Abstract
The ectoderm of the one-day chick embryo generates dorsoventrally oriented short-circuit current (I sc) entirely dependent on extracellular sodium.
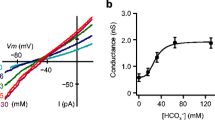
At the dorsal cell membrane, the I sc was modified reversibly and in a concentration-dependent manner by: amiloride (60% decrease at 1 mm, with 2 apparent IC50s: 0.13 and 48 μm), phlorizin (0.1 mm) or removal of glucose (30% decrease, additive to that of amiloride), SITS (1 mm, 13% decrease). Acidification or alkalinization of the dorsal (but not ventral) superfusate produced, respectively, decrease or increase of I sc with a pH50 of 7.64.
Ba2+ (0.1–1 mm) from either side of the ectoderm decreased the I sc by 30%. Anthracene-9-carboxylic acid, furosemide and inducers of cAMP had no effect on electrophysiological properties of the blastoderm.
The chick ectoderm is therefore a highly polarized epithelium containing, at the dorsal membrane, the high and low affinity amiloride-sensitive Na+ channels, Na+-glucose cotransporter, K+ channels and pH sensitivity, and, at the ventral membrane, the Na+, K+-ATPase and K+ channels. The Na+ transport reacts to pH, but lacks the cAMP regulatory system, well known in many epithelia.
The active Na+ transport drives glucose and fluid into the intraembryonic space, across and around the blastoderm which, in the absence of blood circulation, could secure renewal of extracellular fluid and disposal of wastes and thus maintain the cell homeostasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abriel, H., Ksontini, R., Kučera, P. 1993. Influence of the extracellular pH on the active transports in the chick embryo. Experientia 49:A47 (Abstr.)
Abriel, H., Nuccitelli, R. 1992. Measurement of the endogenous electric field and transectodermal potential in living chick embryo. Experientia 48:A33 (Abstr.)
Alper, S.L. 1991. The band 3-related anion exchanger (AE) gene family. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 53:549–564
Aronson, P.S. 1989. The renal proximal tubule: a model for diversity of anion exchangers and stilbene-sensitive anion transporters. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 51:419–441
Benos, D.J. 1981. Developmental changes in epithelial transport characteristics of preimplantation rabbit blastocysts. J. Physiol. 316:191–202
Benos, D.J., Cunningham, S., Baker, R.R., Beason, K.B., Oh, Y., Smith, P.R. 1992. Molecular characteristics of amiloride-sensitive sodium channels. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 120:31–113
Biggers, J.D., Baltz, J.M., Lechene, C. 1991. Ions and preimplantation development. In: Current Communications in Cell and Molecular Biology 4. Animal Applications of Research in Mammalian Development. R.A. Pedersen, A. McLaren, N.L. First, pp. 121–146. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory NY
Cross, M.H. 1973. Active sodium and chloride transport across the rabbit blastocoele wall. Biol. Reprod. 8:566–575
Cross, M.H., Brinster, R.L. 1970. Influence of ions, inhibitors and anoxia on transtrophoblast potential of rabbit blastocyst. Exp. Cell Res. 62:303–309
Duffey, M.E., Hainau, B., Ho, S., Bentzel, C.J. 1981. Regulation of epithelial tight junction permeability by cyclic AMP. Nature 294:451–453
Elias, S. 1964. The subembryonic liquid in the hen's egg: Formation and biochemistry. Rev. Roum. Embr. Cytol. 1:165–192
Elsas, L.J., Longo, N. 1992. Glucose transporters. Annu. Rev. Med. 43:377–393
Gillespie, J.I., Greenwell, J.R. 1988. Changes in intracellular pH and pH regulating mechanisms in somitic cells of the early chick embryo: a study using fluorescent pH-sensitive dye. J. Physiology 405:385–395
Hall, W.J., O'Donoghue, J.P., O'Regan, M.G., Penny, W.H. 1976. Endogenous prostaglandins, adenosine 3′, 5′-monophosphate and sodium transport across isolated frog skin. J. Physiol. 258:731–753
Hamburger, V., Hamilton, H. 1951. A series of normal stages in the development of the chick embryo. J. Morphol 88:49–92
Harvey, B.J., Ehrenfeld, J. 1988. Proton passage across cell membranes. pp. 139–164. Wiley, Chichester (Ciba Foundation Symposium 139)
Höfer, M. 1981. Transport across biological membranes. pp. 133–145. Pitman, London, Marshfield
Howard, E. 1957. Ontogenetic changes in the freezing point and sodium and potassium content of the subgerminal fluid and blood plasma of the chick embryo. J. Comp. Physiol. 50:451–470
Hwang, E.-S., Hirayama, B.A., Wright, E.M. 1991. Distribution of the SGLT1 Na+/glucose cotransporter and mRNA along the crypt-villus axis of rabbit small intestine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 181:1208–1217
Kleyman, T.R., Cragoe, E.J., Jr. 1988. Amiloride and its analogs as tools in the study of ion transport. J. Membrane Biol. 105:1–21
Komazaki, S., Takada, M. 1988. Amiloride-sensitive potential difference across the blastocoelic wall of early embryos of the newt, Cynops pyrrhogaster. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 91A:129–133
Kučera, P., Abriel, H., Katz, U. 1994. Ion transport across the early chick embryo: I. Electrical measurements, ionic fluxes and regional heterogeneity. J. Membrane Biol. 141:149–157
Kučera, P., de Ribaupierre, Y. 1989. Extracellular electrical currents in the chick blastoderm. Biol. Bull. 176(S):118–122
Kučera, P., Raddatz, E., Baroffio, A. 1984. Oxygen and glucose uptakes in the early chick embryo. In: Respiration and metabolism of embryonic vertebrates. W. Seymour, editor. pp. 299–309. Junk publ., Dordrecht, Boston, London
Manejwala, F.M., Cragoe, E.J., Schultz, R.M. 1989. Blastocoel expansion in the preimplantation mouse embryo: role of extracellular sodium and chloride and possible apical routes of their entry. Dev. Biol. 133:210–220
Manejwala, F.M., Schultz, R.M. 1989. Blastocoel expansion in the preimplantation mouse embryo: stimulation of sodium uptake by cAMP and possible involvement of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Dev. Biol. 136:560–563
New, D.A.T. 1956. The formation of sub-blastodermic fluid in hen's eggs. J. Embryol. Exp. Morph. 4:221–227
Palmer, L.G., Frindt, G. 1987. Effects of cell Ca and pH on Na channels from rat cortical collecting tubule. Am. J. Physiol. 253:F333-F339
Powers, R.D., Borland, R.W., Biggers, J.D. 1977. Amiloride-sensitive rheogenic Na+ transport in rabbit blastocyst. Nature 270:603–604
Powers, R.D., Tupper, J.T. 1977. Developmental changes in membrane transport and permeability in the early mouse embryo. Dev. Biol. 56:306–315
Prod'hom, B., Kučera, P. 1992. Ion channels in the chick embryonic ectoderm. Experientia 48:A33 (Abstr.)
Robinson, D.H., Smith, P.R., Benos, D.J. 1990. Hexose transport in preimplantation rabbit blastocysts. J. Reprod. Fert. 89:1–11
Robinson, D.H., Bubien, J.K., Smith, P.R., Benos, D.J. 1991. Epithelial sodium conductance in rabbit preimplantation trophectodermal cells. Dev. Biol. 147:313–321
Romanoff, A.L. 1967. Biochemistry of the Avian Egg. pp. 295–329. Wiley, New York
Smith, M.W. 1970. Active transport in the rabbit blastocyst. Experientia 26:736–738
Stein, W.D. 1990. Channels, Carriers, and Pumps: An Introduction to Membrane Transport. pp. 286–305. Academic, San Diego, London
Stern, C.D., MacKenzie, D.O. 1983. Sodium transport and the control of epiblast polarity in the early chick embryo. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 77:73–98
Stern, C.D., Manning, S., Gillespie, J.I. 1985. Fluid transport across the epiblast of the chick embryo. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 88:365–384
Ussing, H.H., Zerahn, K. 1951. Active transport of sodium as the source of electric current in the short-circuited isolated frog skin. Acta Physiol. Scand. 23:110–127
Van Driessche, W., Zeiske, W. 1985. Ionic channels in epithelial cell membranes. Physiol. Rev. 65:833–903
Wiley, L.M., Obasaju, M.F. 1989. Effects of phlorizin and ouabain on the polarity of mouse 4-cell/16-cell stage blastomere heterokaryons. Dev. Biol. 133:375–384
Wiley, L.M., Lever, J.E., Pape, C., Kidder, G. 1991. Antibodies to a renal Na+/glucose cotransport system localize to the apical plasma membrane domain of polar mouse embryo blastomeres. Dev. Biol. 143:149–161
Wright, E.M. 1993. The intestinal Na+/glucose cotransporter. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 55:575–589
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by the Swiss National Research Foundation (grant 3.418-0.86 to P.K.), by the Roche Research Foundation (grant to U.K.), the Fond du 450ème anniversaire de l'Université de Lausanne and the Société Académique Vaudoise (grants to H.A.). We thank C. Bareyre, G. de Torrenté and R. Ksontini for excellent technical assistance and Drs. E. Raddatz, Y. de Ribaupierre and B. Prod'hom for helpful discussions.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abriel, H., Katz, U. & Kučera, P. Ion transport across the early chick embryo: II. Characterization and pH sensitivity of the transembryonic short-circuit current. J. Membarin Biol. 141, 159–166 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238249
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238249