Abstract
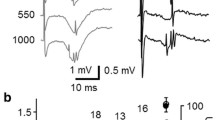
Transmembrane potentials from medial septal and diagonal band of Broca (MS-DBB) neurons and hippocampal field activity were recorded in curarized and urethanized rats. MS-DBB cells were studied during large amplitude irregular activity and during hippocampal θ rhythm, elicited by either sensory (i.e. stroking the fur on the animal's back) or electrical stimulation of the reticularis pontis oralis nucleus (RPO). Three types of cells were described according to their firing pattern and the characteristics of their “intracellular θ” rhythm. Type A neurons displayed continuous rhythmic oscillations in the membrane potential (Vm) of approximately 17 mV. These oscillations generated rhythmic high-frequency spike trains which were phase-locked with hippocampal θ rhythm. Type A cells revealed intracellular θ rhythm even in the absence of hippocampal θ rhythm, suggesting that the activity of this type of cell was the most important in hippocampal θ genesis. Type B cells were characterized by marked postspike afterhyperpolarization and intracellular θ oscillations of smaller amplitude than in type A cells. Type C cells revealed a post-spike afterdepolarization and a lower amplitude, intracellular θ rhythm only in the presence of hippocampal θ rhythm. Type C neurons could fire slow spikes at depolarizing (46% of cells) or hyperpolarizing (15% of cells) Vms. Type B and C cells were intracellularly stained with Lucifer yellow. Although type B and C neurons revealed dissimilar electrophysiological properties, they had comparable morphological shapes. RPO electrical stimulation generated hippocampal θ rhythm and intracellular θ rhythm in types A and B cells but not in type C cells, and increased the spike rate in type C neurons. Electrical stimulation of the fornix only evoked synaptic responses in type B and C neurons, with antidromic responses being elicited in 12% of type C cells. These results indicate that probably most of the type A rhythmic cells did not receive direct hippocampal feedback and that at least some type C cells were projecting neurons. The present findings demonstrate that θ rhythm oscillations in the Vm of MS-DBB neurons elicit different rhythmic discharge patterns.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso A, Gaztelu JM, Buño W Jr, García-Austt E (1987) Crosscorrelation analysis of septohippocampal neurons during θ-rhythm. Brain Res 413: 135–146
Alvarez de Toledo G, Lopez-Barneo J (1988) Ionic basis of the differential neuronal activity of guinea-pig septal nucleus studied in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 396: 399–415
Apostol G, Creuzfeldt OD (1974) Crosscorrelation between the activity of septal units and HPC EEG during arousal. Brain Res 67: 65–75
Ashwood TJ, Lancaster B, Wheal HV (1984) In vivo and in vitro studies on putative interneurones in the rat hippocampus: possible mediators of feed-forward inhibition. Brain Res 293: 279–291
Barrenechea C, Pedemonte M, Nuñez A, García-Austt E (1989) Actividad theta en el potencial transmembrana de las neuronas del septum y la banda diagonal de Broca. Soc Esp Neurosci: 81
Bland SK, Bland BH (1986) Medial septal modulation of hippocampal theta cell discharges. Brain Res 375: 102–116
Bland BH, Whishaw IQ (1976) Generators and topography of hippocampal theta (RSA) in the anaesthetized and freely moving rat. Brain Res 118: 259–280
Bland BH, Oddie SD, Dickson CT, Trepel C (1993) Discharge patterns of posterior supramammillary hypothalamic cells in relation to hippocampal theta field activity. Soc Neurosci Abstr 19: 355
Brazhnik ES, Fox SE (1992) Intracellular recordings from medial septal pacemaker neurons during hippocampal theta rhythm. Soc Neurosci Abstr 18: 319
Buño W Jr, García-Sanchez JL, García-Austt E (1978) Reset of hippocampal rhythmical activities by afferent stimulation. Brain Res Bull 3: 21–28
Dutar P, Lamour Y, Jobert A (1985) Septohippocampal neurons in the rat: an in vivo intracellular study. Brain Res 340: 135–142
Fibiger HC (1982) The organization and some projections of cholinergic neurons of the mammalian forebrain. Brain Res Rev 4: 327–388
Fisher RS, Buchwald NA, Hull CD, Levine MS (1988) GABAergic basal forebrain neurons project to the neocortex: the localization of glutamic acid decarboxylase and choline acetyltransferase in feline corticopetal neurons. J Comp Neurol 272: 489–502
Ford RD, Colom LV, Bland BH (1989) The classification of medial septum-diagonal band cells as theta-on or theta-off in relation to hippocampal EEG states. Brain Res 493: 269–282
García-Sanchez JL, Buño W Jr, Fuentes J, García-Austt E (1978) Non-rhythmical hippocampal units, theta-rhythm and afferent stimulation. Brain Res Bull 3: 213–219
Gaztelu JM, Buño W Jr (1982) Septo-hippocampal relationships during EEG theta rhythm. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 54: 375–387
Gogolak G, Stumpf C, Petsche H, Sterc J (1968) The firing pattern of septal neurons and the form of the hippocampal theta wave. Brain Res 7: 201–207
Green JD, Arduini AA (1954) Hippocampal electrical activity in arousal. J Neurophysiol 17: 533–557
Griffith WH (1988) Membrane properties of cell types within guinea pig basal forebrain nuclei in vitro. J Neurophysiol 59: 1590–1612
Griffith WH, Matthews RT (1986) Electrophysiology of AChE-positive neurons in basal forebrain slices. Neurosci Lett 71: 169–174
Kirk IJ, McNaughton N (1991) Supramammillary cell firing and hippocampal rhythmical slow activity. Neuroreport 2: 723–725
Kocsis BT, Vertes RP (1992) Dorsal raphe neurons: synchronous discharge with the theta rhythm of the hippocampus in the freely behaving rat. J Neurophysiol 68: 1463–1467
Köning JFR, Klippel RA (1963) The rat brain: a stereotaxic atlas of the forebrain and lower parts of the brain stem. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Leung L-WS, Lopes Da Silva FH, Waddman WJ (1982) Spectral characteristics of the hippocampal EEG in the freely moving rat. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 54: 203–219
Lopez-Barneo J, Alvarez de Toledo G, Yarom Y (1985) Electrophysiological properties of guinea pig septal neurons in vitro. Brain Res 347: 358–362
Macadar O, Roig JA, Monti JM, Budelli R (1970) The functional relationship between septal and hippocampal unit activity and hippocampal theta rhythm. Physiol Behav 5: 1443–1449
Markram H, Segal M (1990) Electrophysiological characteristics of cholinergic and non-cholinergic neurons in the rat medial septum-diagonal band complex. Brain Res 513: 171–174
Matthews RT, Lee WL (1991) A comparison of extracellular and intracellular recordings from medial septum-diagonal band neurons in vitro. Neuroscience 42: 451–462
McCormick DA, Connors BW, Lighthall JW, Prince DA (1985) Comparative electrophysiology of pyramidal and sparsely spiny stellate neurons of the neocortex. J Neurophysiol 54: 782–806
Mesulam M, Mufson EJ, Wainer BH, Levey AI (1983) Central cholinergic pathways in the rat: an overview based on an alternative nomenclature. Neuroscience 10: 1185–1201
Mitchel SJ, Rawlins JNP, Steward O, Olton DS (1982) Medial septal area lesions disrupt theta rhythm and cholinergic staining in medial entorhinal cortex and produce impaired radial arm maze behavior in rats. J Neurosci 2: 292–302
Nuñez A, García-Austt E, Buño W Jr (1987) Intracellular θrhythm generation in identified hippocampal pyramids. Brain Res 416: 289–300
Nuñez A, de Andres I, García-Austt E (1991) Relationships of nucleus reticularis pontis oralis neuronal discharge with sensory and carbachol evoked hippocampal theta rhythm. Exp Brain Res 87: 303–308
Oddie SD, Colom LV, Bland BH (1993) The posterior hypothalamus and hippocampal synchrony. Soc Neurosci Abstr 19: 356
Onteniente B, Tago H, Kimura H, Maeda T (1986) Distribution of γ-aminobutyric acid-immunoreactive neurons in the septal region of the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 248: 422–430
Panula P, Revuelta AV, Cheney DL, Wu JY, Costa E (1984) An immunohistochemical study on the location of GABAergic neurons in the rat septum. J Comp Neurol 222: 69–80
Petsche H, Stumpf CH, Gogolak G (1962) The significance of the rabbit's septum as a relay station between the midbrain and the hippocampus. I. The control of hippocampus arousal activity by the septum cells. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 14: 202–211
Rawlins JNP, Feldon J, Gray JA (1979) Septo-hippocampal connections and the hippocampal theta-rhythm. Exp Brain Res 37: 49–63
Schwartzkroin PA, Mathers LH (1978) Physiological and morphological identification of a nonpyramidal hippocampal cell type. Brain Res 157: 1–10
Segal M (1986) Properties of rat medial septal neurones recorded in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 379: 309–330
Stewart M, Fox SE (1989) Firing relations of medial septal neurons to the hippocampal theta rhythm in urethane anesthetized rats. Exp Brain Res 77: 507–516
Vertes RP (1981) An analysis of ascending brain stem systems involved in hippocampal synchronization and desynchronization. J Neurophysiol 46: 1140–1159
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barrenechea, C., Pedemonte, M., Nuñez, A. et al. In vivo intracellular recordings of medial septal and diagonal band of Broca neurons: relationships with theta rhythm. Exp Brain Res 103, 31–40 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00241962
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00241962