Summary
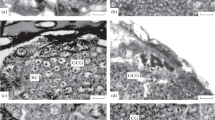
The DNA-binding drug, bleomycin, has a profound effect on neural repair following selective glial disruption by ethidium bromide. The contribution of the granule-containing cells (which normally appear in the early stages of repair) is greatly reduced, the restoration of the blood-brain barrier is delayed and the ultrastructural organization of the reorganising perineurium is dramatically changed. The aberrant perineurial structure and function observed in the presence of bleomycin are postulated to result from the effects of the drug on haemocytes which, together with endogenous reactive cells, contribute to the normal process of glial repair.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian EK, Schelper RL (1981) Microglia, monocytes and macro-phages. In: E.A. Vidrio, F. Federoff (eds) Glial and neuronal cell biology. Alan Liss Inc., New York, pp 113–124
Blakemore WF (1982) Ethidium bromide induced demyelination in the spinal cord of the cat. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 8:365–375
Brockes JP (1984) Mitogenic growth factors and nerve dependence of limb regeneration. Science 225:1280–1287
Crossley AC (1975) The cytophysiology of insect blood. Adv Insect Physiol 11:117–221
Howes EA, Leech CA (1985) Organ culture of adult cockroach CNS: ultrastructural and physiological characteristics. Tissue and Cell 17:000–000
Kuo MT (1981) Preferential damage of active chromatin by bleomycin. Cancer Res 41:2439–2443
Lane NJ, Skaer H.leB. (1980) Intercellular junctions in insect tissues. Adv Ins Physiol 15:35–213
Lane NJ, Treherne JE (1980) Functional organisation of arthropod neuroglia. In: Locke M, Smith DS (eds) Insect biology in the future. Academic Press, London
Latov N, Nilaver G, Zimmerman EA, Johnson WG, Silverman A, Defendini R, Cote L (1979) Fibrillary astrocytes proliferate in response to brain injury. Dev Biol 72:381–384
Leech CA (1984) Effects of ethidium bromide on cells of the cockroach central nervous system. J Cell Sci 70:17–24
Ludwin SK (1984) Proliferation of mature oligodendrocytes after trauma to the central nervous system. Nature 308:274–275
Morgese VJ, Elliott EJ, Muller KJ (1983) Microglial movement to sites of nerve lesion in the leech CNS. Brain Res 272:166–170
Nelson JW, Tinoco I Jr (1984) Intercalation of ethidium ion into DNA and RNA oligonucleotides. Biopolymers 23:213–233
Raff MC, Miller RH, Noble M (1983) A glial progenitor cell that develops in vitro into an astrocyte or an oligodendrocyte depending of culture medium. Nature 303:390–396
Sausville EA, Horwitz SB (1979) A mechanism for the degradation of DNA by bleomycin. In: Busch H, Crooke ST, Daskal Y (eds) Effects of drugs on the cell nucleus. Academic Press, New York London, pp 181–205
Scharrer B (1972) Cytophysiological features of hemocytes in cockroaches. Z Zellforsch 129:301–319
Schofield PK, Treherne JE (1984) Localization of the blood-brain barrier in an insect: electrical model and analysis. J Exp Biol 109:319–331
Schofield PK, Swales LS, Treherne JE (1984) Potentials associated with the blood-brain barrier of an insect: recording from identified neuroglia. J Exp Biol 109:307–318
Smith PJS, Leech CA, Treherne JE (1984) Glial repair in an insect central nervous system: effects of selective glial disruption. J Neurosci 4(11): 2698–2711
Smith PJS, Howes EA, Leech CA, Treherne JE (1985) Haemocyte contribution to glial repair in an insect central nervous system. Cell and Tissue Res 243:367–374
Treherne JE, Harrison JB, Treherne JM, Lane NJ (1984) Glial repair in an insect central nervous system: effects of surgical lesioning. J Neurosci 4(11): 2689–2697
Yajima K, Suzuki K (1979) Demyelination and remyelination in the rat CNS following ethidium bromide injection. Lab Invest 41:385–392
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Treherne, J.E., Howes, E.A., Leech, C.A. et al. The effects of an anti-mitotic drug, bleomycin, on glial repair in an insect central nervous system. Cell Tissue Res. 243, 375–384 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00251054
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00251054