Abstract
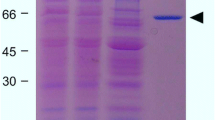
The first step in attachment of Rhizobiaceae cells to plant root hair tips is mediated by a Ca2+-dependent, Ca2+-binding protein, rhicadhesin. The possible role of Ca2+ in synthesis, anchoring and activity of rhicadhesin was investigated. Growth of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae cells under Ca2+-limitation was found to result in loss of attachment ability. Under these conditions, rhicadhesin could not be usolated from the bacterial cell surface, but was found to be excreted in the growth medium. Divalent ions appeared to be essential for the ability of purified rhicadhesin to inhibit attachment of R. leguminosarum biovar viciae cells to pea root hair tips. Calcium ions were found not to be involved in binding of rhicadhesin to the plant surface, but appeared to be involved in anchoring of the adhesin to the bacterial cell surface. A model for the role of Ca2+ in activity of rhicadhesin is presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badenoch-Jones J, Flanders DJ, Rolfe BG (1985) Association of Rhizobium strains with roots of Trifolium repens. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:1511–1520
Beringer JE, Beynon JL, Buchanan-Wollaston AV, Johnston AWB (1978) Transfer of the drug-resistence transposon Tn5 to Rhizobium. Nature 276:633–634
Caetano-Anolles G, Wall LG, De Micheli AT, Macchi EM, Bauer WD, Favelukes G (1988) Role of motility and chemotaxis in efficiency of nodulation by Rhizobium meliloti. Plant Physiol 86:1228–1235
Dazzo FB, Napoli CA, Hubbell DH (1976) Adsorption of bacteria to roots as related to host specificity in the Rhizobium-clover symbiosis. Appl Environ Microbiol 32:166–171
Dazzo FB, Truchet GI, Sherwood JE, Hrabak EM, Abe M, Pankratz SH (1984) Specific phases of root hair attachment in the Rhizobium trifolii clover symbiosis. Appl Environ Microbiol 48:1140–1150
De Weger LA, Boxtel Rvan, Burg Bvan der, Gruters R, Geels FP, Schippers B, Lugtenberg B (1986) Siderophores and outer membrane proteins of antagonistic plant-growth-stimulating, root-colonizing Pseudomodas spp. J Bacteriol 165:585–594
El-Haloui NE, Ochin D, Tailliez R (1986) Competitivité pour l'infection entre souches de Rhizobium meliloti: role de la mobilité. Plant Soil 95:337–344
Ho S-C, Wang JL, Schindler M (1990a) Carbohydrate binding activities of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. I. Saccharide-specific inhibition of homotypic and heterotypic adhesion. J Cell Biol 111:1631–1638
Ho S-C, Schindler M, Wang JL (1990b) Carbohydrate binding activities of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. II. Isolation and characterization of a galactose-specific lectin. J Cell Biol 111:1639–1643
Hunter WJ, Fahring CJ (1980) Movement by Rhizobium and nodulation of legumes. Soil Biol Biochem 12:537–561
Johnston AWB, Beynon JL, Buchanan-Wollaston AV, Setchell SM, Hirsch PR, Beringer JE (1978) High frequency transfer of nodulating ability between strains and species of Rhizobium. Nature 276:635–636
Josey DP, Beynon JL, Johnston AWB, Beringer JE (1979) Strain identification in Rhizobium using intrinsic antibiotic resistance. J Appl Microbiol 46:343–350
Kijne JW, Smit G, Díaz CL, Lugtenberg BJJ (1986) Attachment of Rhizobium leguminosarum to pea root hair tips. In: Lugtenberg B (ed) Recognition in microbe-plant symbiotic and pathogenic interactions (NATO ASI Series vol H4). Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 101–111
Kijne JW, Smit G, Díaz CL, Lugtenberg BJJ (1988) Lectin-enhanced accumulation of manganese-limited Rhizobium leguminosarum cells on pea root hair tips. J Bacteriol 170:2994–3000
Koekman BP, Hooykaas PJJ, Schilperoort RA (1982) A functional map of the replicator region of the octopine Ti plasmid. Plasmid 7:119–132
Krens FA, Molendijk L, Wullems GJ, Schilperoort RA (1985) The role of bacterial attachment in the transformation of cell-wall-regenerating tobacco protoplasts by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Planta 166:300–308
Mellor HY, Glenn AR, Arwas R, Dilworth MJ (1987) Symbiotic and competitive properties of motility mutants of R. trifolii TA1. Arch Microbiol 148:34–39
Smit G, Kijne JW, Lugtenberg BJJ (1986) Correlation between extracellular fibrils and attachment of Rhizobium leguminosarum to pea root hair tips. J Bacteriol 168:821–827
Smit G, Kijne JW, Lugtenberg BJJ (1987) Both cellulose fibrils and a Ca2+-dependent adhesin are involved in the attachement of Rhizobium leguminosarum to pea root hair tips. J Bacteriol 169:4294–4301
Smit G, Kijne JW, Lugtenberg BJJ (1989a) Roles of flagella, lipopolysaccharide and a Ca2+-dependent cell surface protein in attachment of Rhizobium leguminosarum to pea root hair tips. J Bacteriol 171:569–572
Smit G, Logman TJJ, Boerrigter METI, Kijne JW, Lugtenberg BJJ (1989b) Purification and partial characterization of the Ca2+-dependent adhesin from Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae, which mediates the first step in attachment of Rhizobiaceae cells to plant root hair tips. J Bacteriol 171:4054–4062
Teintze M, Inouye M, Inouye S (1988) Characterization of calcium-binding sites in development-specific protein S of Myxococcus xanthus using site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem 263: 1199–1203
Zurkowski W (1980) Specific adsorption of bacteria to clover root hairs, related to the presence of plasmid pWZ2 in cells of Rhizobium trifolii. Microbios 27:27–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smit, G., Tubbing, D.M.J., Kijne, J.W. et al. Role of Ca2+ in the activity of rhicadhesin from Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae, which mediates the first step in attachment of Rhizobiaceae cells to plant root hair tips. Arch. Microbiol. 155, 278–283 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252212
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252212