Abstract
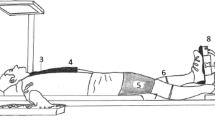
The responses of mean arterial blood pressure (BPa) and heart rate (f c) to isometric contraction and passive stretch were compared in seven healthy male subjects at identical external forces. They were investigated in the sitting position with the hip and knee joint flexed to 90°. Each subject performed two tests, separated by a day, in which the stimuli were applied in random order. After 5 min of rest they performed either 10-min static plantar flexion of one calf (200 N) or 10 min of passive calf muscle stretch at the same load. After 5-min rest, the second stimulus was applied for a further 10 min followed by 5-min rest. The second test was identical except for the sequence of the stimuli. The BPa was measured by a noninvasive and continuous method. Contraction of the vastus lateralis, gastrocnemius lateralis, and soleus muscles were determined by the myo-electric activity (electromyogram, EMG) by means of surface electrodes. The EMG activity of the vastus lateralis muscle remained at resting values throughout the experiments. Increases in EMG activity could only be detected for the triceps surae muscles during isometric contraction. During the initial 2 min of stimulation the BPa and (f c), responses to active contraction and passive stretch were comparable. Thereafter, both parameters showed significantly higher values during contraction. It was concluded that mechanical stress may have contributed to the early response of BPa during both passive stretch and voluntary contraction but that chemical stimuli were needed to maintain the peripheral cardiovascular drive.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam M, Smirk FH (1938) Observation in man on a pulse accelerating reflex from the voluntary muscles of the legs. J Physiol (Lond) 92:167–177
Barcroft H, Millen JLE (1939) The blood flow through muscle during sustained contraction. J Physiol (Lond) 97:17–31
Baum K, Essfeld D, Stegemann J (1988) The influence of muscle interstitial volume on K+-induced heart rate drive in rats. Eur J Appl Physiol 57:33–38
Baum K, Essfeld D, Sondermann C, Leyk D, Stegemann J (1993) Effect of graded changes in extracellular muscle volume on cardiovascular drives during static exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 67:245–249
De Vries HA (1968) Method for evaluation of muscle fatigue and endurance from electromyographic fatigue curves. Am J Phys Med 47:125–135
Eason R (1968) Electromyographic study of local and generalized muscular impairment. J Appl Physiol 15:479–482
Gravel D, Richards CL, Filion M (1990) Angle dependency in strength measurements of the ankle plantar flexors. Eur J Appl Physiol 61:182–187
Kadefors R, Kaiser E, Petersen I (1968) Dynamic spectrum analysis of myo-potentials with special reference to muscle fatigue. Electromyography 8:39–74
Kalia M, Senapati JM, Parida B, Panda A (1972) Reflex increases in ventilation by muscle receptors in nonmedulated fibres (C fibres). J Appl Physiol 32:189–193
Kaufmann MP, Longhurst JC, Rybicki KJ, Wallach JH, Mitchell JH (1983) Effects of muscular contraction on impulse activity of group III and IV afferents in cats. J App] Physiol 55:105–112
Lasser RP, Myron MD, Schoenfeld R, Allen DF, Friedberg CK (1960) Reflex circulatory effects elicited by hypertonic and hypotonic solutions injected into femoral and brachial arteries of dogs. Circ Res 8:913–919
Liu CT, Huggins RA, Hoff HE (1969) Mechanisms of intraarterial K+-induced cardiovascular and respiratory responses. Am J Physiol 217:969–973
Mense S (1978) Muskelrezeptoren mit dünnen markhaltigen und marklosen afferenten Fasern: Receptive Eigenschaften und mögliche Funktion. Thesis, Christian-Albrechts-University Kiel
Mense S, Stahnke M (1983) Responses in muscle afferent fibres of slow conduction velocity to contractions and ischemia in the cat. J Physiol 342:383–397
McCloskey DI, Mitchell JH (1972) Reflex cardiovascular and ventilatory responses originating in exercising muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 224:173–186
Rohmert W (1960) Statische Haltearbeit des Menschen. Beuth, Berlin
Rowell LB, Savage MV, Chambers J, Blackmon JR (1991) Cardiovascular responses to graded reduction in leg perfusion in exercising humans. Am J Physiol 261: H1545-H1553
Sato A, Schmidt RF (1973) Somatosympathetic reflexes: afferent fibres, central pathways, discharge characteristics. Physiol Rev 53:916–947
Senapati JM (1966) Effect of stimulation of muscle afferents on ventilation of dogs. J Appl Physiol 21:242–246
Stebbins CL, Brown B, Levin D, Longhurst JC (1988) Reflex effect of skeletal muscle chemoreceptor stimulation on the cardiovascular system. J Appl Physiol 65:1539–1547
Stegemann J, Kenner T (1971) A theory on heart rate control by muscular receptors. Arch Kreislaufforsch 64:185–214
Thimm F, Carralho M, Babka M, Meier zu Verl E (1984) Reflex increases in heart rate induced by perfusing the hind leg of the rat with solutions containing lactic acid. Pflugers Arch 400:286–293
Thimm F, Baum K (1987) Response of chemosensitive nerve fibres of group III and IV to metabolic changes in rat muscles. Pflugers Arch 410:143–152
Wilson LB, Wall PT, Matsukawa K, Mitchell JH (1992) Effect of spinal microinjections of an antagonist to substance P or somatostatin on the exercise pressor reflex. Circ Res 70:213–222
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baum, K., Selle, K., Leyk, D. et al. Comparison of blood pressure and heart rate responses to isometric exercise and passive muscle stretch in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 70, 240–245 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238570
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238570