Abstract
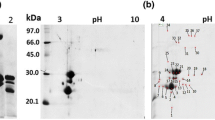
On artificial polyethylene membranes providing a thigmotropic signal, uredospores of the broad bean rust fungus Uromyces viciae-fabae differentiated a series of infection structures which in nature are necessary to invade the host tissue through the stomata. Within 24 h germ tubes, appressoria, substomatal vesicles, infection hyphae and haustorial mother cells were developed successively. Alterations in protein metabolism during infection structure differentiation of this obligate plant pathogen were analyzed in the absence of the host plant by high resolution two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (2-DE) and silver staining. The norm pattern representing the 2-DE protein patterns of the whole developmental sequence of infection structures of U. viciae-fabae showed 733 spots. During infection structure differentiation 55 proteins were newly formed, altered in quantity, or disappeared. Major alterations in the protein pattern occurred during uredospore germination and when infection hyphae were formed. Uredospore germination was characterized by a decrease of acidic proteins and an increase mainly of proteins with isoelectric points ranging from weakly acidic to basic.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2-DE:
-
two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- DAPI:
-
4,6-diamino-phenylindol
- kDa:
-
kilo Dalton
- pl:
-
isoelectric point
- PMSF:
-
phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
- SDS-PAGE:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
References
BhairiSM, StaplesRC, FreveP, YoderOC (1989) Characterization of an infection structure-specific gene from the rust fungus Uromyces appendiculatus. Gene 81: 237–243
BhairiSM, LaccettiL, StaplesRC (1990) Effect of heat shock on expression of thigmo-specific genes from a rust fungus. Exp Mycol 14: 94–98
BradfordMM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254
CarlileMJ (1975) Taxes and tropisms: Diversity, biological significance and evolution. In: CarlileMJ (ed) Primitive sensory and communication systems. The taxes and tropisms of microorganisms and cells. Academic Press, London New York, pp 1–28
DickinsonS (1949) Studies in the physiology of obligate parasitism. II. The behaviour of the germ tubes of certain rusts in contact with various membranes. Ann Bot 13: 219–236
DunnGA, HealthJP (1976) A new hypothesis of contact guidance in tissue cells. Exp Cell Res 101: 1–14
EckerskornC, JungblutP, MewesW, KloseJ, LottspeichF (1988) Identification of mouse brain proteins after two-dimensional electrophoresis and electroblotting by microsequence analysis and amino acid composition analysis. Electrophoresis 9: 830–838
FreytagS, BruscaglioniL, GoldRE, MendgenK (1988) Basidiospores of rust fungi (Uromyces species) differentiate infection structure in vitro. Exp Mycol 12: 275–283
HochHC, StaplesRC (1987) Structural and chemical ranges among the rust fungi during appressorium development. Annu Rev Phytopathol 25: 231–247
HochHC, StaplesRC, WhiteheadB, ComeauJ, WolfED (1987) Signaling for growth orientation and cell differentiation by surface topography in Uromyces. Science 235: 1659–1662
HuangB-F, StaplesRC (1982) Synthesis of proteins during differentiation of the bean rust fungus. Exp Mycol 6: 7–14
JugblutPR, KloseJ (1986) Composition and genetic variability of Heparin-Sepharose CL-6B protein fractions obtained from the solubilized proteins of mouse organs. Biochem Gene 24: 925–939
JungblutPR, SeifertR (1990) Analysis by high resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of differentiation-dependent alternations in cytosolic protein pattern of HL-60 leucemic cells. J Biochem Biophys Methods 21: 47–58
JungblutPR, SchneiderW, KloseJ (1985) Quantitative analysis of two-dimensional electrophoresis protein patterns: Comparison of visual evaluation with computer-assisted evaluation. In: NeuhoffV (ed) Electrophoresis '84. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 301–303
KimWK, HowesNK, RohringerR (1982) Detergent-soluble polypeptides in germinated uredospores and differentiated uredosporelings of wheat stem rust. Can J Plant Pathol 4: 328–333
KloseJ (1975) Protein mapping by combined isoelectric focusing and electrophoresis of mouse tissue. A novel approach to testing for induced point mutations in mammals. Humangenetik 26: 231–243
KunohH, NicholsonRL, KobayashiI (1991) Extracellular materials of fungal structures: Their significance at prepenetration stages of infection. In: MendgenK, LesemannDE (eds) Electronmicroscopy of plant pathogens. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 223–234
MendgenK, SchneiderA, SterkM, FinkW (1988) The differentiation of infection structures as a result of recognition events between some biotrophic parasites and their hosts. J Phytopathol 123: 259–272
ShawM, BoassonR, ScrubbL (1985) Effect of heat shock on protein synthesis in flax rust uredosporelings. Can J Bot 63: 2069–2076
StaplesRC, HuangB-F (1981) Gene activation during differentiation of the rusts and anthracnose fungi. In: TurianG, HohlHR (eds) The fungal spore: Morphogenetic controls. Academic Press, London New York, pp 335–353
StaplesRC, GrambowHJ, HochHC, WynnWK (1983) Contact with membrane grooves induces wheat stem rust uredospore germlings to differentiate appressoria but not vesicles. Phytopathology 73: 1436–1439
StaplesRC, YoderOC, HochHC, EpsteinL, BhairiS (1986) Gene expression during infection structure development by germlings of the rust fungi. In: BaileyJA (ed) Biology and molecular biology of plant-pathogen interactions. NATO ASI Series, vol H1. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 331–341
StaplesRC, HochHC, FreveP, BourettTM (1989) Heat shockinduced development of infection structures by bean rust uredospore germlings. Exp Mycol 13: 149–157
WannerR, FörsterH, MendgenK, StaplesR (1985) Synthesis of differentiation-specific proteins in germlings of the wheat stem rust fungus after heat shock. Exp Mycoll 9: 279–283
WynnWK (1976) Appressrium formation over stomates by the bean rust fungus: Response to a surface contact stimulus. Phytopathology 66: 136–146
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deising, H., Jungblut, P.R. & Mendgen, K. Differentiation-related proteins of the broad bean rust fungus Uromyces viciae-fabae, as revealed by high resolution two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Arch. Microbiol. 155, 191–198 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248616
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248616