Abstract
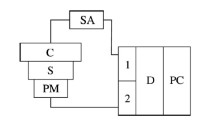
A scanning 6-detector whole body counter is described. Its characteristics include good sensitivity, high energy resolution, good counting efficiency, geometric uniformity and localisation information of incorporated radioactivity using collimators. Problems such as band-width, calibration for air and phantom and measurements on patients, are discussed. The whole body counter is compared to other systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnaby, C.F., Smith, T.: Calibration of a whole body counter suitable for use in routine clinical investigations. Phys. Med. biol. 16, 97–104 (1971)
Boddy, K., Elliott, A., Robertson, I., Mahaff, M.E., Holloway, I.: A high sensitivity dual-detector shadow-shield whole-body counter with an ‘invariant’ response for total body in vivo neutron activation analysis. Phys. Med. Biol. 20, 296–304 (1975)
Budd, R.S.: Whole body counting using a detector scanner. Aust. Radiol. 17, 464–469 (1973)
Cohn S.H., Dombrowki C.S., Pate, H.R., Robertson, J.S.: A whole-body counter with an invariant response to radionuclide distribution and body size. Phys. Med. Biol. 14, 645–658 (1969)
Cohn, S.H., Palmer, H.E.: Recent advances in whole body counting: a review. Int. J. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1, 155–165 (1974)
Dudley, R.A., Ben Haim, A.: Comparison of techniques for wholebody counting of gamma-ray emitting nucleides with NaJ (Tl) detectors. I. Point sources in phantoms. Phys. Med. Biol. 13, 181–193 (1968)
Erlenbach H.R.: Bewertung der physikalischen Strahlenschutzkontrolle in ihrer Ausübung als Inkorporationsüberwachung. In: Der ermächtigte Arzt im Sinne der Strahlenschutzgesetzgebung-spezielle Beiträge der Medizin zum Strahlenschutz. pp. 85–94. Stuttgart: Thieme 1976
Falk, R., Magi, A., Swedjemark, G.A.: Whole body measurement techniques at the Swedish National Institute of Radiation Protection. Acta Radiol. Ser. Diagn. Suppl. 10, 94–113 (1971)
Genna, S.: Analytical methods in whole-body counting. In: Clinical uses of whole-body counting. IAEA, Wien, 37–63 (1966)
Gibbs, W.D., Hodges, H.D., Bailey M., Lushbaugh, C.C.: Accurate whole-body quantification of J-131 retention by counting a scatter window. J. Nucl. Med. 11, 487–490 (1970)
International Atomic Energy Agency: Clinical uses of whole-body counting, Wien (1966)
International Atomic Energy Agency: Directory of whole-body radioactivity monitors, Wien (1970)
Hayes, R.L., Brucer, M.: Compartimentalized phantoms for the standard man, adolescent and child. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 9, 113–118 (1960)
Heinrich, H.C.: Intestinal iron absorption in man-methods of measurement dose relationship, diagnostic and therapeutic applications. In: Iron defiency, hallberg, L., Harwerth, A.-G., Vanotti, A. eds., pp. 213–296. London, New York: Academic Press 1970
Koeppe, P.: Ganzkörper Aktivitätszähler I.. Radiobiol. Radiother. (Berlin) 16, 369–418 (1975)
Kunkel, R., Muth, H., Oberhausen, E.: Ein Ganzkörperzähler für Forschung, klinische Anwendung und Strahlenschutzmessungen. Strahlentherapie 128, 98–108 (1965)
Mariß, P.: Die Ganzkörperradioaktivitäts-Meßtechnik in der Medizin. Habilitation-Thesis. Medizinische Hochschule Hannover, Germany (1977)
Naversten, Y.: A two-crystal scanning-bed couter for accurate determination of whole-body radioactivity. In: Assessment of radioactivity in man, pp. 55–66, Wien: IAEA 1964
Naversten, Y.: Some aspects of whole-body counting geometries. In: Clinical uses of whole-body counting, pp' 64–91. Wien: IAEA 1966
Pollycove, M., Mortimer, R.: The quantitative determination of iron kinetics and hemoglobin synthesis in human subjects. J. Clin. Invest. 40, 753–782 (1961)
Pollycove, M., Tono, M.: Studies of the erythron. Sem. Nucl. Med. 5, 11–61 (1975)
Reizenstein, P.: Clinical whole body counting. Bristol: John Wright & Sons Ltd. 1973
Schneider, C., Linden, W.A.: Ganzkörpermessung mit NaJ-Kristallen, Empfindlichkeit und Genauigkeit der Messung mit verschiedenen Detektoranordnungen. Strahlentherapie 133, 213–232 (1967)
Schober, O., Jahns, E., Mariß, P.: Evaluation of linear profilescans. Mathematical treatment of line spread functions. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 3, (1978)
Sorenson, J.A.: Quantitative measurement of radioactivity in vivo by whole body counting. In: Hine, G.J., Sorenson, K.A. eds., Instrumentation in Nuclear Medicine, Vol. 2, 311–348. New York, London: Academic Press 1974
Warner, G.T., Oliver, R.: A shole-body counter for clinical measurements utilizing the “shadow-shield” technique. Phys. Med. Biol. 11, 83–94 (1966)
Watts, J.R., Erickson, J.J., Kramer, C.E.: Design and evaluation of a scanning-bed whole-body counter for use in clinical studies. Health Phys. 23, 63–66 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mariß, P., Jahns, E. & Schober, O. A whole body counter with an invariant response for whole body analysis. Eur J Nucl Med 3, 129–135 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00251638
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00251638