Abstract
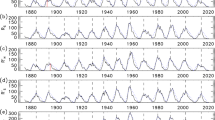
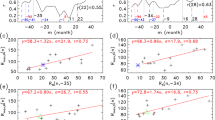
Atmospheric elements at all levels from the surface to the Middle Atmosphere show a probable association with the 11-year solar cycle in northern winter, which can be observed only if the data are grouped according to the phase of the Quasi-Biennial Oscillation. As the correlations are often of opposite sign in the East and West phase of the QBO, the correlation coefficients are mostly small when one uses as full time series of an atmospheric element. The spatial patterns of the correlations resemble well-known teleconnection patterns. The sparse data and short series on the Southern Hemisphere permit only a limited investigation. Good relationships are found in the antarctic stratosphere in spring and at sea level in winter.
Statistical tests suggest that our results did not occur by chance, but since we cannot examine data from before 1952 because we do not know the phase of the QBO before then, and since there is no physical explanation for the large correlation coefficients, we cannot yet exclude the possibility that the results are due to sample variation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, G. M. and John, J. I.: 1979, J. Atmospheric Terrest. Phys. 41, 43.
Effron, B.: 1982, Soc. Industr. Appl. Math., Philadelphia, Penn., J. W. Arrowsmith, Bristol, England, 92 pp.
Labitzke, K.: 1982, J. Meteor, Soc. Japan 60, 124.
Labitzke, K.: 1987a, Geophys. Res. Letters 14, 535.
Labitzke, K.: 1987b, Ann. Geophys. 5A, 95.
Labitzke, K. and Chanin, M. L.: 1988, Ann. Geophys., in press.
Labitzke, K. and van Loon, H.: 1988a, J. Atmospheric Terrest. Phys. 50, 197.
Labitzke, K. and van Loon, H.: 1988b, J. Climate, submitted.
Namias, J.: 1981, CALCOFI Atlas No. 29, Scripps Inst. of Oceanogr., La Jolla, Calif., I-VII + 265 pp.
Rogers, J. C. and van Loon, H.: 1982, Mon. Wea. Rev. 110, 1375.
Tinsley, B. A.: 1988, Geophys. Res. Letters 15, 409.
van Loon, H. and Labitzke, K.: 1988, J. Climate 1, 905.
van Loon, H. and Rogers, J. C.: 1978, Mon. Wea. Rev. 106, 295.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Affiliate Scientist at NCAR.
Visiting Scientist, Freie Universität Berlin.
The National Center for Atmospheric Research is sponsored by the National Science Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Labitzke, K., Van Loon, H. Recent work correlating the 11-year solar cycle with atmospheric elements grouped according to the phase of the Quasi-Biennial Oscillation. Space Sci Rev 49, 239–258 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00241868
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00241868