Abstract
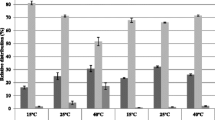
Total fatty acid synthetase (FAS) and cyclopropane fatty acid synthetase (CFAS) activities in cell-free lysates of the moderately-halophilic eubacterium HX, have been determined using radiolabelled malonyl-CoA and S-adenosylmethionine respectively as the precursor. The activities of FAS and CFAS were extremely low in vitro in 100 mM buffers, but were stimulated up to 100-fold by exogenous addition of the compatible-solute glycinebetaine to lysates; optimum activities of FAS and CFAS in vitro were obtained in 2–3 M concentrations of this compatible solute. In contrast, NaCl added to the lysate assay system was strongly inhibitory: CFAS was 97% inhibited by 1 M NaCl whereas FAS was less sensitive with 3 M NaCl giving 82% inhibition. When the culture medium salinity was raised from 1 to 3 M NaCl, the endogenous activity of CFAS measured in vitro in lysates without additional compatible solute was approximately doubled. This increase in CFAS activity is enough to account for the known increase in CFA content which occurs when culture medium salinity is raised, and the data are discussed in the context of the role of intracellular compatible solutes during haloadaptation of membrane lipid composition.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FAS:
-
fatty acid synthetase
- CFA:
-
cyclopropane fatty acid
- CFAS:
-
cyctopropane fatty acid synthetase
References
Adams RL (1988) Salinity effects on membrane lipid composition in halophilic and halotolerant bacteria. MSc Thesis, University of Wales, Cardiff.
Adams RL, Kogut M, Russell NJ (1990) The effect of salinity on growth and lipid composition of a moderately halophilic Gramnegative bacterium HX. Biochem Cell Biol 68: 249–254.
Choquet CG, Kamekura M, Kushner DJ (1989) In vitro protein synthesis by the moderate halophile Vibrio costicola: site of action of Cl- ions. J Bacteriol 171: 880–886.
Csonka LN (1989) Physiological and genetic responses of bacteria to osmotic stress. Microbiol Rev 53: 121–147.
Gilboa H, Kogut M, Chalamish S, Regev R, Avi-Dor Y, Russell NJ (1991) Use of 23Na nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to determine the true intracellular concentration of free sodium in a halophilic eubacterium. J Bacteriol 173: 7021–7023.
Harwood JL, Russell NJ (1984) Lipids in plants and microbes. Allen & Unwin, London.
Imhoff JF (1986) Osmoregulation and compatible solutes in eubacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39: 57–66.
Kamekura M (1986) Production and function of enzymes of eubacterial halophiles. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39: 145–150.
Ken-Dror S, Shnaiderman R, Avi-Dor Y (1983) Uncoupler-stimulated Na+ pump and its possible role in the halotolerant bacterium Ba1. Arch Biochem Biophys 229: 640–649.
Kushner DJ (1986) Molecular adaptation of enzymes, metabolic systems and transport systems in halophilic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39: 121–127.
Kushner DJ, Kamekura M (1988) Physiology of halophilic eubacteria. In: Rodriguez-Valera F (ed) Halophilic bacteria, vol 1 CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fl. pp 109–138.
Lippert K, Galinski EA (1992) Enzyme stabilization by ectoine-type compatible solutes: protection against heating, freezing and drying. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 37: 61–65.
Markwell MAK, Haas SM, Bieber LL, Tolbert NE (1978) A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem 87: 206–210.
Monteoliva-Sanchez M, Ramos-Cormenzana A, Russell NJ (1993) The effect of salinity and compatible solutes on the biosynthesis of cyclopropane fatty acids in Pseudomonas halosaccharolytica. J Gen Microbiol 139: 1877–1884.
Pollard A, Wyn-Jones RG (1979) Enzyme activities in concentrated solutions of glycine betaine and other solutes. Planta 144: 291–298.
Pugh EL, Wassef MK, Kates M (1971) Inhibition of fatty acid synthetase in Halobacterium cutirubrum and Escherichia coli by high salt concentrations. Can J Biochem 49: 953–958.
Russell NJ (1989a) Adaptive modifications in membranes of halotolerant and halophilic microorganisms. J Bioenerg Biomembr 21: 93–113.
Russell NJ (1989b) Functions of lipids: structural roles and membrane functions. In: Wilkinson SG, Ratledge C (eds) Microbial lipids, vol 2, chapter 17. Academic Press, London, pp 279–365.
Russell NJ (1992) Lipids of halophilic and halotolerant microorganisms. In: Vreeland RH, Hochstein L (eds) The biology of halophilic bacteria, chapter 7. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL., pp 163–210.
Russell NJ, Kogut M, Kates M (1985) Phospholipid biosynthesis in the moderately halophilic bacterium Vibrio costicola during adaptation to changing salt concentrations. J Gen Microbiol 131: 781–789.
Severin J, Wohlfarth A, Galinski EA (1992) The predominant role of recently discovered tetrahydropyrimidines for the osmoadaptation of halophilic eubacteria. J Gen Microbiol 138: 1629–1638.
Sutton GC, Russell NJ, Quinn PJ (1990) The effect of salinity on the phase behaviour of purified phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylglycerol isolated from a moderately halophilic eubacterium. Chem Phys Lipids 56: 135–147.
Sutton GC, Russell NJ, Quinn PJ (1991) The effect of salinity on the phase behaviour of total lipid extracts and binary mixtures of the major phospholipids isolated from a moderately halophilic eubacterium. Biochim Biophys Acta 1061: 235–246.
Taylor FR, Cronan Jr JE (1979) Cyclopropane fatty acid synthase of Escherichia coli. Stabilization, purification, and interaction with phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry 18: 3292–3300.
Tokuda H, Unemoto T (1983) Growth of a marine Vibrio alginolyticus and moderately halophilic V. costicola becomes uncoupler resistant when the respiration-dependent Na+ pump functions. J Bacteriol 156: 636–643.
Wohlfarth A, Severin J, Galinski EA (1990) The spectrum of compatible solutes in heterotrophic halophilic eubacteria of the family Halomonadaceae. J Gen Microbiol 136: 705–712.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuchta, T., Russell, N.J. Glycinebetaine stimulates, but NaCl inhibits, fatty acid biosynthesis in the moderately halophilic eubacterium HX. Arch. Microbiol. 161, 234–238 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248698
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248698