787. London: J. & A. Churchill Ltd. 1961.
Rouiller, C.: The liver, vol. II, p. 335–476. New York and London: Academic Press 1964.
Scheunert, A., u. A. Trautman: Lehrbuch der Veterinär-Physiologie, 5 Aufl., S. 247–248. Berlin u. Hamburg: P. Parey 1965.
Schöninger, W.: Eine mikroanalytische Schnellbestimmung von Halogen in organischen Substanzen. Mikrochim. Acta (Wien), 123–129 (1955).
Stahl, E.: Dünnschicht-Chromatographie, S. 320–322. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1962.
Theilheimer, W.: Synthetic methods of organic chemistry, vol. 13, p. 150. Basel: S. Karger 1959.
Thorsell, W., and L.-E. Appelgren: Distribution and fate of C14-hexachlorophene in liver flukes, Fasciola hepatica, L. Helminthologia (1966) (in press).
—, and N. Björkman: Morphological and biochemical studies on absorption and secretion in the alimentary tract of Fasciola hepatica, L. J. Parasit. 51, 217–223 (1965).
Threadgold, L.T.: The tegument and associated structures of Fasciola hepatica. Quart. J. micr. Sci. 104, 505–512 (1963).
Vogel, A. J.: A textbook of practical organic chemistry, 3. ed., p. 1037. London: Longman, Green & Co. 1956.
Witt, O.N., u. F. Schneider: α-Naphtoläthyläther und Abkömmlinge desselben. Ber. dtsch. chem. Ges. 34, 3172–3191 (1901).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thorsell, W., Björkman, N. In vitro studies on the effect of hexachlorophene and its dimethylether on the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica L.. Z. F. Parasitenkunde 28, 116–124 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00260238
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00260238