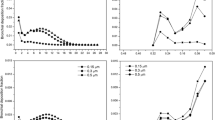
Abstract
Radioaerosols are being used increasingly to assess pulmonary ventilation in patients, and to study patterns distribution and rates of clearance in experimental studies. No completely satisfactory means have been developed to permit the safe and effective administration of suitable aerosols. In this report, a new system is described for producing and delivering monodisperse radioactive aerosol particles. The major advantages of the system are: (1) the monodispersion (σg=1.23) of the particles from modifier A; (2) 95% of the particles are less than 1 μm in diameter from modifier B, and (3) the method is simple and compact.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berglund RN, Liu BYH (1973) Generation of monodisperse aerosol standards. Environ Sci Technol 7:147–153
Conner WD (1966) An inertial-type particle separator for collecting large sample. J Air Pollut Control Assoc 16:35–38
Davis CN, Aylward M (1951) The trajectories of heavy, solid particles in a two-dimensional jet of ideal fluid impinging normally upon a plate. Proc Phys Soc B64:889–911
Friedlander SK (1977) Smoke dust and haze, fundamentals of aerosol behavior. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Fuchs NA (1964) The mechanics of aerosols, Pergamon Press, Oxford
Jones JG, Minty BD, Lawler P, Hulands G, Crawley JCW, Feall N (1980) Increased alveolar epithelial permeability in cigarette smokers. Lancet 66–68
Loo BW, Jaklevic JM, Goulding FS (1976) Dichotomous virtual impactors for large scale monitoring of airborne particulate matter. In: Liu BYH (ed) Fine Particles. Academic Press, New York. pp. 312
Marple VA, Liu BYH (1974) Characteristics of laminar jet impactors. Environ Sci Technol 8:648–654
Marple VA, Willeke K (1976) Impactor design. Atomos Environ 10:891–896
Mason BJ (1957) The physics of clouds, University Press, Oxford, Oxford, pp. 24–34
Masuda H, Hochrainer D, Stober W (1979) An improved virtual impactor for particle classification and generation of test aerosols with narrow size distributions. J Aerosol Sci 10:275–287
McFarland AR, Ortiz CA, Bertch RW Jr (1978) Particle collection characteristics of a single-stage dichotamous sampler. 12:679–682
Mercer TT (1963) On the calibration of cascade impactors. Ann Occup Hyg 6:1–14
Mercer TT (1973) Aerosol technology in hazard evaluation. Academic Press, New York, pp. 197–202
Mercer TT, Stafford RG (1969) Impactor from round jets. Ann Occup Hyg 12:41–48
Mitchell RI, Pilcher JM (1959) Improved cascade impactor for measuring aerosol particle sizes in air pollutants, commercial aerosols, cigarette smoke. Ind Eng Chem 51:1039–1042
Morrow PE (1974) Aerosol characterization and deposition. Am Rev Respir Dis 110:88–99
Raabe OG (1976) The generation of aerosols of fine particles. In: Liu BYH (ed) Fine Particles Academic Press, New York, pp 60–110
Strauss W (1976) Industrial gas cleaning, 2nd ed. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp. 409–430
Taplin GV, Poe ND, Greenberg A (1966) Lung scanning following radioaerosol inhalation. JNM 7:77–87
Taplin GV, Chapra SK (1978) Inhalation lung imaging with radioactive aerosols and gases. In: Guter M (ed), Progress in Nuclear Medicine. S. Karger Basel, pp. 119–43
Willeke K, McFeters JJ (1975) The influence of flow entry and collecting surface on the impaction efficienty of inertial impactors. J Colloid Interface Sci 53:121–127
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (Nos. GM 10548 and HL 19715)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, T., Swift, D.L., Wagner, H.N. et al. A new apparatus for generating hygroscopic radioactive aerosols for inhalation studies. Eur J Nucl Med 7, 474–479 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00253085
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00253085