Summary
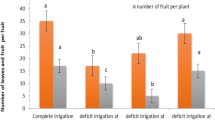
Field experiments carried out on watermelon at the Indian Institute of Horticultural Research, Bangalore, during 1984 and 1985 indicate that frequen irrigations with 100% evaporation replenishment result in highest fruit yield, dry matter production, total soluble solids, sugars, NO3-N, N, P, K, Ca, Mg uptake and higher water use efficiency. However, yield differences were only statistically significant during 1985. Drip irrigation with 1 emitter per 2 plants produced the highest yield and water use efficiency as compared to other irrigation treatments. Dry matter, total soluble solids, sugars, NO3-N, N, P, K, Ca, Mg uptake and WUE under drip irrigation were higher than under furrow irrigation treatments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber SA (1966) International atomic energy agency. Technical Report Series No. 65:39, Vienna
Colman RL, Lazenby A (1975) Effect of moisture on growth and nitrogen response of Lolium perenne. Plant Soil 42:1
Desai JB, Patil VK (1984) Effects of N, P and K on the fruit yield of watermelon. J Maharashtra Agric Univ 9:308
Dasberg S, Steinhardt R (1974) In: Isotopes and radiation techniques in soil physics and irrigation studies. Proc Series 467–474, I.A.E.A., Vienna
Elmstrom GW, Locascio BJ, Myers JM (1981) Watermelon response to drip and sprinkler irrigation. Proc Florida State Hortic Soc 94:161
Goldberg D, Rinet M, Koru N (1971) Effect of trickle irrigation intervals on distribution and utilization of soil moisture in a vineyard. Soil Sci Soc America Proc 35:125
Lemon ER (1956) The potentialities for decreasing soil moisture levaporation loss. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 20:120
Lin SSM, Hubbel JN, Samson, Tsou SCS, Splittstoesser WE (1983) Drip irrigation and tomato yield under tropical conditions. Hort Sci 18(4):460
Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (1982) Methods of soil analysis, Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties. Am Soc Agr Proc 228–599
Singh SD, Singh (1978) Value of drip irrigation compared with conventional irrigation for vegetable production. In: Hot arid climate. Agronomy J 70:945
Yadav AC, Mangal JL (1984) Effect of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on yield and quality of muskmelon. Haryana J Hortic Sci 13:156
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution No. 159/88 from Indian Institute of Horticultural Research, Bangalore, India
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivas, K., Hegde, D.M. & Havanagi, G.V. Irrigation studies on watermelon (Citrullus lanatus (Thunb) Matsum et Nakai). Irrig Sci 10, 293–301 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00257494
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00257494