Abstract
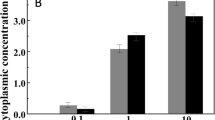
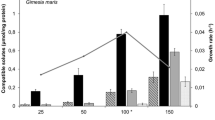
Ectothiorhodospira marismortui, a moderately halophilic purple sulfur bacterium from a hypersaline sulfur spring, contains glycine betaine and Nα-carbamoyl glutamineamide (CGA) as the main intracellular osmotic solutes, with sucrose as a minor component. The concentration of glycine betaine was found to increase with increasing salt concentration of the medium, from 0.47 M to 1.29 M in cells grown from 0.85 to 2.56 M NaCl, while the estimated CGA concentration rose from about 0.2 M to 0.5 M. The concentration of sucrose remained constant at a value of around 0.05 M. Intracellular sodium and potassium concentrations were relatively low (around 0.5 and 0.3 M, respectively, at an external NaCl concentration of 1.8 M). The concentration of the novel compound Nα-carbamoyl glutamineamide was enhanced when l-glutamine was added to the growth medium, suggesting that glutamine served as a precursor for the synthesis of the compound.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CGA:
-
Nα-carbamoyl glutamineamide
References
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1969) A rapid method of lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37: 911–917
Blumwald E, Tel-Or E (1982) Osmoregulation and cell composition in salt-adaptation of Nostoc muscorum. Arch Microbiol 132: 168–172
Brown AD (1976) Microbial water stress. Bacteriol Rev 40: 803–846
Galinski EA, Herzog RM (1990) The role of trehalose as a substitute for nitrogen-containing compatible solutes (Ectothiorhodospira halochloris). Arch Microbiol 153: 607–613
Galinski EA, Oren A (1991) Isolation and structure determination of a novel compatible solute from the moderatley halophilic purple sulfur bacterium Ectothiorhodospira marismortui. Eur J Biochem (in press)
Galinski EA, Trüper HG (1982) Betaine, a compatible solute in the extremely halophilic phototrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira halochloris. FEMS Microbiol Lett 13: 357–360
Galinski EA, Pfeiffer H-P, Trüper HG (1985) 1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinecarboxylic acid. A novel cyclic amino acid from halophilic phototrophic bacteria of the genus Ectothiorhodospira. Eur J Biochem 149: 135–139
Gorham J (1984) Separation of plant betaines and their sulfur analogues by cation-exchange high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 287: 345–351
Imhoff JF (1986) Osmoregulation and compatible solutes in cubacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39: 57–66
Imhoff JF, Riedel T (1989) Requirements for, and cytoplasmic concentrations of, sulphate and chloride, and cytoplasmic volume spaces in the halophilic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira mobilis. J Gen Microbiol 135: 237–244
Imhoff JF, Rodriguez-Valera F (1984) Betaine is the main compatible solute of halophilic eubacteria. J Bacteriol 160: 478–479
Kushner DJ (1978) Life in high salt and solute concentrations: halophilic bacteria. In: Kushner DJ (ed) Microbial life in extreme environments. Academic Press, London, pp 317–368
Mackay MA, Norton RS, Borowitzka LJ (1984) Organic osmoregulatory solutes in cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 130: 2177–2191
Nissen H, Dundas ID (1984) Rhodospirillum salinarium sp. nov., a halophilic photosynthetic bacterium isolated from a Portugese saltern. Arch Microbiol 138: 251–256
Oren A (1989) Photosynthetic and heterotrophic benthic bacterial communities of a hypersaline sulfur spring on the shore of the Dead Sea (Hamei Mazor). In: Cohen Y, Rosenberg E (eds) Microbial mats: physiological ecology of benthic microbial communities. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, pp 64–76
Oren A, Kessel M, Stackebrandt E (1989) Ectothiorhodospira marismortui sp. nov., an obligately anaerobic, moderately halophilic purple sulfur bacterium from a hypersaline sulfur spring on the shore of the Dead Sea. Arch Microbiol 151: 524–529
Pfennig N, Lippert DT (1966) Über das Vitamin B12-Bedürfnis phototropher Schwefelbakterien. Arch Mikrobiol 55: 245–256
Reed RH, Richardson DL, Warr SRC, Stewart WDP (1984) Carbohydrate accumulation and osmotic stress in cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 130: 1–4
Reed RH, Borowitzka LJ, Mackay MA, Chudek JA, Foster R, Warr SRC, Moore DJ, Stewart WDP (1986) Organic solute accumulation in osmotically stressed cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39: 51–56
Remsen CC, Watson SW, Waterbury JB, Trüper HG (1968) Fine structure of Ectothiorhodospira mobilis Pelsh. J Bacteriol 95: 2374–2392
Shindler DB, Wydro RM, Kushner DJ (1977) Cell-bound cations of the moderately halophilic bacterium, Vibrio costicola. J Bacteriol 130: 698–703
Speed D, Richardson M (1968) Chromatographic methods for the isolation and identification of the products of choline oxidation. J Chromatogr 35: 479–505
Trüper HG, Galinski EA (1986) Concentrated brines as habitats for microorganisms. Experientia 42: 1182–1187
Ventura S, DePhilippis R, Materassi R, Balloni W (1988) Two halophilic Ectothiorhodospira strains with unusual morphological, physiological and biochemical characters. Arch Microbiol 149: 273–279
Wanner G, Steiner R, Scheer H (1986) A three dimensional model of the photosynthetic membranes of Ectothiorhodospira halochloris. Arch Microbiol 146: 267–274
Wohlfarth A, Severin J, Galinski EA (1990) The spectrum of compatible solutes in heterotrophic halophilic eubacteria of the family Halomonadaceae. J Gen Microbiol 136: 705–712
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oren, A., Simon, G. & Galinski, E.A. Intracellular salt and solute concentrations in Ectothiorhodospira marismortui: glycine betaine and Nα-carbamoyl glutamineamide as osmotic solutes. Arch. Microbiol. 156, 350–355 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248709
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248709