Summary
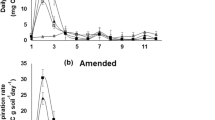
The effects of white, black and clear polyethylene mulches on temporal fluctuations in protease, sulphatase and phosphatase activities and levels of available and biomass N, S and P in raised beds of soil under a strawberry crop were investigated under field conditions. During spring, summer and early autumn, clear and, to a lesser extent black, polyethylene mulch increased both maximum and minimum mean monthly temperatures over those recorded with white mulch or no mulch. During summer and autumn, soil moisture content measured at monthly intervals was higher under mulched than unmulched conditions. Levels of extractable nitrate and sulphate in soils during autumn followed the order: clear mulch = black mulch > white mulch > no mulch. However, there were no significant differences in levels of enzyme activity or concentrations of biomass N, S or P between treatments. There were significant seasonal fluctuations in estimates of biomass N, S and P, but there was no close relationship between fluctuations in any estimate. This discrepancy was attributed to errors in the chloroform fumigation technique. Enzyme activities showed significant temporal fluctuations but the three enzymes did not show similar times of minimum and maximum activity. The complexity of interactions between soil microbial and biochemical properties and nutrient availability was exemplified by the absence of a discernible relationship between seasonal fluctuations in enzyme activities and levels of biomass N, S and P and/or levels of extractable mineral N, S and P in the soil. Strawberry fruit yields and vegetative growth followed the order : clear mulch = black mulch>white mulch>no mulch. Clear, and to a lesser extent black mulch increased the percentage of total yields produced in the first 2 months of cropping.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaudhry IA, Cornfield AH (1967) Effect of temperature of incubation on sulphate levels in aerobic and sulphide levels in anaerobic soils. J Sci Food Agric 18:82–84
Haynes RJ (1986) The decomposition process: mineralization, immobilization, humus formation and degradation. In: Haynes RJ (ed) Mineral in the plant-soil system. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 52–126
Haynes RJ, Swift RS (1986) Effect of soil amendments and sawdust mulching on growth, yield and leaf nutrient content of highbush blueberry plants. Scientia Hort 29:229–238
Hedley MJ, Stewart JWB (1982) Method to measure microbial phosphate in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 14:377–385
Jenkinson DS, Ladd JN (1981) Microbial biomass in soil: measurement and turnover. In: Paul EA, Ladd JN (eds) Soil biochemistry, vol 5. Dekker, New York, pp 415–471
Johnson CM, Nishita H (1952) Microestimation of sulphur in plant materials, soil and irrigation waters. Anal Chem 24:736–742
Kowalenko CG, Lowe LE (1975) Mineralization of sulphur from four soils and its relationship to soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. Can J Soil Sci 55:9–14
Ladd IN (1978) Origin and range of enzymes in soil. In: Burns RG (ed) Soil enzymes. Academic Press, New York, pp 51–96
Ladd JN, Butler JHA (1972) Short-term assays of soil proteolytic enzymes using proteins and dipeptide derivatives as substrates. Soil Biol Biochem 15:251–256
Ladd JN, Butler JHA (1975) Humus-enzyme systems and synthetic organic polymer-enzyme analogs. In: Paul EA, McLaren AD (eds) Soil biochemistry, vol 4. Dekker, New York, pp 143–194
McGill WB, Cole CV (1981) Comparative aspects of cycling of organic C, N, S and P through soil organic matter. Geoderma 26:267–286
McLaren RG, Keer JI, Swift RS (1985) Sulphur transformations in soils using sulphur-35 labelling. Soil Biol Biochem 17:73–79
Nannipiera P (1984) Microbial biomass and activity measurements in soil: ecological significance. In: Klug MJ, Reddy CA (eds) Current perspectives in microbial ecology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 515–521
Ross DJ, Bridger BA (1978) Nitrogen availability in some soils from tussock grasslands and introduced pastures. 3. Counts of ammonifiers and nitrifiers: relationships with rates of nitrogen mineralization and protease activity. NZ J Sci 21:443–450
Ross DJ, Speir TW, Cowling JC, Whale KN (1984) Temporal fluctuations in biochemical properties of soil under pasture. II. Nitrogen mineralization and enzyme activities. Aust J Soil Res 22:319–330
Saggar S, Bettany JR, Stewart JWB (1981) Measurement of microbial sulphur in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 13:493–498
Shen SM, Pruden G, Jenkinson DS (1984) Mineralization and immobilization of nitrogen in fumigated soil and the measurement of microbial biomass nitrogen. Soil Biol Biochem 16:437–444
Speir TW, Ross DJ (1975) Effects of storage on the activities of protease urease, phosphatase and sulphatase in three soils under pasture. NZ J Sci 18:231–237
Speir TW, Ross DJ (1978) Soil phosphatase. In: Burns RG (ed) Soil enzymes. Academic Press, New York, pp 197–250
Voth V, Bringhurst RS, Bowen HJ (1967) Effect of bed system, bed height and clear polyethylene mulch on yield, salt accumulation and soil temperature in California strawberries. Proc Am Soc Hort Sci 91:242–248
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haynes, R.J. The use of polyethylene mulches to change soil microclimate as revealed by enzyme activity and biomass nitrogen, sulphur and phosphorus. Biol Fert Soils 5, 235–240 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00256907
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00256907