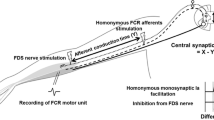
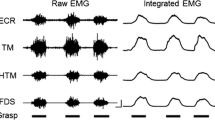
Summary
Transmission in the Ia inhibitory pathway from wrist extensor muscles onto flexor MNs was studied at various times after the onset of voluntary wrist extension or flexion. At the very onset of wrist movements Ia inhibition was not changed, as compared to at rest, whereas later it progressively increased during wrist extension and decreased during wrist flexion. These results are discussed in relation to the different inputs converging onto Ia interneurones and it is suggested that their inhibition by Renshaw cells might be responsible for the results found at the onset of contraction
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldissera F, Campadelli P, Cavallari P (1983) Inhibition from radial group I afferents of H-reflex in wrist flexors. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 23: 187–193
Baldissera F, Hultborn H, Illert M (1981) Integration in spinal neuronal system. In: Brook VB (ed) Handbook of Physiology, Sect I, The Nervous System, Vol II. Motor Control. Am Physiol Soc Bethesda, pp 509–595
Day BL, Marsden CD, Obeso JA, Rothwell JC (1984) Reciprocal inhibition between the muscles of the human forearm. J Physiol (Lond) 349: 519–534
Day BL, Rothwell JC, Marsden CD (1983) Transmission in the spinal reciprocal Ia inhibitory pathway preceding willed movements of the human wrist. Neurosci Lett 37: 245–250
Hultborn H, Illert M, Santini M (1976) Convergence on interneurones mediating the reciprocal Ia inhibition of motoneurones. I. Disynaptic Ia inhibition of Ia inhibitory interneurones. Acta Physiol Scand 96: 193–201
Hultborn H, Jankowska E, Lindström S (1971) Relative contribution from different nerves to recurrent depression of Ia IPSPs in motoneurones. J Physiol (Lond) 215: 637–664
Hultborn H, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (1979) Changes in recurrent inhibition during voluntary soleus contractions in man studied by an H-reflex technique. J Physiol (Lond) 297: 229–251
Shindo M, Harayama H, Kondo K, Yanagisawa N, Tanaka R (1984) Changes in reciprocal Ia inhibition during voluntary contraction in man. Exp Brain Res 53: 400–408
Vallbo ÅB, Hagbarth KE, Torebjörk HE, Wallin BG (1979) Somatosensory, proprioceptive, and sympathetic activity in human peripheral nerves. Physiol Rev 59: 919–957
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cavallari, P., Fournier, E., Katz, R. et al. Changes in reciprocal Ia inhibition from wrist extensors to wrist flexors during voluntary movement in man. Exp Brain Res 56, 574–576 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237999
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237999