Abstract
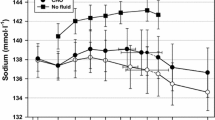
We examined the recovery of plasma volume, plasma osmolality, renal water and sodium handling and fluid-regulating hormones to dehydrating exercise in well-trained women and compared them to men. Ten male and eight female athletes cycled at anaerobic threshold at an ambient temperature of 32°C until dehydration by 3 % of their body mass (Mb). After exercise, they drank water equal to 1 % Mb and rested for 240 min. Plasma renin activity (PRA), serum aldosterone [ALDO]s, plasma arginine vasopressin [AVP]pl, norepinephrine concentrations and plasma osmolality (Osmpl) were determined at baseline, end of exercise, 30, 60, 120 and 240 min postexercise. Urine was collected at baseline, end of exercise, 60, 120 and 240 min postexercise. Renal free water and sodium handling were assessed. The recovery of OSMpl and plasma volume occurred within the first 60 min of recovery and at similar rates between the groups. However, women had lower PRA at the end of exercise (P = 0.05), an earlier recovery of [ALDO]s, and a slower [AVP]pl recovery. Overall fluid balance was similar between the men and women, as were the early recovery of renal free water clearance (C H 2O). During the last 120 min of recovery C H 2O was more negative (greater water reabsorption) and fractional sodium excretion was increased in the women compared to the men. Despite small differences in sodium and water reabsorption following dehydration, it appears from other study that recovery from dehydrating exercise in well-trained men and women is remarkably similar.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken J, Lindsay R, Hart D (1974) The redistribution of body sodium in women on long-term oestrogen therapy. Clin Sci Mol Med 47:179–187
Blahd W, Lederer M, Tyler E (1974) Effect of oral contraceptives on body water and electrolytes. J Reprod Physiol 13:222–225
Convertino V, Keil L, Bernauer E, Greenleaf J (1981) Plasma volume, osmolality, vasopressin, and renin activity during graded exercise in man. J Appl Physiol 50:123–128
Costill D, Branum G, Fink W, Nelson R (1974). Exercise-induced sodium conservation: changes in plasma renin and aldosterone. Med Sci Sports 8:209–331
Davison J, Gilmore E, Durr J, Robertson G, Lindheimer M (1984) Altered osmotic thresholds for vasopressin and thirst in human pregnancy. Am J Physiol 246 15:17105–17109
De Souza M, Maresh C, Maguire M. Kraemer W, Flora-Ginter G, Goetz K (1989) Menstrual cycle status and plasma vasopressin, renin activity, and aldosterone exercise responses. J Appl Physiol 67:736–743
Dill D, Costill D (1974) Changes in volume of blood, plasma, and red cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37:247–284
Forsling M, Akerlund M, Stromberg P (1981) Variations in plasma concentrations of vasopressin during the menstrual cycle. J Endocrinol 89:263–266
Forsling M, Stromberg P, Akerlund M (1982) Effect of ovarian steroids on vasopressin secretion. J Endocrinol 90:147–151
Francesconi R, Sawka M, Pandolf K, Hubbard R, Young A, Muza S (1985) Plasma hormonal response at graded hypohydration levels during exercise-heat stress. J Appl Physiol 59:1855–1860
Frye A, Kamon E (1983) Sweating efficiency in acclimated men and women exercise in humid and dry heat. J Appl Physiol 54: 972–977
Geelen G, Keil L, Kravik S, Wade C, Thrasher T, Barnes P, Pyka G, Nesvig C, Greenleaf J (1984) Inhibition of plasma vaso-pressin after drinking in dehydrated humans. Am J Physiol 247R968-R971
Gillen C, Lee R, Mack G, Tomaselli C, Nishiyasu T, Nadel E (1991) Plasma volume expansion after a single exercise protocol. J Appl Physiol 71:1914–1921
Gleim G, Zabetakis P, Depasquale E, Michelis M, Nicholas J (1984) Plasma osmolality, volume and renin activity at the anaerobic threshold. J Appl Physiol 56:57–63
Greenleaf J (1992) Problem: thirst, drinking behavior, and involuntary dehydration. Med Sci Sports Exerc 24:645–656
Keoppen B. (1990) Mechanisms of segmental sodium and chloride reabsorption. In: Seldin D, Giebish G (eds) The regulation of sodium and chloride balance. Raven Press, New York, p. 68
Kirk Ŕ (1982) Experimental design. Brooks/Cole, Pacific Grove, Calif
Kolka M, Stephenson L (1989) Control of sweating during the human menstrual cycle. Eur J Appl Physiol 58:890–895
Kolka M, Stephenson L, Rock P, Gonzalez R (1987) Local sweating and cutaneous blood flow during exercise in hypoxic environments. J Appl Physiol 62:2224–2229
Kotchen T, Hartley L, Rice T, Mongey E, Jones L, Mason J (1971) Renin, norepinephrine, and epinephrine responses to graded exercise in humans. J Appl Physiol 31:178–184
Moritmoto T (1990) Thermoregulation and body fluids: role of blood volume and central venous pressure. Jpn J Physiol 40:165–179
Morimoto T, Slabochova C, Naman R, Sargent F (1967) Sex differences in the physiological reactions to thermal stress. J Appl Physiol 22:526–532
Nose H, Mack G, Shi X, Nadel E (1988a) Involvement of sodium retention hormones during rehydration in humans. J Appl Physiol 65:332–336
Nose H, Mack G, Shi X, Nadel E (1988b) Role of osmolality and plasma volume during rehydration in humans. J Appl Physiol 65:325–331
Nose H, Mack G, Shi X, Nadel E (1988c) Shift in body fluid compartments after dehydration in man. J Appl Physiol 65:318–324
Nose H, Takamata A, Mack G, Kawabata T, Oda Y, Hashimoto S, Hirose M, Chihara E, Morimoto T (1994) Right atrial pressure and ANP release during prolonged exercise in a hot environment. J Appl Physiol 76:1882–1887
Opstad P, Oktedalen O, Aakvaag A, Fonnum F, Lund P (1985) Plasma renin activity and serum aldosterone during prolonged physical strain. Eur J Appl Physiol 54:1–6
Paolone A, Wells C, Kelly G (1978) Sexual variations in thermoregulation during heat stress. Aviat Space Environ Med 49:715–719
Pitts R (1974) physiology of the kidney and body fluids. Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago, Ill.
Sawka M, Toner M, Francesconi R, Pandolf K (1983) Hypohydration and exercise: effects of heat acclimation, gender, and environment. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 55:1147–1153
Sawka MN, Young A, Francesconi P, Muza S, Pandolf K (1985) Thermoregulatory and blood pressure responses during exercise at graded hypohydration levels. J Appl Physiol 59:1394–1401
Senay L, Roger G, Jooste P (1980) Changes in blood plasma during progressive treadmill and cycle exercise. J Appl Physiol 49:59–65
Shapiro Y, Pandolf K, Avellini B, Pimental N, Goldman R (1980) Physiological responses to men and women to humid heat. Am J Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 49:1–8
Shenker Y (1989) Atrial natriuretic hormone and aldosterone regulation in salt depleted state. Am J Physiol 257:E583-E587
Shoup RE, Keefe SA (1980) Plasma catecholamines assayed conveniently and repidly by LCEC. Curr Separations 2:1–3
Stachenfeld N, Gleim G, Coplan N, Glace G, Butt S, Michelis M, Nicholas J (1995) Hormonal responses to exercise and the anaerobic and respiratory compensation thresholds. Med Exerc Nut Health 4:349–354
Stephenson L, Kolka M (1988) Plasma volume during heat stress and exercise in women. Eur J Appl Physiol 57:573–581
Stephenson L, Kolka M (1993) Thermoregulation in women. In: Holloszy J (ed) Exercise and sport science reviews, vol 21. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 231–262
Stephenson L, Kolka M, Francesconi R, Gonzalez R (1989) Circadian variations in plasma renin activity, catecholamines and aldosterone during exercise in women. Eur J Appl Physiol 58:756–764
Takamata A, Mack G, Gillen C, Nadel E (1994) Sodium appetite, thirst and body fluid regulation in humans during rehydration without sodium replacement. Am J Physiol 266:R1493-R1502
Tanaka H, Shindo M, Gutkowska J, Kinoshita A, Urata H, Ikeda M, Arakawa K (1986) Effect of acute exercise on plasma immunoreactive atrial natriuretic factor. Life Sci 39:1685–1693
Tankersley C, Nicholas W, Deaver D, Mikita D, Kenny W (1992) Estrogen replacement in middle-aged women: thermoregulatory responses to exercise in the heat. J Appl Physiol 73:1238–1245
Thompson C, Burd J, Baylis P (1987) Acute suppression of plasma vasopressin and thirst after drinking in hypernatremic humans. Am J Physiol 252:R1138-R1142.
Wade C (1984) Response, regulation and actions of vasopressin during exercise: a review. Med Sci Sports Exerc 16:506–511
Wasserman K (1984) The anaerobic threshold measurement to evaluate exercise performance. Am Rev Respir Dis 129:S35-S40
Weinman K, Slabochova Z, Bernauer E, Morimoto T, Sargent F (1967) Reactions of men and women to repeated exposure to humid heat. J Appl Physiol 22:533–538
Wyndham C, Morrison J, Williams C (1967) Heat reactions of male and female caucasians. J Appl Physiol 20:357–364
Yallow R, Berson S (1971) Principle of competitive protein binding assays chapter 1. Lippincott, Philadelphia
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stachenfeld, N.S., Gleim, G.W., Zabetakis, P.M. et al. Fluid balance and renal response following dehydrating exercise in well-trained men and women. Eur J Appl Physiol 72, 468–477 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00242277
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00242277