Summary
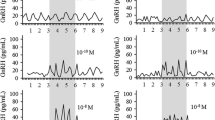
The release of gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (Gn-RH), in response to electrical stimulation of the mediobasal part of the hypothalamus incubated in vitro, was studied in both male and female rats. In male rats significant release of Gn-RH occurred during the 10-min experimental period only when the incubated tissue was stimulated at frequencies of 10 Hz or greater. There was no release when stimulated at 5 Hz. There was also no release of hormone when the mediobasal hypothalami were incubated in a Ca2+ free medium. The amount of Gn-RH released during a 10-min incubation period increased progressively as the frequency of stimulation was raised from 10–100 Hz. During short (4-min) incubation periods the effectiveness of each stimulus pulse for Gn-RH release also increased with the frequency of stimulation. However, when stimulated for 10 min there was no increase in hormone released per stimulus pulse when frequency of stimulation was raised above 10 Hz. The amount of Gn-RH released in response to stimulation at 50 Hz was greater in male rats than in females. For the females, there was no significant difference between the amounts of Gn-RH released at dioestrus and pro-oestrus. In both male and female rats gonadectomised 4 weeks prior to hypothalamic incubation, the response to electrical stimulation at 50 Hz was reduced when compared with intact controls. Indeed, for the females there was no longer a statistically significant increase in the amount of Gn-RH in the incubation medium after 50 Hz stimulation. Ovariectomised female rats, injected twice daily for 3.5 days with 20 μg of oestradiol benzoate released Gn-RH in response to 50 Hz stimulation in the same amounts as intact control animals. By contrast, there was no recovery of Gn-RH release to normal levels in castrated male rats similarly treated with 1.25 mg testosterone propionate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-Jonathan N, Mical RS, Porter JC (1974) Transport of LRF from CSF to hypophysial portal and systemic blood and the release of LH. Endocrinology 95: 18–25
Bennet GW, Edwardson JA, HoUand D, Jeffcoate SL, White N (1975) Release of immunoreactive luteinising hormone-releasing hormone and thyrotropin-releasing hormone from hypothalamic synaptosomes. Nature 257: 323–325
Brown-Grant K, Exley D, Naftolin F (1970) Peripheral plasma oestradiol and luteinizing hormone concentrations during the oestrous cycle of the rat. J Endocrinol 48: 295–296
Burford GD, Clifford P, Jones CW, Pickering BT (1973) A model for the passage of the neurohypophysial hormones and their related proteins through the rat neurohypophysis. Biochem J 136: 1053–1058
Critchlow V (1958) Ovulation induced by hypothalamic stimulation in the anaesthetised rat. Am J Physiol 195: 171–174
Cross BA, Dyball REJ, Dyer RG, Jones CW, Lincoln DW, Morris JF, Pickering BT (1975) Endocrine neurones. Recent Prog Horm Res 31: 243–294
Cross BA, Dyer RG (1971) Ovarian modulation of unit activity in the anterior hypothalamus of the cyclic rat. J Physiol (Lond) 222: 5P
Davidson JM, Bloch GJ (1969) Neuroendocrine aspects of male reproduction. Biol Reprod 1: 67–92
Douglas WW, Poisner AM (1964) Stimulus-secretion coupling in a neurosecretory organ: the role of calcium in the release of vasopressin from the neurohypophysis. J Physiol (Lond) 172: 1–18
Dutton A, Dyball REJ (1979) Phasic firing enhances vasopressin release from the rat neurohypophysis. J Physiol (Lond) 290: 433–440
Dyer RG, Mayes LC (1978) Electrical stimulation of the hypothalamus. New observations on the parameters necessary for ovulation in rats anaesthetised with pentobarbitone during the pro-oestrous “critical period”. Exp Brain Res 33: 583–592
Dyer RG, Mayes LC, ter Haar MB, Yates JO (1978) Ovulation in the rat: duration of hypothalamic activation, and not frequency, is the critical parameter. J Physiol (Lond) 277: 63P-64P
Everett JW (1961) The mammalian female reproductive cycle and its controlling mechanisms. In: Young WC (ed) Sex and internal secretions, vol 1. Balliere, Tindall & Cox, London, pp 497–555
Fink G, Jamieson MG (1976) Immunoreactive luteinizing hormone releasing factor in rat pituitary stalk blood: effects of electrical stimulation of the medial preoptic area. J Endocrinol 68: 71–87
Gans E, van Rees GP (1962) Effect of small doses of oestradiol benzoate on pituitary production and release of I.C.S.H. in gonadectomized male and female rats. Acta Endocrinol (Copenhagen) 39: 245–252
Kalra SP (1976) Tissue levels of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone in the preoptic area and hypothalamus, and serum concentrations of gonadotrophins following anterior hypothalamic deafferentation and estrogen treatment of the female rat. Endocrinology 99: 101–107
Kalra SP, Kalra PS, Mitchell EO (1977) Differential response of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone in the basal hypothalamus and the preoptic area following anterior hypothalamic deafferentation and/or castration in male rats. Endocrinology 100: 201–204
Kelly MJ, Moss RL, Dudley CA (1976) Differential sensitivity of preoptic-septal neurons to microelectrophoresed oestrogen during the oestrous cycle. Brain Res 114: 152–157
Kingsley TR, Bogdanore EM (1973) Direct feedback of androgens: Localised effects of intrapituitary implants of androgens on gonadotrophic cells and hormone stores. Endocrinology 93: 1398–1409
König JFR, Klippel RA (1963) The rat brain. A stereotaxic atlas of the forebrain and lower parts of the brain stem. WilUams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Lincoln DW (1967) Unit activity in the hypothalamus, septum and preoptic area of the rat: characteristics of spontaneous activity and the effect of oestrogen. J Endocrinol 37: 177–189
Markee JE, Sawyer CH, Hollinshead WH (1946) Activation of the anterior hypophysis by electrical stimulation in the rabbit. Endocrinology 38: 345–357
Matsuo H, Baba Y, Nair RMG, Arimura A, Schally, AV (1971) Structure of the procine LH- and FSH-releasing hormone. I. The proposed amino acid sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 43: 1334–1339
McKelvy JF, LeBlanc P, Laudes C, Perrie S, Grimm-Jorgensen Y, Kordon C (1976) The use of bacitracin as an inhibitor of the degradation of thyrotropin releasing factor and luteinising hormone releasing factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 73: 507–515
Nett TM, Akbar AM, Niswender GD, Hedlund MT, White WF (1973) A radioimmunoassay for gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (Gn-RH) in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 36: 880–885
Porter JC, Hines MFM, Smith KR, Repass RL, Smith AJK (1967) Quantitative evaluation of local blood flow of the adenohypophysis in rats. Endocrinology 80: 583–598
Quinn DL (1969) Neural activation of gonadotropic hormone release by electrical stimulation in the hypothalamus of the guinea pig and the rat. Neuroendocrinology 4: 254–263
Rotsztejn WH, Charli JL, Pattou E, Epelbaum J, Kordon C (1976) In vitro release of luteinising hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) from rat mediobasal hypothalamus: Effects of potassium, calcium, and dopamine. Endocrinology 99: 1663–1666
Rotsztejn WH, Charli JL, Pattou E, Kordon C (1977) Stimulation by dopamine of luteinising hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) release from the mediobasal hypothalamus in male rats. Endocrinology 101: 1475–1483
Sachs H, Share L, Osinchak J, Carpi A (1967) Capacity of the neurohypophysis to release vasopressin. Endocrinology 81: 755–770
Terasawa E, Sawyer CH (1969) Changes in electrical activity in the rat hypothalamus related to electrochemical stimulation of adenohypophysial function. Endocrinology 85: 143–149
Thorn NA (1966) In vitro studies of the release mechanism for vasopressin in rats. Acta Endocrinol (Copenhagen) 53: 644–654
Yagi K (1970) Effects of oestrogen on the unit activity of the hypothalamus. J Physiol Soc Jpn 32: 692–693
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dyer, R.G., Mansfield, S. & Yates, J.O. Discharge of gonadotrophin-releasing hormone from the mediobasal part of the hypothalamus: Effect of stimulation frequency and gonadal steroids. Exp Brain Res 39, 453–460 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239310
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239310