Summary
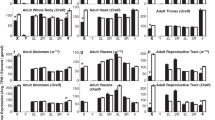
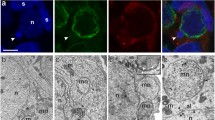
Two competing hypotheses have been proposed for the function of the Y chromosomal fertility factors in Drosophila, which form giant lampbrush loops during the primary spermatocyte stage. The first hypothesis suggests a conventional coding function, the second proposes an unconventional gene function mediated through protein binding by nascent transcripts. Therefore, we studied the genetics and cytogenetics of the two Y chromosomal fertility genes A and C ofDrosophila hydei (which form the lampbrush loops threads and pseudonucleolus) in order to test the validity of these different hypotheses. Both lampbrush loops bind specific proteins, which are recognized by different antisera. Absence of either of the lampbrush loops does not interfere with the synthesis of the antigens but completely prevents the binding of the particular antigen to other lampbrush loops. Absence of the loops also does not interfere with the postmeiotic presence and localization of the particular antigen. Deletion (or inactivation) of either of the lampbrush loops threads or pseudonucleolus causes sterility of the male flies as do other male-sterile alleles of both fertility genes, which do not affect the morphology of the lampbrush loops. The phenotypic effects of these mutations on sperm morphogenesis are identical for all various male-sterile alleles of each of the fertility genes A and C, regardless of whether a particular allele leaves the loop intact, modifies that loop, or deletes (or inactivates) the loop completely. Finally, the isolation of fertile Y chromosomal mutations which modify the morphology of the lampbrush loops demonstrates that it is possible to uncouple loop morphology and genetic function. These findings do not support the hypothesis that the binding of proteins to a lampbrush loop has a substantial impact on spermiogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker BS (1989) Sex in flies: the splice of life. Nature 340:521–524
Bonaccorsi S, Pisano C, Puoti F, Gatti M (1988) Y chromosome loops in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 120:1015–1034
Doolittle WF, Sapienza C (1980) Selfish genes, the phenotype paradigm and genome evolution. Nature 284:601–603
Glätzer KH (1984) Preservation of nuclear RNP antigens in male germ cell development of Drosophila hydei. Mol Gen Genet 196:236–243
Glätzer KH, Kloetzel PM (1986) Differential chromosomal distribution of ribonucleoprotein antigens in nuclei of Drosophila spermatocytes. J Cell Biol 103:2113–2119
Goldstein LSB, Hardy RW, Lindsley DL (1982) Structural genes on the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:7405–7409
Grond CJ, Siegmund I, Hennig W (1983) Visualization of a lampbrush loop-forming fertility gene in Drosophila hydei. Chromosoma 88:50–56
Grond CJ, Rutten RGJ, Hennig W (1984) Ultrastructure of the Y chromosomal lampbrush loops in primary spermatocytes of Drosophila hydei. Chromosoma 89:85–95
Hackstein JHP (1985) Genetic fine structure of the “Th-Ps” region of the Y chromosome of Drosophila hydei. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler 366:117
Hackstein JHP (1987) Spermatogenesis in Drosophila. In: Hennig W (ed) Spermatogenesis, genetic aspects. Results and problems in cell differentiation, vol 15. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 61–116
Hackstein JHP, Hennig W (1982) New mutants of Drosophila hydei. Dros Inf Serv 58:195–203
Hackstein JHP, Leoncini O, Beck H, Peelen G, Hennig W (1982) Genetic fine structure of the Y chromosome of Drosophila hydei. Genetics 101:257–277
Hackstein JHP, Hennig W, Siegmund I (1987) Y chromosomespecific mutations induced by a giant transposon in Drosophila hydei. Mol Gen Genet 207:455–465
Hackstein JHP, Beck H, Hochstenbach R, Kremer H, Zacharias H (1990) Spermatogenesis in Drosophila hydei: a genetic survey. Roux's Arch Dev Biol 199:251–280
Hardy RW, Tokuyasu KT, Lindsley DL (1981) Analysis of spermatogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster bearing deletions for Y chromosome fertility genes. Chromosoma 83:593–617
Hennig W (1985) Y chromosome function and spermatogenesis in Drosophila hydei. Adv Genet 23:179–234
Hennig W (1986) Heterochromatin and germ line-restricted DNA. In: Hennig W (ed) Germ Line — Soma differentiation. Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation, vol 13. Springer Verlag, Berlin, pp 176–192
Hennig W (1987) The Y chromosomal lampbrush loops of Drosophila. In: Hennig W (ed) Structure and function of eukaryotic chromosomes. Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation, vol 14. Springer Verlag, Berlin, pp 133–146
Hennig W (1990) The Y chromosome of Drosophila. In: Adolph KW (ed) Chromosomes: eukaryotic, prokaryotic and viral. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fl, USA, pp 213–238
Hennig W, Brand RC, Hackstein J, Huijser P, Kirchhoff C, Kremer H, Lankenau D-H, Vogt P (1987) Structure and function of Y chromosomal genes in Drosophila. Chromosomes Today 9:48–58
Hennig W, Brand RC, Hackstein J, Hochstenbach R, Kremer H, Lankenau D-H, Lankenau S, Miedema K, Pötgens A (1989) Y chromosomal fertility genes of Drosophila: a new type of eukaryotic genes. Genome 31:561–571
Hess O (1965) Strukturdifferenzierungen im Y Chromosom von Drosophila hydei und ihre Beziehungen zu Gen-Aktivitäten. I. Mutanten der Funktionsstrukturen. Verh Dtsch Zool Ges 28:156–163
Hess O (1967) Morphologische Variabilität der chromosomalen Funktionsstrukturen in den Spermatocytenkernen von Drosophila-Arten. Chromosoma 21:429–445
Huijser P, Hennig W (1987) Ribosomal DNA-related sequences in a Y chromosomal lampbrush loop of Drosophila hydei. Mol Gen Genet 206:441–451
Huijser P, Kirchhoff C, Lankenau D-H, Hennig W (1988) Retrotransposon-like sequences are expressed in Y chromosomal lampbrush loops of Drosophila hydei. J Mol Biol 203:689–697
Hulsebos T, Hackstein J, Hennig W (1982) Regulation of structural sperm protein synthesis by Y chromosomal loci. In: Jaenicke L (ed) Biochemistry of differentiation and morphogenesis. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 184–188
Hulsebos TIM, Hackstein JHP, Hennig W (1983) Involvement of Y chromosomal loci in the synthesis of Drosophila hydei sperm proteins. Dev Biol 100:238–243
Hulsebos TJM, Hackstein JHP, Hennig W (1984) Lampbrush loop specific protein of Drosophila hydei. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:3404–3408
Ising G, Block K (1984) A transposon as a cytogenetic marker in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet 196:6–16
Kociok N (1984) Morphogenetische Defekte in der Spermiogenese von Y-defizienten Männchen von Drosophila hydei. Diplomarbeit, Institut fur Genetik der Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, Germany
Koenig M, Hoffman EP, Bertelson CJ, Monaco AP, Feener C, Kunkel LM (1987) Complete cloning of the Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell 50: 509–517
Koenig M, Monaco AP, Kunkel LM (1988) The complete sequence of dystrophin predicts a rod-shaped cytoskeletal protein. Cell 53:219–228
Kremer H, Hennig W, Dijkhof R (1986) Chromatin organization in the male germ line of Drosophila hydei. Chromosoma 94:147–161
Lankenau D-H, Huijser P, Jansen E, Miedema K, Hennig W (1989) DNA sequence comparison of micropia transposable elements from Drosophila hydei and Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 99:111–117
Lifschytz E (1987) The developmental program of spermiogenesis in Drosophila: A genetic analysis. Int Rev Cytol 109:211–258
Lifschytz E, Hareven D, Azriel A, Brodsly H (1983) DNA clones and RNA transcripts of four lampbrush loops from the Y chromosome of Drosophila hydei. Cell 32:191–199
Melzer S, Glätzer KH (1985) Localization of RNP antigens in primary spermatocytes of Drosophila melanogaster by indirect immunofluorescence and their correlation to fertility factors. Dros Inf Serv 61:121–122
Orgel LE, Crick FHC (1980) Selfish DNA: the ultimate parasite. Nature 284:604–607
Saumweber H, Symmons P, Kabisch R, Will H, Bonhoeffer F (1980) Monoclonal antibodies against chromosomal proteins of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 80:253–275
Tiong S, Bone LM, Whittle JRS (1985) Recessive lethal mutations within the bithorax-complex in Drosophila. Mol Gen Genet 200:335–342
Trapitz P, Wlaschek M, Bünemann H (1988) Structure and function of Y chromosomal DNA. II. Analysis of lampbrush loop associated transcripts in nuclei of primary spermatocytes of Drosophila hydei by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes of four different families of repetitive DNA. Chromosome 96:159–170
Vogt P, Hennig W (1986a) Molecular structure of the lampbrush loop nooses of the Y chromosome of Drosophila hydei. I. The Y chromosome-specific repetitive DNA sequence family ayl is dispersed in the loop DNA. Chromosoma 94:449–458
Vogt P, Hennig W (1986b) Molecular structure of the lampbrush loop nooses of the Y chromosome of Drosophila hydei. II. DNA sequences with homologies to multiple genomic locations are a major constituent of the loop. Chromosoma 94:459–467
Wlaschek M, Awgulewitsch A, Bünemann H (1988) Structure and function of Y chromosomal DNA. I. Sequence organization and localization of four families of repetitive DNA on the Y chromosome of Drosophila hydei. Chromosoma 96:145–158
Yamasaki N (1977) Selective staining of Y chromosomal loop DNA in Drosophila hydei, D. neohydei and D. eohydei. Chromosoma 60:27–37
Yamasaki N (1981) Differential staining of Y chromosome lampbrush loops of Drosophila hydei. Chromosoma 83:679–684
Zacharias H, Hennig W, Leoncini O (1982) Microspectrophotometric comparison of the genome sizes of Drosophila hydei and some related species. Genetica 58:153–157
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J.A. Campos-Ortega
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hackstein, J.H., Glätzer, K.H. & Hulsebos, T.J. Genetic and cytogenetic analysis of the “Th-Ps” region of the Y chromosome of Drosophila hydei: evidence for dual functions of the lampbrush loop-forming fertility genes?. Molec. Gen. Genet. 227, 293–305 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00259683
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00259683