Abstract
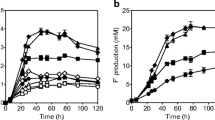
The ruminal bacterium Synergistes jonesii strain 78-1, which is able to degrade the pyridinediol toxin in the plant Leucaena leucephala, was studied for its ability to utilise amino acids. The organism used arginine, histidine and glycine from a complex mixture of amino acids, and both arginine and histidine supported growth in a semi-defined medium. The products of (U-14C)-arginine metabolism were CO2 acetate, butyrate, citrulline and ornithine. The labelling pattern of end products from (U-14C)-histidine metabolism differed in that carbon also flowed into formate and propionate. Arginine was catabolised by the arginine deiminase pathway which was characterised by the presence of arginine deiminase, ornithine transcarbamylase and carbamate kinase. This is the first report of a rumen bacterium that uses arginine and histidine as major energy yielding substrates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison MJ, Cook HM, Stahl DA (1987) Characterization of rumen bacteria that degrade dihydrosypyridine compounds produced from mimosine. In: Rose M (ed) Herbivore nutrition research Australian Society of Animal Production, Brisbane, Australia, pp 55–56
Allison MJ, Hammond AC, Jones RJ (1990) Detection of ruminal bacterial that degrade toxic dihydroxypyridine compounds produced from mimosine. Appl Environ Microbiol 56: 590–594
Allison MJ, Mayberry WR, McSweeney CS, Stahl DA (1992) Synergistes jonesii, gen. nov., sp. nov.: a rumen bacterium that degrades toxic pyridinediols. Syst Appl Microbiol (in press)
Barker HA (1961) Fermentations of nitrogenous organic compounds. In: Gunsalus IC, Stanier RY (eds) The bacteria, vol 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 151–207
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein, utilising the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254
Bryant MP (1972) Commentary on the Hungate technique for culture of anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr 25: 1324–1328
Caldwell DR, Bryant MP (1966) Medium without rumen fluid for nonselective enumeration and isolation of rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol 14: 794–801
Canale A, Valente ME, Ciotti A (1984) Determination of volatile carboxylic acids (C1−C5) and lactic acid in aqueous extracts of silage by high performance liquid chromatography. J Sci Food Agri 38: 1178–1182
Crow VL, Thomas TD (1982) Arginine metabolism in lactic streptococci. J Bacteriol 150: 1024–1032
Cunin R, Glansdorff N, Pierard A, Stalon V (1986) Biosynthesis and metabolism of arginine in bacteria. Microbiol Rev 50: 314–352
Driessen AJM, Molenaar D, Konings WN (1989) Kinetic mechanism and specificity of the arginine-ornithine antiporter of Lactococcus lactis. J Biol Chem 264: 10361–10370
Dominguez-Bello MG, Stewart CS (1990) Degradation of mimosine, 2,3-dihydroxy pyridine and 3-hydroxy-4 (1H)-pyridone by bacteria from the rumen of sheep in Venezuela. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 73: 283–289
Gottschalk G (1986) Fermentation of nitrogenous compounds. In: Gottschalk G (ed) Bacterial metabolism, vol 2. Springer, New York Berlin Heidelberg, pp 269–282
Hammond AC, Allison MJ, Williams MJ, Prine GM, Bates DB (1989) Prevention of Leucaena toxicosis of cattle in Florida by ruminal inoculation with 3-hydroxy-4-(1H)-pyridone-degrading bacteria. Am J Vet Res 50: 2176–2180
Hart NK, Hofmann A, Lamberton JA, Richards CM (1977) Mimosine, mimosinamine and 3,4 dihydroxypyridine. Heterocycles 7: 265–272
Hegarty MP, Schinckel PG, Court RD (1964) Reaction of sheep to the consumption of Leucaena glauca benth and to its toxic principle mimosine. Aust J Agric Res 15: 153–167
Hungate RE (1969) A roll tube method for cultivation of strict anoerobes. In: Norris IR, Ribbons EW (eds) Methods in microbiology, vol 3. Academic Press, New York London, pp 117–132
Jones RJ (1979) The value of Leucaena leucocephala as a feed for ruminants in the tropics. World Anim Rev 31: 13–23
Jones RJ (1981) Does ruminal metabolism of mimosine explain the absence of Leucaena toxicity in Hawaii? Aust Vet J 57: 55
Jones RJ, Megarrity RG (1983) Comparable toxicity responses of goats fed Leucaena leucocephala in Australia and Hawaii. Aust J Agric Res 34: 781–790
Jones RJ, Lowry JB (1984) Australian goats detoxify the goitrogen 3-hydroxy-4(1H)pyridone (DHP) after rumen infusions from an Indonesian goat. Experientia 40: 1435–1436
Jones RJ, Megarrity RG (1986) Successful transfer of DHP-degrading bacteria from Hawaiian goats to Australian ruminants to overcome the toxicity of Leucaena. Aust Vet J 63: 259–262
Lowry JB, Maryanto, Tangendjaja B (1983) Autolysis of mimosine to 3-hydroxy-4–1 (H)pyridone in green tissues of Leucaena leucocephala. J Sci Fd Agric 34: 529–533
Monstadt GM, Holldorf AW (1990) Arginine deiminase from Halobacterium salinarium. Biochem J 273: 739–745
Russell JB, Wallace RJ (1988) Energy yielding and consuming reactions. In: Hobson PN (ed) The rumen microbial ecosystem. Elsevier Applied Science, New York, pp 185–215
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McSweeny, C.S., Allison, M.J. & Mackie, R.I. Amino acid utilization by the ruminal bacterium Synergistes jonesii strain 78-1. Arch. Microbiol. 159, 131–135 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00250272
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00250272