Summary
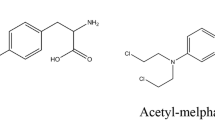
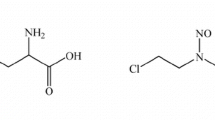
A simple and specific quantitative high-performance thin-layer chromatographic (HPTLC) assay for melphalan in plasma is described. This assay was linear over the investigated range of 50–3,000 ng/ml, with a minimum level of detection of 20 ng/ml. Comparison with a high-pressure liquid chromatographic (HPLC) technique yielded similar estimates for melphalan concentrations in human plasma samples. The HPTLC method, unlike the HPLC technique, does not resolve monohydroxymelphalan satisfactorily. The HPTLC method was used to determine the activation energy for in vitro melphalan hydrolysis: this was 14.5 kcal/mole. The pharmacokinetics of melphalan in rabbits were also investigated. The mean t1/2 in four animals was 32.6±10.3 (S.D.) min and following IV administration to two animals the apparent volumes of distribution were 2.20 and 1.73 l/kg.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberts DS, Chang SY, Cheng H-SG, Moon TE, Evans TL, Furner RL, Himmelstein K, Gross JF (1979a) Kinetics of intravenous melphalan. Clin Pharmacol Ther 26:73
Alberts DS, Sai Y, Chang H-S, Chen G, Evans TL, Moon TE (1979b) Systemic availability of oral melphalan. Cancer Treat Rev [Suppl] 6:51
Brox L, Birkett L, Belch A (1979) Pharmacology of intravenous melphalan in patients with multiple myeloma. Cancer Treat Rev [Suppl] 6:27
Chang SY, Alberts DS, Melrick LR, Walson PD, Salmon SE (1978a) High pressure liquid chromatographic analysis of melphalan in plasma. J Pharm Sci 67:679
Chang SY, Alberts DS, Farquhar D, Melrick LR, Walson PD, Salmon SE (1978b) Hydrolysis and protein binding of melphalan. J Pharm Sci 67:682
Cohn P (1957) The distribution of radioactivity in tissues of the rat following administration of a nitrogen mustard derivative. Br J Cancer 11:258
Flora KP, Smith SL, Cradock JC (1979) Application of a simple high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of melphalan in the presence of its hydrolysis products. J Chromatogr 177:91
Furner RL, Mellet LB, Brown RK, Duncan G (1976) A method for the measurement of L-phenylalanine mustard in the mouse and dog by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Drug Metab Dispos 4:577
Tattersall MHN, Jarman M, Newlands ES, Holyhead L, Milstead RAV, Weinberg A (1978) Pharmacokinetics of melphalan following oral or intravenous administration in patients with malignant disease. Eur J Cancer 14:507
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taha, I.AK., Ahmad, R.AJ. & Rogers, H.J. Melphalan estimation by quantitative thin-layer chromatography. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 5, 181–184 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00258477
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00258477