Abstract
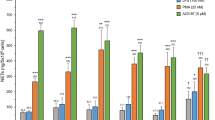
We studied the effect of C5a pretreatment on phosphatidyl-inositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) hydrolysis and on the increase in peak and resting cytosolic calcium levels induced by C5a (0.1 and 10 nM) and/or N-formyl hexapeptide (FLPEP; 10 nM) in neutrophils isolated from patients with end-stage renal failure (ESRF) and those from healthy controls. We also investigated superoxide anion production under the same conditions using the fluorescent para-hydroxyphenylacetic acid assay. The hydrolysis of PIP2 induced by C5a or FLPEP alone was similar in neutrophils from patients with ESRF and in control cells. Likewise, pretreatment of patients' neutrophils with C5a prior to FLPEP did not affect hydrolysis or the increase in cytosolic calcium concentration as shown previously for control neutrophils. Resting calcium levels in both ESRF and control neutrophils, however, were significantly increased after priming with low C5a concentrations. After priming with low C5a, prior to FLPEP, there was also a significant increase in superoxide production. This increase was significantly lower in cells from uremic patients than in those from healthy controls. Our data suggest that priming-induced superoxide production in neutrophils is reduced in patients with ESRF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ESRF:
-
end-stage renal failure
- FLPEP:
-
N-formyl-norleucyl-leucyl-phenylalanyl-norleucyl-tyrosyl-lysine
- PIP2 :
-
phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate
- PMN:
-
polymorphonuclear neutropbil
References
Baum J, Cestero RVM, Freeman RB (1975) Chemotaxis of the polymorphonuclear leukocyte and delayed hypersensitivity in uremia. Kidney Int 7 [Suppl 2]:147–153
Berridge MJ, Irvine RF (1984) Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature 312:315–321
Bingel M, Arndt W, Schulze M, Floege J, Shaldon S, Koch KM, Goetze O (1989) Comparative study of C5a plasma levels with different hemodialysis membranes using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Nephron 51:320–324
Burton BT, Hirschman GH (1979) Demographic analysis: endstage renal disease and its treatment in the United States. Clin Nephrol 11:47–51
Chenoweth DE, Cheung AK, Ward DM, Henderson LW (1983) Anaphylatoxin formation during hemodialysis: comparison of new and re-used dialyzers. Kidney Int 24:770–774
Craddock PR, Fehr J, Brigham KL, Kronenberg RS, Jacob HS (1977) Complement and leukocyte-mediated pulmonary dysfunction in hemodialysis. N Eng J Med 296:760–774
Dobos GJ, Norgauer J, Eberle M, Schollmeyer P, Traynor-Kaplan AE (1992) C5a reduces formyl peptide induced actin olymerization and PIP3 formation, but not PIP2 hydrolysis and superoxide production in human neutrophils. J Imm 149:609–614
Forehand JR, Pabst MJ, Phillips WA, Johnston RB (1989) Lipopolysaccharide priming of human neutrophils for an enhanced respiratory burst: role of intracellular free Calcium. J Clin Invest 83:74–83
Haag-Weber M, Hable M, Schollmeyer P, Hörl WH (1989) Metabolic response of neutrophils to uremia and dialysis. Kidney Int 36 [Suppl 27]:293–298
Haag-Weber M, Hörl W (1993) Uremia and infection: mechanisms of impaired cellular host defense. Nephron 63:125–131
Hakim RM, Breillatt J, Lazarus M, Port FK (1984) Complement activation and hypersensity reaction to dialysis membranes. N Eng J Med 311:878–82
Hörl WH, Haag-Weber M, Georgopoulos A, Block LH (1990) Physicochemical characterization of a polypeptide present in uremic serum that inhibits the biological activity of polymorphonuclear cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6353–6357
Hosea S, Brown E, Hammer C, Frank M (1980) Role of complement activation in a model of adult respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest 66:375–38
Hyslop PA, Sklar LA (1984) A quantitative fluorimetric assay for the determination of oxidant production by polymorphonuclear leukocytes: its use in the simultaneous fluorimetric assay of cellular activation processes. Anal Biochem 141:280–286
Lazzari KG, Proto PJ, Simons ER (1986) Simulataneous measurement of stimulus-induced changes in cytosolic Ca++ and in membrane potential of human neutrophils. J Biol Chem 261:9710–9713
Lewis SL, Van Epps DE, Chenoweth DE (1986) C5a receptor modulation on neutrophils and monocytes from chronic hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients. Clin Nephrol 26 [Suppl 1]:37–44
McIntosh J, Hansen P, Ziegler J, Penny M (1976) Defective immune and phagocytic functions in uremia and renal transplantation. Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 51:544–559
Schacht, J (1978) Purification of polyphosphoinositides by chromatography on immobilized neonycin. J Lipid Res 19:1063–1067
Traynor-Kaplan AE, Harris AL, Thompson BL, Taylor P, Sklar LA (1988) An inositol tetrakisphosphate-containing phospholipid in activated neutrophils. Nature 334:353–356
Traynor-Kaplan AE, Harris AL, Thompson BL, Taylor P, Omann GM, Sklar LA (1989) Transient increase in PI(3,4)P2 and PIP3 during activation of human neutrophils. J Biol Chem 264:15668–15678
Zimmerli W, Reber AM, Dahinten CA (1990) The role of formylpeptide receptors, C5a receptors and cytosolic-free calcium in neutrophil priming. J Infect Dis 161:242–249
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dobos, G.J., Traynor-Kaplan, A.E., Ward, D. et al. Neutrophil dysfunction in end-stage renal failure: reduced response to priming by C5a. Clin Investig 72, 353–357 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252827
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252827