Abstract
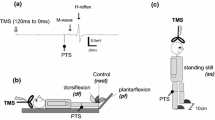
Transcranial stimulation in man evokes multiple descending volleys in the spinal cord giving rise to multiple subpeaks in a peri-stimulus-time histogram (PSTH) obtained from a cross-correlation of motor unit discharges with transcranial stimuli. The first volley is termed the D wave, as it is assumed to be evoked by direct excitation of pyramidal tract neurons, whereas the subsequent I waves appear to be generated by indirect excitation of the pyramidal tract neurons via cortical interneurons. It was the aim of this study to obtain an estimate of the effect induced by multiple volleys evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation on the entire motoneuron pool of the tibialis anterior in awake subjects. A considerable part of a particular motoneuron pool was investigated by sampling responses of a large number (at least 19) from each muscle investigated. In total, three tibialis anterior muscles from three normal volunteers were studied. From each of the 63 units included in this study, a PSTH to 100 transcranial magnetic stimuli and a PSTH to 100 electrical stimuli given to the peroneal nerve were compiled. From the motor unit response to the peripheral nerve stimulation, the latency of the single-unit H reflex peak was obtained. This yielded, the timing of the subpeaks in response to the magnetic stimulation relative to the timing of the H reflex of the same unit, thus eliminating the influence of the peripheral conduction time from the motoneuron to the recording electrode. It was found that 50 (79%) of the motor units exhibited at least two subpeaks in response to the cortical stimulus. All peaks encountered appeared either 1.5 ms–4 ms before or 0 ms–2 ms after the corresponding H reflex. The first peak was assumed to represent the D-wave effect and the second peak an I-wave effect on the motor unit investigated. The relative sizes of the subpeaks exhibited large differences between different units from a single subject. Thus, although the “average unit” showed a larger D- than I-wave effect, in some units the I-wave effect was much more pronounced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashby P, Labelle K (1977) Effects of extensor and flexor group I afferent volleys on the excitability of individual soleus motoneurones in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 40:910–919
Ashby P, Zilm D (1982a) Characteristics of postsynaptic potentials produced in single human motoneurons by homonymous group I volleys. Exp Brain Res 47:41–48
Ashby P, Zilm D (1982b) Relationship between EPSP shape and cross-correlation profile explored by computer simulation for studies on human motoneurons. Exp Brain Res 47:33–40
Awiszus F (1992a) The RIPP density estimate: an alternative method for the estimation of peri-stimulus spike density. J Neurosci Methods 45:55–62
Awiszus F (1992b) The relationship between a neuronal cross-correlogram and the underlying postsynaptic current. Biol Cybern 67:279–283
Awiszus F (1993a) Sensitivity of different stimulus-timing strategies for the detection of small excitations in noisy spike train data. Biol Cybern 68:553–558
Awiszus F (1993b) Quantification and statistical verification of neuronal stimulus responses from noisy spike train data. Biol Cybern 68:267–274
Awiszus F, Feistner H (1993) The relationship between estimates of Ia-EPSP amplitude and conduction velocity in human soleus motoneurons. Exp Brain Res 95:365–370
Awiszus F, Feistner H (1994) Correlations between size parameters and the EPSP amplitude evoked by magnetic brain stimulation in human hand-muscle motoneurons. Exp Brain Res 98:128–134
Awiszus F, Feistner H, Schäfer SS (1991) On a method to detect long-latency excitations and inhibitions of single hand muscle motoneurons in man. Exp Brain Res 86:440–446
Brouwer B, Ashby P (1992) Corticospinal projections to lower limb motoneurons in man. Exp Brain Res 89:649–654
Burke D, Hicks RG, Stephen JP (1990) Corticospinal volleys evoked by anodal and cathodal stimulation of the motor cortex. J Physiol (Lond) 425:283–299
Burke D, Hicks R, Stephen J (1992) Anodal and cathodal stimulation of the upper-limb area of the human motor cortex. Brain 115:1497–1508
Datta AK, Harrison LM, Stephens JA (1989) Task-dependent changes in the size of response to magnetic brain stimulation in human first dorsal interosseus muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 418:13–23
Day BL, Dressler D, Maertens de Noordhout A, Marsden CD, Nakashima K, Rothwell JC, Thompson PD (1989) Electric and magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex: surface EMG and single motor unit responses. J Physiol (Lond) 412:449–473
Flament D, Goldsmith P, Buckley CJ, Lemon RN (1993) Task dependence of responses in first dorsal interosseus muscle to magnetic brain stimulation in man. J Physiol (Lond) 464:361–378
Hicks R, Burke D, Stephen J, Woodforth I, Crawford M (1992) Corticospinal volleys evoked by electrical stimulation of human motor cortex after withdrawal of volatile anaesthetics. J Physiol (Lond) 456:393–404
Miles TS, Türker KS, Le TH (1989) Ia reflexes and EPSPs in human soleus motor neurones. Exp Brain Res 77:628–636
Panizza M, Nilsson J, Hallett M (1989) Optimal stimulus duration for the H reflex. Muscle Nerve 12:576–579
Panizza M, Nilsson J, Roth BJ, Basser PJ, Hallett M (1992) Relevance of stimulus duration for activation of motor and sensory nerve fibers: implications for the study of H-reflexes and magnetic stimulation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 85:22–29
Patton HD, Amassian VE (1954) Single and multiple-unit analysis of cortical stage of pyramidal tract activation. J Neurophysiol 17:345–363
Priori A, Bertolasi L, Dressler D, Rothwell JC, Day BL, Thompson PD, Morsden CD (1993) Transcranial electric and magnetic stimulation of the leg area of the human motor cortex: single motor unit and surface EMG responses in the tibialis anterior muscle. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 89:131–137
Rothwell JC, Thompson PD, Day BL, Boyd SG, Marsden CD (1991) Stimulation of the human motor cortex through the scalp. Exp Physiol 76:159–200
Thompson PD, Day BL, Crockard HA, Calder I, Murray NMF, Rothwell JC, Marsden CD (1991a) Intra-operative recording of motor tract potentials at the cervico-medullary junction following scalp electrical and magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 54:618–623
Thompson PD, Day BL, Rothwell JC, Dressler D, Maertens de Noordhout A, Marsden CD (1991b) Further observations on the facilitation of muscle responses to cortical stimulation by voluntary contraction. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 81:397–402
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Awiszus, F., Feistner, H. Quantification of D- and I-wave effects evoked by transcranial magnetic brain stimulation on the tibialis anterior motoneuron pool in man. Exp Brain Res 101, 153–158 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00243225
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00243225