Summary
The cholinesterase inhibiting organophosphates induce a dangerous or lethal depression of respiratory activity by central and peripheral effects. In many species the laryngospasm is an important factor for death by asphyxia.
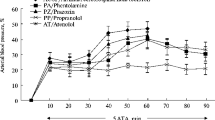
It was found, that the peripherally acting antidotes pralidoxime or methylatropine have no protective or therapeutical effects on the spastic paralysis of the respiratory movements of the glottis. An excellent antidotal action, however, was obtained with the central acting substances Toxogonin® or atropine.
Now, the effect of paraoxon on the electrical activity of the efferent recurrent laryngeal and phrenic nerves has been investigated in anaesthetised rabbits and rats. Paraoxon caused an excessive and permanent excitation in the efferent N. recurrens vagi.
In experiments on single fibre preparations of this nerve it has been proved that the excitation of the recurrent nerve is caused by a central stimulation of exspiratory active neurons, accompanied by a tendence to an exspiratory apnoe. At the same time the inspiratory active fibres, which induce an opening of glottis for inspiration, are suppressed. Atropine and Toxogonin® are powerful antagonists.
The possible central cholinergic mechanisms of the investigated effects are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Barnes, J. M.: The reactions of rabbits to poisoning by p-nitrophenyldiethyl-phosphate (E 600). Brit. J. Pharmacol. 8, 208–211 (1953).
-- Anticholinesterases, the effects of repeated doses of some anticholinesterases. Chem. and Industr. 1954, 620–621.
Baumgarten, R. von, and E. Kanzow: The interaction of two types of inspiratory neurons in the region of the tractus solitarius of the cat. Arch. ital. Biol. 96, 361–373 (1958).
Berendes, J.: Neuere Ergebnisse über Bewegungsstörungen des Kehlkopfes. Arch. Ohr.-, Nas.-, u. Kehlk.-Heilk. 169, 1–172 (1956).
— Hals-Nasen-Ohren-Heilkunde, ein kurzgefaßtes Handbuch. Bd. II, Teil 2. Stuttgart: G. Thieme 1963.
Borison, H. L., and S. C. Wang: Physiology and pharmacology of vomiting. Pharmacol. Rev. 5, 193–230 (1953).
Bucher, K.: Reflektorische Beeinflußbarkeit der Lungenatmung. Wien: Springer 1952.
Candole, C. A. de, W. W. Douglas, C. L. Evans, R. Holmes, K. E. V. Spencer, R. W. Torrance, and K. M. Wilson: The failure of respiration in death by anticholinesterase poisoning. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 8, 466–475 (1953).
Clarmann, M. von: persönliche Mitteilung (1964).
Corbett, C. E., P. A. P. Saraiva, S. A. Pereira, and V. C. Massola: The influence of atropine on the contraction of the vocal cords (“plica vocalis”). Experimental study in dogs. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 129, 216–222 (1960).
Dirnhuber, P., and H. Cullumbine: The effect of anti-cholinesterase agents on the rat's blood pressure. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 10, 12–15 (1955).
Duensing, F., u. W. D. Erdmann: Hirnelektrische Untersuchungen über die Wirkung von Diäthyl-p-nitrophenyl-thiophosphat (E 605) an Kaninchen und über einen begrenzten Antagonismus zwischen E 605 und Atropin an Katzen. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 223, 506–518 (1954).
Eccles, J. C., R. M. Eccles, and P. Fatt: Pharmacological investigations on a central synapse operated by acetylcholine. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 131, 154–169 (1956).
— P. Fatt, and K. Koketsu: Cholinergic and inhibitory synapses in a pathway from motoraxon collaterals to motoneurones. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 126, 524–562 (1954).
Erdmann, W. D.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen über das Penetrationsvermögen einiger esterasereaktivierender Oxime in das zentrale Nervensystem. Arzneimittel-Forsch. 15, 135–139 (1965).
Frey, R.: Atropin-Prämedikation (Antwort auf Fragen aus der Praxis). Dtsch. med. Wschr. 85, 203–204 (1960).
Frick, H.: Berechtigt die Anordnung der Myofibrillen in den Muskelfasern der Säuger zur Annahme eines morphologischen Dualismus (Krüger)? Z. Anat. 117, 485–496 (1954).
Green, J. H., and E. Neil: The respiratory function of the laryngeal muscles. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 129, 134–141 (1955).
Heymans, C., A. Pochet et H. van Houtte: Contribution à la pharmacologie du sarin et du tabun. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 104, 293–332 (1956).
Holtz, P., H. Balzer u. E. Westermann: Beeinflussung der Narkosedauer durch Hemmung der Cholinesterase des Gehirns. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 233, 438–467 (1958).
Hornykiewicz, O., u. W. Kobinger: Über den Einfluß von Eserin, Tetraäthylpyrophosphat (TEPP) und Neostigmin auf den Blutdruck und die pressorischen Carotissinusreflexe der Ratte. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 228, 493–500 (1956).
Just, O.: Prämedikation mit Atropin (Antwort auf Leserfrage). Anaesthesist 9, 373 (1960).
Krüger, P.: Tetanus und Tonus der quergestreiften Skelettmuskeln der Wirbeltiere und des Menschen. Leipzig: Akad. Verlagsges. 1952.
—, u. P. G. Günther: Fasern mit „Fibrillenstruktur“ und Fasern mit „Felderstruktur“ in der quergestreiften Skelettmuskulatur der Säuger und des Menschen. (Eine Entgegnung.) Z. Anat. 118, 313–323 (1955).
L'Allemand, H.: Über Narkoseprobleme in der allgemeinen Praxis. Ther. d. Gegenw. 99, 151–154 (1960).
Machne, X., and K. R. Unna: Cholinesterases and anticholinesterase agents. Actions at the central nervous system. Heffter-Heubners Handb. d. exp. Pharmak. 15, 679–700 (1963).
Mitchell, R. A., H. H. Loeschke, W. H. Massion, and J. W. Severinghaus: Respiratory responses mediated through superficial chemosensitive areas on the medulla. J. appl. Physiol. 18, 523–533 (1963).
Mündnich, K.: Neuere Forschungsergebnisse über die Anatomie und die Physiologie der Kehlkopfnerven des Menschen und ihre Bedeutung für die Klinik. Eine Übersicht aufgrund von autoptischen und bioptischen Untersuchungen am Menschen. Klin. Wschr. 35, 802–808 (1957).
Nicholson, H. C., and S. Sobin: Respiratory effects from the application of cocaine, nicotine and lobeline to the floor of the fourth ventricle. Amer. J. Physiol. 123, 766–774 (1938).
Pfeiffer, C. C.: Parasympathetic neurohumors; possible precursors and effect on behavior. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 1, 195–244 (1959).
Reichel, H.: Muskelphysiologie, S. 156. Berlin, Göttingen, Heidelberg: Springer 1960.
Renshaw, B.: Observations on interaction of nerve impulse in the gray matter and on the nature of central inhibition. Amer. J. Physiol. 146, 443–448 (1946).
Ri, H. dal, u. G. Schmidt: Zentrale und periphere Beeinflussung der Atmung durch toxische Herzglykoside an der Ratte. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 239, 158–169 (1960).
Sakai, F., H. dal Ri, W. D. Erdmann u. G. Schmidt: Über die Atemlähmung durch Parathion oder Paraoxon und ihre antagonistische Beeinflußbarkeit. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 234, 210–219 (1958).
Schaefer, H.: Besprechung der Monographie von Krüger (1952). Klin. Wschr. 30, 719–720 (1952).
Schaumann, W.: Über den Einfluß von Atropin auf die zentrale Hemmung der Atmung durch Anticholinesterasen. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 236, 415–420 (1959).
Schmidt, G., u. H. dal Ri: Die Beeinflussung vagaler Atemreflexe der Ratte durch Cholinesterase-Gifte. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 243, 316 (1962).
-- -- Über die Auslösung der zentralen Wirkung von Nicotin auf Atmung und efferente Vagusinnervation der Ratte. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. (im Druck) (1965).
— u. L. Lendle: Der Einfluß hoher Nicotindosen auf die elektrische Aktivität im efferenten N. vagus und N. phrenicus der Ratte. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 248, 464–482 (1964).
Suzuki, M., R. Kusachi, S. Mishima, M. Shonai, and I. Sasaki: Spontaneous efferent impulse and reflex response of the recurrent laryngeal nerve in the cat and rabbit. Jap. J. vet. Res. 8, 65–73 (1960).
Tauberger, G.: Die vegetativen Summenaktionspotentiale des efferenten Halsvagus der Katze. Med. exp. (Basel) 9, 217–232 (1963).
Wang, S. C., and H. L. Borison: A new concept of organization of the central emetic mechanism: recent studies on the sites of action of apomorphine, copper sulfate and cardiac glycosides. Gastroenterology 22, 1–12 (1952).
Wills, J. H.: Cholinesterase and anticholinesterase agents. Pharmacological antagonists of the anticholinesterase agents. Heffter-Heubners Handb. d. exp. Pharmak. 15, 883–920 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herrn Prof. Dr. med. H. Kumagai, Tokio, zum 60. Geburtstag gewidmet.
Mit 7 Textabbildungen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuga, T., Erdmann, W.D. Versuche zur Wirkung von Paraoxon auf Atem- und Vaguszentren und der Einfluß verschiedener Antidote. Naunyn - Schmiedebergs Arch 251, 445–464 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00246133
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00246133