Summary
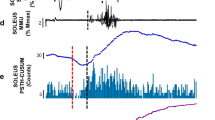
The reflex responses of single motor units in the soleus muscle to electrical stimulation of the tibial nerve were recorded in human volunteers. A feature of the experiments was the stimulation paradigm used. In order to control the peristimulus firing rate, a computer triggered the stimulus isolator only when 2 interspike intervals of specified duration occurred in succession. In addition, the timing of the stimulus in relation to the preceding action potential was controlled in a manner similar to a conditioning/testing paradigm. The general pattern of response was an initial, “H-reflex” excitation at monosynaptic latency, followed first by a silent period due to the refractoriness of the motor neurone, then by other phases of reduced activity. When the stimulus intensity was increased, the intensity of the excitation and the duration of the silent period increased in parallel. When the pre-stimulus firing rate of the motor unit was varied, the amplitude of the H-reflex response, normalized to the number of stimulus trials, was similar at 6, 8 and 10 Hz, but was greater at 4 Hz in most units tested. These findings were consistent with a simple model of the events occurring at the cell membrane in this reflex which was proposed by Ashby and Zilm (1982a), although some modification of the model was necessary to account for the different response at 4 Hz. The improved stimulation paradigm enabled a direct estimate to be made of the amplitude and shape of the rising phase of the Ia EPSP in human motor neurones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashby P, Labelle K (1977) Effects of extensor and flexor group I afferent volleys on the excitability of individual soleus motoneurones in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 40:910–919
Ashby P, Zilm D (1982a) Relationship between EPSP shape and cross-correlation profile explored by computer simulation for studies of human motoneurones. Exp Brain Res 47:33–40
Ashby P, Zilm D (1982b) Characteristics of postsynaptic potentials produced in single human motoneurons by homonymous group I volleys. Exp Brain Res 47:41–47
Baldissera F, Gustafsson B (1974) Afterhyperpolarization conductance time course in lumbar motoneurones of the cat. Acta Physiol Scand 91:512–527
Calvin WH (1974) Three modes of repetitive firing and the role of threshold time course between spikes. Brain Res 69:341–346
Calvin WH, Stevens CF (1968) Synaptic noise and other sources of randomness in motoneurone interspike intervals. J Neurophysiol 31:574–587
Cope TC, Fetz EE, Matsumura M (1987) Cross-correlation assessment of synaptic strength of single Ia fibre connections with triceps surae motoneurones in cats. J Physiol (Lond) 390:161–188
Ellaway PH (1978) Cumulative sum technique and its application to the analysis of peristimulus time histogram. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 45:302–304
Fetz EE, Gustafsson B (1983) Relation between shapes of postsynaptic potentials and changes in firing probability of catmotoneurones. J Physiol (Lond) 341:387–410
Gustafsson B, McCrea D (1984) Influence of stretch-evoked synaptic potentials of firing probability of cat spinal motoneurones. J Physiol (Lond) 347:431–451
Kirkwood PA (1979) On the use and interpretation of cross-correlation measurements in the mammalian central nervous system. J Neurosci Meth 1:107–132
Matsumura M, Cope T, Fetz EE (1988) Sustained excitatory synaptic input to motor cortex neurons in awake animals revealed by intracellular recording of membrane potentials. Exp Brain Res 70:463–469
Miles TS, Le TH, Türker KS (1989) Biphasic inhibitory responses and their IPSPs evoked by tibial nerve stimulation in human soleus motor neurones. Exp Brain Res 77:637–645
Miles TS, Türker KS, Nordstrom MA (1987) Reflex responses of motor units in human masseter muscle to electrical stimulation of the lip. Exp Brain Res 65:331–336
Moore GP, Segundo JP, Perkel DH, Levitan H (1970) Statistical signs of synaptic interactions in neurons. Biophys J 10:876–900
Schwindt PC, Calvin WH (1972) Membrane potential trajectories between spikes underlying motoneurone firing rates. J Neurophysiol 35:311–325
Trontelj JV (1968) H-reflex of single motoneurones in man. Nature 220:1043–1044
Trontelj JV (1973) A study of the H-reflex by single fibre EMG. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 36:951–959
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miles, T.S., Türker, K.S. & Le, T.H. Ia reflexes and EPSPs in human soleus motor neurones. Exp Brain Res 77, 628–636 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00249616
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00249616