Summary
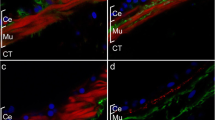
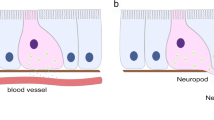
The organisation of the basiepithelial nerve plexus in the alimentary canal of a starfish and the water vascular system of a sea-urchin is described. The plexus contains varicose aminergic neurones which terminate adjacent to the ciliated epithelial cells. It is proposed that the basiepithelial plexus innervates these cells and controls ciliary beating. The distribution of the basiepithelial plexus in various tissues described by other workers is dicscussed particularly in relation to whether it is the coelomic epithelium or the luminal epithelium which is innervated. It is concluded that where there is both an endothelium and a coelomic epithelium only one is innervated. The muscles, where present, of the viscera are innervated by a separate nervous system. The muscles are always on the opposite side of the non-cellular connective tissue sheath to the basiepithelial plexus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiello, E.L.: Factors affecting ciliary activity in the gill of the mussel, Mytilus edulis. Physiol. Zool. 33, 120–135 (1960)
Aiello, E.L.: Control of ciliary activity in metazoa. In Cilia and Flagella (M.A. Sliegh, Ed.), pp. 353–378. London: Academic Press (1974)
Aiello, E.L., Guideri, G.: Distribution and function of the branchial nerve in the mussel. Biol. Bull. 129, 431–438 (1965)
Bacetti, B., Rosati, F.: The fine structure of the Polian vesicles of holothurians. Z. Zellforsch. 90, 148–160 (1968)
Bachmann, S., Goldschmid, A.: Fine structure of the axial complex of Sphaerechinus granularis (Lam.). Cell Tissue Res. 193, 107–123 (1978a)
Bachmann, S., Goldschmid, A.: Ultrastructural, fluorescence microscopic and microfluorimetric study of the innervation of the axial complex in the sea urchin, Spaerechinus granularis (Lam.). Cell Tissue Res. 194, 315–326 (1978b)
Bargmann, W., Hehn, G. von.: Über das Axialorgan (“mysterious gland”) von Asterias rubens L. Z. Zellforsch. 88, 262–277 (1968)
Bouillon, J., Jangoux, M.: Anatomie, histologie et histochimie des caecums rectaux d'Asterias rubens L. Cahiers de Biol. Marine. 11, 259–277 (1970)
Burke, R.D.: The structure of the nervous system of the pluteus larva of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Cell Tissue Res. 197, 233–247 (1978)
Cobb, J.L.S.: The innervation of the oesophagus of the sea urchin Heliocidaris erythrogramma. Z. Zellforsch. 98, 323–332 (1969)
Cobb, J.L.S.: The significance of the radial nerve cords in asteroids and echinoids. Z. Zellforsch. 108, 457–474 (1970)
Cobb, J.L.S.: An ultrastructural study of the dermal papulae of the starfish, Asterias rubens with special reference to the innervation of the muscles. Cell Tissue Res. 187, 515–523 (1978)
Cobb, J.L.S., Pentreath, V.W.: Anatomical studies of simple invertebrate synapses using stage rotation electron microscopy and densitometry. Tissue Cell 9, 125–135 (1977)
Cobb, J.L.S., Sneddon, E.: An ultrastructural study of the gills of Echinus esculentus. Cell Tissue Res. 182, 265–274 (1977)
Doyle, W.L.: Vesiculated axons in haemal vessels of an holothurian, Cucumaria frondosa. Biol. Bull. 132, 329–336 (1967)
Fenner, D.: The respiratory adaptations of the podia and ampullae of Echinoids (Echinodermata). Biol. Bull. 145, 323–339 (1973)
Hyman, L.M.: The invertebrates. Echinodermata. vol. IV. New York-Toronto-London: McGrawHill Book C. (1955)
Jangoux, M., Schaltin, P.: Le complex axial de Psammechinus miliaris (Gmelin) Arch. Zool. Exp. Gen. 118, 285–303 (1977)
Mackie, G.O., Spencer, A.N., Strathmann, R.: Electrical activity associated with ciliary reversal in echinoderm larvae. Nature, 223, 1384–1385 (1969)
Malanga, C.J.: Effects of dopamine on anaerobic metabolism and ciliary activity in bivalve gills. Comp. Gen. Pharmac. 5, 51–59 (1974)
Malanga, C.J.: Dopaminergic stimulation of frontal ciliary activity in the gill of Mytilus edulis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 21C, 25–34 (1975)
Malanga, C.J., Young, S.I.: The metabolic fate of dopamine in the ciliated gill epithelium of bivalve molluscs. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 60C, [A], [B], [C], 129–136 (1978)
Paparo, A., Aiello, E.: Cilio-inhibitory effects of branchial nerve stimulation in the mussel, Mytilus edulis. Comp. Gen. Pharmac. 1, 241–250 (1970)
Pentreath, V.W., Cobb, J.L.S.: Neurobiology of Echinodermata. Biol. Rev. 47, 369–392 (1972)
Ryberg, E.: The localization of biogenic amines in the echinopluteus. Acta Zoll. Pathol Antvesp. 55, 179–189 (1974)
Sweeney, D.: Dopamine: Its occurrence in molluscan ganglia. Science 139, 1051 (1963)
Weber, W., Grosmann, M.: Ultrastructure of the basepithelial nerve plexus of the sea urchin, Centrostephanus longispinus. Cell Tissue Res., 175, 551–562 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cobb, J.L.S., Raymond, A.M. The basiepithelial nerve plexus of the viscera and coelom of eleutherozoan echinodermata. Cell Tissue Res. 202, 155–163 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239228
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239228