Summary
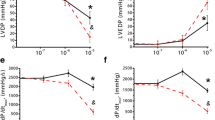
The effects of adenosine receptor agonists and antagonists on field-stimulated release of radioactivity from superfused guinea-pig papillary muscles preincubated with [3H]noradrenaline were studied. N 6-cyclopentyladenosine (CPA), N 6-(R-phenylisopropyl)-adenosine, and 5′-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine caused concentration-dependent inhibition of evoked overflow with a rank order of potency typical for interaction of the compounds with the A1-subtype of adenosine receptors. Maximum inhibition was 80%. The A1-selective antagonist 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropyl-xanthine (DPCPX) induced a rightward shift of the concentration-response curve for CPA with a pA 2 of 8.35. However, DPCPX per se had no effect on stimulation-evoked tritium overflow. On the other hand, in the presence of 4-nitrobenzylthioinosine (2 μmol/l) and deoxycoformycin (1 μmol/l), inhibitors of adenosine uptake and deamination, respectively, DPCPX produced a concentration-dependent increase in overflow with a pD 2 of 8.1. Pretreatment of the animals with pertussis toxin caused a substantial reduction in the activity of toxin-sensitive G proteins, as indicated by a lack of [32P]ADP ribosylation in a ventricular membrane preparation. Nevertheless, the inhibitory effect of the adenosine receptor agonists on stimulus-evoked overflow remained unaffected. These results are compatible with the existence of inhibitory prejunctional adenosine receptors in guinea-pig papillary muscle, which appear to be coupled to a pertussis toxin-insensitive G protein. The role of endogenous adenosine in occupying these receptors seems minimal under basal conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allgaier C, Feuerstein TJ, Heating G (1986) N-Ethylmaleimide (NEM) diminishes α2-adrenoceptor mediated effects on noradrenaline release. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 333:104–109
Allgaier C, Hertting G, von Kügelgen O (1987) The adenosine receptor-mediated inhibition of noradrenaline release possibly involves an N-protein and is increased by α2-autoreceptor blockade. Br J Pharmacol 90:403–412
Asano T, Ogasawara N (1986) Uncoupling of γ-aminobutyric acidB receptors from GTP-binding proteins by N-ethylmaleimide: effect of N-ethylmaleimide on purified GTP-binding proteins. Mol Pharmacol 29:244–249
Bokoch GM, Katada T, Northup JK, Hewlett EL, Gilman AG (1983) Identification of the predominant substrate for ADP-ribosylation by islet activating protein. J Biol Chem 258:2071–2075
Clanachan AS, Johns A, Paton DM (1977) Presynaptic inhibitory actions of adenine nucleotides and adensoine on neurotransmission in the rat vas deferens. Neurosci 2:597–602
Docherty JR (1988) Pertussis toxin and pre-junctional α2-adrenoceptors in rat heart and vas deferens. J Anton Pharmacol 8:197–201
Enero MA, Saidman BQ (1977) Possible feed-back inhibition of noradrenaline release by purine compounds. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 297:39–46
Fredholm BB, Hedqvist P, Lindström K, Wennmalm M (1982) Release of nucleosides, and nucleotides from the rabbit heart by sympathetic nerve stimulation. Acta Physiol Scand 116:285–295
Fredholm BB, Lindgren E (1987) Effects of N-ethylmaleimide and forskolin on noradrenaline release from rat hippocampal slices. Evidence that prejunctional adenosine and α-receptors arc linked to N-proteins but not to adenylate cyclase. Acta Physiol Scand 130:95–105
Fredholm BB, Dunwiddie TV (1988) How does adenosine inhibit transmitter release? Trends Pharmacol Sci 9:130–134
Fredholm BB, Proctor W, van der Ploeg J, Dunwiddie TV (1989) In vivo pertussis toxin treatment attenuates some, but not all, adenosine A1 effects in slices of the rat hippocampas. Eur J Pharmacol (Mol Pharmacol Sect) 172:249–262
Hedqvist P, Fredholm BB (1975) Inhibitory effect of adenosine on adrenergic neuroeffector transmission in the rabbit heart. Acta Physiol Scand 105:120–122
Hedqvist P, Fredholm BB, Ölundh S (1978) Antagonistic effects of theophylline and adenosine on adrenergic neuroeffector transmission in the rabbit kidney. Circ Res 43:592–598
Jackisch R, Fehr R, Hertting G (1985) Adenosine: an endogenous modulator of hippocampal noradrenaline release. Neuropharmacol 24:499–507
Jakobs KH, Aktories K, Schulz G (1984) Mechanisms and components involved in adenylate cyclase inhibition by hormones. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res 17:135–143
Murphy TV, Majewski H (1990) Pertussis toxin differentiates between α1- and α2-adrenoceptor-mediated inhibition of noradrenaline release from rat kidney cortex. Eur J Pharmacol 179:435–439
Musgrave IF, Marley P, Majewski H (1987) Pertussis toxin does not attenuate α2-adrenoceptor mediated inhibition of noradrenaline release in mouse atria. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 336:280–286
Musgrave IF, Majewski H (1989) Effect of phorbol ester and pertussis toxin on the enhancement of noradrenaline release by angiotensin II in mouse atria. Br J Pharmacol 96:609–616
Nabika T, Velletri P, Lovenberg W, Beaven MA (1985) Increase in cytosolic calcium and phosphoinositide metabolism induced by antiotensin II and [arg]vasopressin in vascular smooth muscle. J Biol Chem 260:4661–4670
Reichenbacher D, Reimann W, Starke K (1982) Alpha-adrenoceptor-mediated inhibition of noradrenaline release in rabbit brain cortex slices. Receptor properties and role of the biophase concentration of noradrenaline. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 319:71–77
Richardt G, Waas W, Kranzhöfer R, Mayer E, Schömig A (1987) Adenosine inhibits exocytotic release of endogenous noradrenaline in rat heart: a protective mechanism in early myocardial ischemia. Circ Res 61:117–123
Singer EA (1988) Transmitter release from brain slices elicited by single pulses: a powerful method to study presynaptic mechanisms. Trends Pharmacol Sci 9:274–276
Smith MM, Harden TK (1984) Modification of receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase in NG 108–15 neuroblastoma × glioma cells by N-ethylmaleimide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 228:425–433
Sternweis PC, Robishaw JD (1984) Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem 256:11517–11526
Su C (1978) Purinergic inhibition of adrenergic transmission in rabbit blood vessels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 204:351–361
Valenta A, Pittner H, Singer EA (1989) Evidence for β-adrenoceptor-mediated facilitation of [3H]noradrenaline release from isolated guinea pig papillary muscles. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 14:846–850
Verhaeghe RH, Vanhoutte PM, Sheperd JT (1977) Inhibition of sympathetic neurotransmission in canine blood vessels by adenosine and adenine nucleotides. Circ Res 40:208–215
Wakade AR, Wakade TD (1978) Inhibition of noradrenaline release by adenosine. J Physiol (London) 282:35–49
Wakade AR, Wakade TD (1982) Mechanism of presynaptic actions of adenosine and acetylcholine on noradrenaline release in the guinea-pig heart. Neurosci 7:2267–2276
Wennmalm M, Fredholm BB, Hedqvist P (1988) Adenosine as a modulator of sympathetic nerve-stimulation-induced release of noradrenaline from the isolated rabbit heart. Acta Physiol Scand 132:487–494
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schütz, W., Ströher, M., Freissmuth, M. et al. Adenosine receptors mediate a pertussis toxin-insensitive prejunctional inhibition of noradrenaline release on a papillary muscle model. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 343, 311–316 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00251132
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00251132