Summary
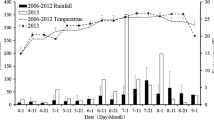
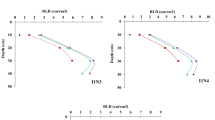
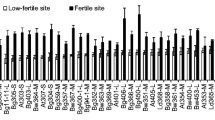
Field experiments carried out at the Indian Institute of Horticultural Research, Bangalore during 1983 and 1984 on radish indicated that frequent irrigations when soil matric potential reached −20 kPa at 18 cm depth resulted in maximum root yield, lower NO3-N content in roots, higher N, P, K, Ca and WUE of radish.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber SA (1966) International Atomic Energy Agency, Technical Report Series No. 65:39, Vienna
Barker AV, Laplante JF, Daman RA Jr (1983) Growth and composition of radish under various regimes of nitrogen nutrition. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 108:1035
Begg JE, Turner NC (1976) Crop water deficits. Adv Agron 28:161
Colman RL, Lazenby A (1975) Effect of moisture on growth and nitrogen response of Lolium perenne. Plant Soil 42:1
Dastane NG (1967) A practical mannual for water use research in agriculture. Navbharat Prakashan, Pune
Davenport DC (1962) Irrigation requirements of root vegetables. M. Sc. Thesis, Agronomy Division, I.A.R.I., New Delhi
Huffaker RC, Radin J, Kleinkopf GE, Cox EL (1970) Effect of mild water stress on enzymes of nitrate assimilation and of the carboxylative phase of photosynthesis in barley. Crop Sci 10:471
Jackson ML (1967) Soil chemical analysis. Prentice Hall of India Ltd., New Delhi
Maynard DN, Barker AV, Minotti PL, Peek NK (1976) Nitrate accumulation in vegetables. Adv Agron 28:71
Pandey SL (1966) Effect of different levels of potassium and soil moisture on the chemical composition and yield of radish, turnip and beet root. Ph.D. Thesis, Agronomy Division, I.A.R.I., New Delhi
Park KW, Fritz D (1982) Study on radish quality (Raphanus sativus L. var. niger (Mill) S. Kerner). Part I. Effect of soil moisture, seasons, havesting period and fertilization on texture of radish. J Korea Soc Hortic Sci 23:188
Singh K, Cheema GS (1972) Effect of nutrition and irrigation on radish seed production. Indian J Hortic 29:330
Singh AR, Singh R, Shankar M (1983) Effect of nitrogen, sulphur and potash fertilizers on the mineral composition and metabolites of radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Haryana J Hortic Sci 12:71
Work P, Carew J (1955) Vegetable production and marketing. John Wiley, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution No. 63/86 from Indian Institute of Horticultural Research, Bangalore, India
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hegde, D.M. Effect of soil matric potential, method of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on yield, quality, nutrient uptake and water use of radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Irrig Sci 8, 13–22 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00256812
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00256812