Summary
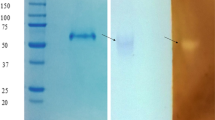
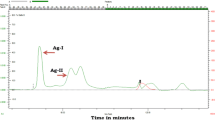
A higher yielding mutant of Aspergillus candidus Link var. aureus has been isolated using the chemical mutagen N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG) at 5 μg/ml concentration of the mutagen. This mutant produces 88 to 111 U/ml of glucoamylase compared with 40 to 50 U/ml produced by the parent strain. The enzyme from this mutant has been purified to homogeneity using hydrophobic interaction chromatography and a DEAE-cellulose column with over 65% recovery of the enzyme activity and 21-fold purification. The mutant protein is very similar to the enzyme from the parent strain in that it cochromatographs with the parent enzyme on phenylglycyl-Sepharose, norleucyl-Sepharose, Sepharose-CL-6B, Concanavalin A-Sepharose, DEAE-cellulose and DEAE-Sephadex-A-50. The two proteins exhibit similar electrophoretic behavior and have similar molecular weights and amino acid composition. However, the specific activity of the purified mutant protein is 1125 U/mg compared with 560 U/mg for the parent enzyme. Further genetic analysis of the mutant is needed to explain these observations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelberg EA, Mandel M, Ching Chein G (1965) Optimal conditions for mutagenesis by N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine in Escherichia coli K 12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 18:788–795
Aunstrup K (1977) Production of industrial enzymes. In: Meyrath J, Bu'lock JD (ed) Biotechnology and fungal differentiation. Academic Press pp 27–69
Bode HE (1966) US Patent 3,249,514
Boel E, Hjort I, Svensson B, Norris F, Norris KE, Fiil NP (1984) Glucoamylases G1 and G2 from Aspergillus niger are synthesized from two different but closely related mRNAs. EMBO 3:1097–1102
Fogarty WM (1983) Microbial amylases. In: Fogarty WM (ed) Microbial enzymes and biotechnology. Applied Science Publs Ltd, London, pp 1–92
Fogarty WM, Benson CP (1983) Purification and properties of a thermophilic amyloglucosidase from Aspergillus niger. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 18:271–278
Gabriel O (1971) Analytical dise gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol 22:565–575
Iyer MS (1973) Investigations on amyloglucosidase (glucoamylase) production by a new variety of Aspergillus candidus Link var. aureus. Ph. D. Thesis University of Poona, Poona, India
Lineback DR, Aira LA, Horner RL (1972) Structural characterization of the two forms of glucoamylase from Aspergillus niger. Cereal Chem 49:293–298
Lowry OH, Rosebrough A, Farr L, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mahajan PB, Kolhekar SR, Borkar PS (1983) Purification of amyloglucosidase. Analyt biochem 133:482–485
Manjunath P, Rao MRR (1979) Comparative studies on glucoamylases from three fungal sources. J Biosci 1:409–425
Morrissey JH (1981) Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: A modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Analyt Biochem 117:307–310
Muthukumaran N, Dhar SC (1983) Purification and properties of a glucoamylase fraction from the culture filtrate of Rhizopus nodosus. Ital J Biochem 32:239–253
Nunberg JH, Meade JH, Cole G, Lawyer FC, McCabe P, Schweickart V, Tal R, Wittman VP, Flatgaard JE, Innis MA (1984) Molecular cloning and characterization of the glucoamylase gene of Aspergillus awamori. Mol Cell Biol 4:2306–2315
Porath J (1974) General methods and coupling procedure. Methods Enzymol 34:13–29
Ramasesh N, Sreekantiah KR, Murthy VS (1982) Studies on the two forms of amyloglucosidase of Aspergillus niger var. Tieghem Starke 34:346–351
Solomon B (1978) Starch hydrolysis by immobilized enzymes: Industrial applications. In: Ghose TK, Fiechter A, Blakebrough N (eds) Advances in Biochemical Engineering vol 10. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 131–177
Takahashi T, Tsuchida Y, Irie M (1978) Purification and properties of three forms of glucoamylase from Rhizopus species. J Biochem 84:1183–1194
Weber K, Osborn M (1969) The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem 244:4406–4412
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolhekar, S.R., Mahajan, P.B., Ambedkar, S.S. et al. Purification and characterization of glucoamylase from a higher yielding mutant of Aspergillus candidus Link var. aureus . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 22, 181–186 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00253606
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00253606