Summary
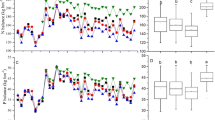
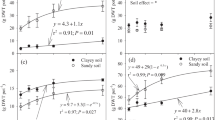
A field experiment was conducted to evaluate the effect of 0, 1 and 2 weeks' submergence prior to the transplantation of rice (presubmergence), with and without Sesbania aculeata green manure, on the yield and nutrition of rice in a highly sodic soil [pH 10.3, exchangeable sodium percentage (ESP) 86.4]. Green manuring significantly enhanced the yield of rice and contributed 112 kg N/ha. One week's presubmergence with incorporated green manure improved the yield of rice significantly over that obtained with no previous flooding, giving a yield on a par with that obtained with 2 weeks' submergence. The beneficial effect of presubmergence without green manure on rice yield was of lesser magnitude and was significant only when it was continued for 2 weeks. Cultivation of rice under submerged conditions improved the sodic soil, and green manuring enhanced the process of reclamation by further decreasing the pH value and the exchangeable Na of soil. Green manuring considerably improved organic C, available N, P, and K status of the soil and enhanced the uptake of N, P, Ca, Mg, S, Fe, Mn, and Zn by the crop. Effects of submergence and green manuring on the availability of Fe, Mn, Zn, and P in soil and their role in the nutrition of rice are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benckiser G, Santiago S, Neue HU, Watanabe I, Ottow JCG (1984) Effect of fertilization on exudation, dehydrogenase activity, iron-reducing populations and Fe++ formation in the rhizosphere of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in relation to iron toxicity. Plant Soil 79:305–316
Bhardwaj KKR (1982) Effect of the age and decomposition period of dhaincha on the yield of rice. Indian J Agron 27:284–285
Ghai SK, Batra Lalita, Rao DLN (1984) Annual Report. Central Soil Salinity Research Institute, Karnal, India, pp 65–67
Jackson ML (1967) Soil chemical analysis. Prentice-Hall of India, New Delhi
Lindsay WL (1972) Inorganic phase equilibria of micronutrients in soils. In: Mortvedt JJ, Giordano PM, Lindsay WL (eds) Micronutrients in agriculture. Soil Sci Soc Am, Madison, Wis
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA-soil test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:421–428
Milap Chand, Abrol IP, Bhumbla DR (1977) A comparison of the effect of eight amendments on soil properties and crop growth in a highly sodic soil. Indian J Agric Sci 47:348–354
Munch JC, Ottow JCG (1983) Reductive transformation mechanism of ferric oxides in hydromorphic soils. Ecol Bull (Stockh) 35:383–394
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. US Dept Agric Circ 939
Oster JD (1982) Gypsum use in irrigated agriculture — a review. Fertil Res 3:73–89
Ponnamperuma FN (1972) The chemistry of submerged soils. Adv Agron 24:29–96
Ponnamperuma FN (1978) Electrochemical changes in submerged soils and the growth of rice. Int Rice Res Inst, pp 421–441
Sherman GD, McHargue JS, Hodgkiss WS (1942) Determination of active manganese in soil. Soil Sci 54:253–257
Singh NT (1984) Green manures as sources of nutrients in rice production. In: Organic matter and rice. Int Rice Res Inst, pp 217–228
Subbiah BV, Asija GL (1956) A rapid method for the estimation of available nitrogen in soils. Curr Sci 25:259–260
Swarup Anand (1981) Effect of flooding on physico-chemical changes in sodic soils. Z Pflanzenernähr Bodenkd 144:136–142
Swarup Anand (1985a) Effect of exchangeable sodium percentage and presubmergence on yield and nutrition of rice under field conditions. Plant Soil 85:279–288
Swarup Anand (1985b) Yield and nutrition of rice as influenced by presubmergence and amendments in a highly sodic soil. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 33:352–257
Tadano T, Yoshida S (1978) Chemical changes in submerged soils and their effect on rice growth. Int Rice Res Inst, pp 399–420
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swarup, A. Effect of presubmergence and green manuring (Sesbania aculeata) on nutrition and yield of wetland rice (Oryza sativa L.) on a sodic soil. Biol Fert Soils 5, 203–208 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00256901
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00256901