Summary
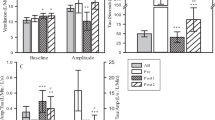
The reduced early mortality and the increased life span of persons with spinal cord injury (SCI) and other chronically disabling conditions which result in loss of use of the legs places them at increased risk of coronary heart disease, diabetes, and hypertension. Exercise testing in this population is becoming more common, but there is a need for assessment of protocols in order to determine the best method to elicita maximal response in a reasonable time without endangering the patient. Three wheelchair treadmill protocols were compared in seven men with paraplegia aged 21–44 years (five SCI, two post-polio). Subjects repeated each protocol to estimate reliability. Protocol G consisted of increasing treadmill grade at a constant speed (4.8 km·h−1); in protocol S, the speed was increased at a constant grade (0%), and in protocol C, speed and grade were increased. Two-minute stages were used in all protocols. Peak oxygen uptake [\(\dot V\)O2max; mean (SD): 23.6 (5.8) ml·kg−1·min−1; 1.66 (0.37) l·min−1], \(\dot V\)CO2 production [1.98 (0.46) l·min−1], ventilation volume [83.0 (25.6) l·min−1], respiratory exchange ratio [1.2 (0.12)], and heart rate [173 (18)] were determined. Over all trials none of the variables was significantly different among the three protocols, but all were highest in C and lowest in S. Reliability coefficients for absolute and relative \(\dot V\)O2max ranged from 0.76 and 0.81 in G to 0.95 and 0.98 in C (all P<0.05). These data suggest that an incremental treadmill test similar to the C protocol may be the optimal method to use when evaluating the exercise capacity of wheelchair users.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhambhani YN, Eriksson P, Steadward RD (1991) Reliability of peak physiological responses during wheelchair ergometry in persons with spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 72:559–562
Cowell LL, Squires WG, Raven PB (1986) Benefits of aerobic exercise for the paraplegic: a brief review. Med Sci Sports Exerc 18:501–508
Crews D, Wells CL, Burkett L, McKeeman-Hopkins V (1982) A physiological profile of four wheelchair marathon racers. Physician Sportsmed 10:134–143
Eriksson P, Lofstrom L, Ekblom B (1988) Aerobic power during maximal exercise in untrained and well-trained persons with quadriplegia and paraplegia. Scand J Rehabil Med 20:141–147
Flandrois R, Grandmontagen M, Gerin H, Mayet MH, Jehl JL, Eyssette M (1986) Aerobic performance capacity in paraplegic subjects. Eur J Appl Physiol 55:604–609
Gass GC, Camp EM (1979) Physiological characteristics of trained Australian paraplegic and tetraplegic subjects. Med Sci Sports 11:256–259
Gass GC, Camp EM (1984) The maximum physiological responses during incremental wheelchair and arm cranking exercise in male paraplegics. Med Sci Sports Exerc 16:355–359
Gass GC, Camp EM, Davis HA, Eager D, Grout L (1981) The effects of prolonged exercise on spinally injured subjects. Med Sci Sports Exerc 13:277–283
Glaser EM, Sawka MN, Brune MF, Wilde SW (1980) Physiological responses to maximal effort wheelchair and arm crank ergometry. J Appl Physiol 48:1060–1064
Golding LA, Horvat MA, Beutel-Horvat T, McConnell TJ (1986) A graded exercise test protocol for spinal cord injured individuals. J Cardiopulmonary Rehabil 6:362–367
Hoffman MD (1986) Cardiorespiratory fitness and training in quadriplegics and paraplegics. Sports Med 3:312–330
Horvat MA, Golding LA, Beutel-Horvat T, McConnell TJ (1984) A treadmill modification for wheelchairs. Res Q Exerc Sport 55:297–301
Lakomy HKA, Campbell I, Williams C (1987) Treadmill performance and selected physiological characteristics of wheelchair athletes. Br J Sports Med 21:130–133
Lasko-McCarthey P, Davis JA (1991) Protocol dependency of 365–4O2max during arm cycle ergometry in males with quadriplegia. Med Sci Sports Exerc 23:1097–1101
Le CT, Price M (1982) Survival from spinal cord injury. J Chronic Dis 35:487–492
Pitetti KH, Snell PG, Stray-Gundersen J (1987) Maximal response of wheelchair-confined subjects to four types of arm exercise. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 68:10–13
Sawka MN, Glaser RM, Wilde SW, Luhrte TC von (1980) Metabolic and circulatory responses to wheelchair and arm crank exercise. J Appl Physiol 49:784–788
Veeger HEJ, Yahmed MH, Woude LHV van der, Charpentier P (1991) Peak oxygen uptake and maximal power output of Olympic wheelchair-dependent athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 23:1201–1209
Voigt E-D, Balm D (1969) Metabolism and pulse rate in physically handicapped when propelling a wheelchair up an incline. Scand J Rehabil Med 1:101–106
Wicks JR, Lymburner K, Dinsdale SM, Jones NL (1977–1978) The use of multistage exercise testing with wheelchair ergometry and arm cranking in subjects with spinal cord lesions. Paraplegia 15:252–261
Winer BJ (1962) Statistical principles in experimental design. McGraw-Hill,New York, pp 124–132
Woude LHV van der, Hendrich KMM, Veeger HEJ, van Ingen Schenau GJ, Rozendal RH, Grout G de, Hollander AP (1988) Manual wheelchair propulsion: effects of power output on physiology and technique. Med Sci Sports Exerc 20:70–78
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartung, G.H., Lally, D.A. & Blancq, R.J. Comparison of treadmill exercise testing protocols for wheelchair users. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 66, 362–365 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237783
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237783