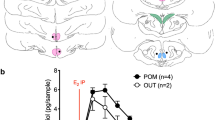
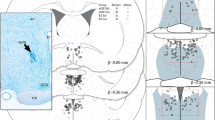
Summary
The technique of microelectrophoresis was utilized to study the effects of 17β-estradiol hemisuccinate (17βE2S), cortisol hemisuccinate (CS), and acetylcholine (Ach) on medial preoptic-septal (mPOA-S) neurons throughout the estrous cycle in urethane anesthetized rats. A total of 23 cells were identified antidromically as having their projections to the arcuate-median eminence region of the hypothalamus, and 18 of these were tested with 17βE2S. Only four cells showed an inhibition to the gonadal steroid, while the remaining neurons did not respond. Twelve antidromically identified (AI) neurons were tested with CS, none of which responded, and 2 out of 16 AI neurons showed an excitation to Ach. Extracellular potentials were recorded from 273 non-antidromically identified neurons, 138 of which were successfully tested with 17βE2S. Sixty-two of these responded to the steroid. The predominant response on late diestrus I was excitation, and the majority of estrogen-sensitive cells showed an inhibitory response on late diestrus 2, proestrus and estrus. A Chi-square analysis showed that the response varied significantly throughout the estrous cycle.
Cortisol hemisuccinate was tested on 154 non-antidromically identified mPOA-S neurons. The response to the corticosteroid also varied significantly throughout the cycle, but further analysis determined that the response was different from that of 17βE2S. Acetylcholine was also applied to 180 mPOA-S neurons, but no significant change in the response was found from one day of the cycle to the next.
It is apparent from these studies that (1) 17βE2S can bring about direct and rapid changes in the firing frequency of neurons, (2) the non-antidromically identified neuron is a site for these effects, and (3) the response differs significantly throughout the estrous cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, C.H., Greenwald, G.S.: Autoradiographic analysis of estradiol uptake in the brain and pituitary of the female rat. Endocrinology 85, 1160–1165 (1969)
Barry, F., Dubois, M.P.: Immunofluorescence study of the preoptico-infundibular LH-RH neurosecretory pathway of the guinea pig during the estrous cycle. Neuroendocrinology 15, 200–208 (1974)
Barry, F., Dubois, M.P., Carette, B.: Immunofluorescence study of the preoptico-infundibular LRF neurosecretory pathway in the normal, castrated or testosterone-treated male guinea pig. Endocrinology 95, 1416–1423 (1974)
Bueno, F., Pfaff, D.W.: Single unit recording in hypothalamus and preoptic area of estrogen-treated and untreated ovariectomized female rats. Brain Res. 101, 67–78 (1976)
Colombo, J.A., Whitmoyer, D.I., Sawyer, C.H.: Local changes in multiple unit activity induced by electrochemical means in preoptic and hypothalamic areas in the female rat. Brain Res. 71, 35–45 (1974)
Cross, B.A., Dyer, R.G.: Characterization of unit activity in hypothalamic islands with special reference to hormone effects. In: The Hypothalamus (eds. L. Martini, M. Motta and F. Fraschini), pp. 115–122. New York: Academic Press 1970
Cross, B.A., Dyer, R.G.: Unit activity in rat diencephalic islands — the effect of anesthetics. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 212, 467–481 (1971)
DeGroot, J.: The rat hypothalamus in stereotaxic coordinates. J. comp. Neurol. 113, 389–400 (1959)
Dyer, R.G.: An electrophysiological dissection of the hypothalamic regions which regulate the pre-ovulatory secretion of luteinizing hormone in the rat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 234, 421–442 (1973)
Dyer, R.G.: Inhibition and destruction of preoptic neurons by iron. Physiologist 18, 201 (1975)
Dyer, R.G., Burnet, F.: Effects of ferrous ions on preoptic area neurons and luteinizing hormone secretion in the rat. J. Endocr. 69, 1–8 (1976)
Dyer, R.G., Pritchett, C.J., Cross, B.A.: Unit activity in the diencephalon of female rats during the oestrous cycle. J. Endocr. 53, 151–160 (1972)
Eskay, R.L., Mical, R.S., Porter, J.C.: The relationships between the concentration of LHRH in hypophysial portal blood and LH release in intact, castrated, and electrochemical-stimulated rats. Endocrinology 100, 263–270 (1977)
Feldman, S., Dalith, M., Conforti, N.: Effects of cortisol on evoked potentials and recovery cycles in the rat hypothalamus. J. Neural Transmission 34, 1–9 (1973)
Fichera, S.: Projection of the medial preoptic area and the nucleus of the diagonal band in the rat. Anat. Rec. 184, 402 (1976)
Jacobowitz, D.M., Palkovits, M.: Topographic atlas of catecholamine and acetylcholinesterase-containing neurons in the rat brain. J. comp. Neurol. 157, 13–22 (1974)
Jensen, E.V., Brecher, P.I., Mohla, S., Desombre, E.R.: Receptor transformation in estrogen action. Acta endocr. (Kbh.) 191, 159–172 (1974)
Kelly, M.J., Dudley, C.A., Moss, R.L.: Identification of estrogen-sensitive neurons in the preoptic-septal area of the normal cyclic female rat. Soc. Neurosci. 709A (1975)
Kelly, M.J., Moss, R.L., Dudley, C.A.: Differential sensitivity of preoptic-septal neurons to microelectrophoresed estrogen during the estrous cycles. Brain Res. 114, 152–157 (1976)
Kelly, M.J., Moss, R. L., Dudley, C.A.: The effects of ovariectomy on the responsiveness of preoptic-septal neurons to micro-electrophoresed estrogen. Neuroendocrinology (in press)
Lincoln, D.W.: Unit activity in the hypothalamus, septum and preoptic area of the rat: characteristics of spontaneous activity and the effect of oestrogen. J. Endocr. 37, 177–189 (1967)
Mandelbrod, J., Feldman, S., Werman, R.: Inhibition of firing is the primary effect of microelectrophoresis of cortisol to units in the rat tuberal hypothalamus. Brain Res. 80, 303–315 (1974)
McEwen, B.S., Zigmond, R.E., Gerlach, J.L.: Sites of steroid binding and action in the brain. In: The Structure and Function of Nervous Tissue, Vol. V. (ed. G. Bourne), pp. 205–291. New York: Academic Press 1972
Means, A.R., Hamilton, T.H.: Early estrogen action: concomitant stimulations within two minutes of nuclear RNA synthesis and uptake of RNA precursor by the uterus. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 56, 1594–1598 (1966)
Moss, R.L.: Unit responses in preoptic and arcuate neurons related to anterior pituitary function. In: Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, Vol. 4 (eds. L. Martini and W.F. Ganong), pp. 95–128 New York: Raven Press 1976
Moss, R.L., Kelly, M.J., Riskind, P.: Tuberoinfundibular neurons: dopaminergic and norepinephrinergic sensitivity. Brain Res. 89, 265–277 (1975)
Moss, R.L., Law, O.T.: The estrous cycle: its influence on single unit activity in the forebrain. Brain Res. 30, 435–438 (1971)
Moss, R.L., Paloutzian, R.F., Law, O.T.: Electrical stimulation of forebrain structures and its effect on copulatory as well as stimulus-bound behavior in ovariectomized hormone-primed rats. Physiol. Behav. 12, 997–1004 (1974)
Napoli, A., Powers, J.B., Valenstein, E.S.: Hormonal induction of behavioral estrus modified by electrical stimulation of hypothalamus. Physiol. Behav. 9, 115–117 (1972)
Nequin, L.G., Alvarez, F., Schwartz, N.B.: Steroid control of gonadotropin release. J. Steroid Biochem. 6, 1007–1012 (1975)
Pfaff, D.W.: Autoradiographic localization of radioactivity in rat brain after injection of tritiated sex hormones. Science 161, 1355–1356 (1968)
Pfaff, D.W., Keiner, M.: Atlas of estradiol-concentrating cells in the central nervous system of the female rat. J. comp. Neurol. 151, 121–158 (1973)
Powers, B., Valenstein, E.S.: Sexual receptivity: facilitation by medial preoptic lesions in female rats. Science 175, 1003–1005 (1971)
Ruf, K., Steiner, F.A.: Steroid-sensitive single neurons in rat hypothalamus and midbrain: identification by microelectrophoresis. Science 165, 667–669 (1967)
Setalo, G., Vigh, S., Schally, A.V., Arimura, A., Flerko, B.: Immunohistological study of the origin of LH-RH containing nerve fibers of the rat hypothalamus. Brain Res. 103, 597–602 (1976)
Steiner, F.A.: Effects of locally applied hormones and neurotransmitters on hypothalamic neurons. In: Proceedings of Fourth International Congress of Endocrinology (Washington, D. C.) (ed. R. Scow), pp. 202–204. New York: American Elsevier 1973
Steiner, F.A., Ruf, K., Akert, K.: Steroid-sensitive neurons in rat brain: anatomical localization and responses to neurohumours and ACTH. Brain Res. 12, 74–85 (1969)
Stumpf, W.E.: Estradiol-concentrating neurons: topography in the hypothalamus by dry-mount autoradiography. Science 162, 1001–1003 (1968)
Turgeon, J., Barraclough, C.A.: Temporal patterns of LH release following graded preoptic electrochemical stimulation in proestrous rats. Endocrinology 92, 755–761 (1973)
Whitehead, S.A., Ruf, K.B.: Responses of antidromically identified preoptic neurons in the rat for neurotransmitters and to estrogen. Brain Res. 79, 185–198 (1974)
Wilks, S.S.: Mathematical Statistics, pp. 408–411. New York: J. Wiley 1962
Wuttke, W.: Preoptic unit activity and gonadotropin release. Exp. Brain Res. 19, 205–216 (1974)
Yagi, K.: Effects of estrogen on the unit activity of the rat hypothalamus. J. Physiol. Soc. Japan. 32, 692–693 (1970)
Yagi, K.: Changes in firing rates of single preoptic and hypothalamic units following an intravenous administration of estrogen in the castrated female rat. Brain Res. 53, 343–352 (1973)
Yamada, Y.: Effects of iontophoretically-applied prolactin on unit activity of the rat brain. Neuroendocrinology 18, 263–271 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by NIH Grant NS10434-END, awarded to R. L. Moss
Presently an NIH Postdoctoral Fellow at Max-Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Göttingen, West Germany
Recipient of an USPHS Career Development Award No. HD00146
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kelly, M.J., Moss, R.L. & Dudley, C.A. The effects of microelectrophoretically applied estrogen, cortisol and acetylcholine on medial preoptic-septal unit activity throughout the estrous cycle of the female rat. Exp Brain Res 30, 53–64 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237858
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237858