Summary
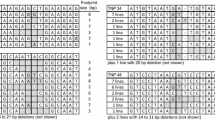
A mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene (DHFR), encoding an enzyme conferring methotrexate (MTX) resistance, under the control of the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35 S promoter, was inserted within a maize nonautonomous Ds transposable element. The presence of at least one element (Ds-DHFR) can easily be monitored using methotrexate selection in plants. This chimeric element is able to transpose at a frequency similar to its unmodified progenitor in transgenic tobacco callus containing an autonomous Ac element. The orientation of the selectable marker cassette in the Ds element does not affect relative excision frequencies. Approximately two-thirds of these elements can be detected after excision while the remaining one-third cannot. The Ds-DHFR element is useful in elucidating the mechanism by which Ac/Ds transposition occurs, and allows for a rapid identification of mutants in which methotrexate resistance cosegregates with a mutant phenotype.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker B, Schell J, Loerz H, Federoff N (1986) Transposition of the maize controlling element Activator in tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4844–4848
Baker B, Coupland G, Federoff N, Starlinger P, Schell J (1987) Phenotypic assay for excision of the maize controlling element Ac in tobacco. EMBO J 6:1547–1554
Coupland G, Baker B, Schell J, Starlinger P (1988) Characterization of the maize transposable element Ac by internal deletions. EMBO 7:3653–3659
Eichholtz DA, Rogers SG, Horsch RB, Klee HJ, Hayford M, Hoffmann NL, Braford SB, Fink C, Flick J, O'Connell KM, Fraley RT (1987) Expression of mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene confers methotrexate resistance in transgenic petunia plants. Somatic Cell Mol Genet 13:67–76
Federoff NV (1983) Controlling elements in maize. In: Shapiro JA (ed) Mobile genetic elements. Academic Press, New York
Federoff NV, Furtek DB, Nelson OE (1984) Cloning of the bronze locus in maize by a simple and generalizable procedure using the transposable controlling element Activator (Ac). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:3825–3829
Greenblatt IM (1974) Movement of Modulator in maize: a test of an hypothesis. Genetics 77:671–678
Greenblatt IM, Brink RA (1963) Transposition of Modulator in maize into divided and undivided chromosome segments. Nature 197:412–413
Knapp S, Coupland G, Uhrig U, Starlinger P, Salamini F (1988) Transposition of the maize transposable element Ac in Solanum tuberosum. Mol Gen Genet 213:285–290
Kunze R, Stochaj U, Laufs J, Starlinger P (1987) Transcription of the transposable element Activator (Ac) of Zea mays L. EMBO 16:1555–1563
Lloyd AM, Barnason AR, Rogers SG, Byrne MC, Fraley RT, Horsch RB (1986) Transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Science 234:464–466
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Masterson RV, Schell JS (1989) Transgenic plants and the study of plant development. In: Eckstein F, Lilley D (eds) Nucleic acids and molecular biology, vol 3. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, in press
McClintock B (1951) Chromosome organization and genic expression. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 16:13–47
Meyerowitz EM, Pruitt RE (1985) Arabidopsis thaliana and Plant Molecular Genetics. Science 229:1214–1218
Müller-Neumann M, Yoder JI, Starlinger P (1984) The DNA sequence of the transposable element Ac of Zea mays L. Mol Gen Genet 198:19–24
Pohlman R, Federoff NV, Messing J (1984) The nucleotide sequence of the maize controlling element Activator. Cell 37:635–643
Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S, Scharf SJ, Higuchi R, Horn GT, Mullis KB, Erlich HA (1988) Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239:487–491
Van Sluys MA, Tempe J, Federoff N (1987) Studies on the introduction and mobility of the maize Activator element in Arabidopsis thaliana and Daucus carota. EMBO J 6:3881–3889
Yoder JI, Pals J, Alpert K, Lassner M (1988) Ac transposition in transgenic tomato plants. Mol Gen Genet 213:291–296
Zambryski P, Joos H, Genetello C, Leemans J, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1983) Ti plasmid vector for the introduction of DNA into plant cells without alteration of their normal regeneration capacity. EMBO J 2:2143–2150
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by H. Saedler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masterson, R.V., Furtek, D.B., Grevelding, C. et al. A maize Ds transposable element containing a dihydrofolate reductase gene transposes in Nicotiana tabacum and Arabidopsis thaliana . Mol Gen Genet 219, 461–466 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00259620
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00259620