Summary
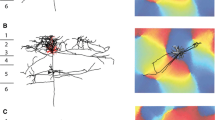
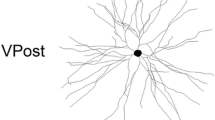
Observations of neurons in dorsal horn laminae IV–VI of the lumbosacral segments of Golgi-stained spinal cords in kittens and adult cats revealed laminar differences in dendritic architecture. Many neurons in lamina IV had dense, bushy dendritic fields. Lamina V contained, in addition to bushy cells similar in appearance to those of lamina IV, increasing numbers of neurons with radiating dendritic fields. Lamina VI was composed almost exclusively of neurons with radiating dendritic fields. These qualitative differences among laminae were accompanied by systematic variations in mean dendritic spread, which increased more than two-fold in adult cats between laminae IV and VI. A second gradient of dendritic spread was found within individual laminae: dendritic spread, particularly medial to lateral spread, increased for successively more lateral cells within a lamina. These differences in the spread of dendrites for neurons in different regions of the dorsal horn may be related to variations in the areas of peripheral receptive fields of dorsal horn neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken, J.T., Bridger, J.E.: Neuron size and neuron population density in the lumbosacral region of the cat's spinal cord. J. Anat. (Lond.) 95, 38–53 (1961)
Applebaum, A.E., Beall, J.E., Foreman, R.D., Willis, W.D.: Organization and receptive fields of primate spinothalamic tract neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 38, 572–586 (1975)
Brown, A.G., House, C.R., Rose, R.K., Snow, P.J.: The morphology of spinocervical tract neurones in the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 260, 719–738 (1976)
Brown, P.B.: Response of cat dorsal horn cells to variations of intensity, location, and area of cutaneous stimuli. Exp. Neurol. 23, 249–265 (1969)
Brown, P.B., Fuchs, J.L.: Somatotopic representation of hindlimb skin in cat dorsal horn. J. Neurophysiol. 38, 1–9 (1975)
Brown, P.B., Fuchs, J.L., Tapper, D.N.: Parametric studies of dorsal horn neurons responding to tactile stimulation. J. Neurophysiol. 38, 19–25 (1975)
Bryan, R.N., Trevino, D.L., Coulter, J.D., Willis, W.D.: Location and somatotopic organization of the cells of origin of the spino-cervical tract. Exp. Brain Re. 17, 177–189 (1973)
Cervero, F., Iggo, A., Ogawa, H.: Nociceptor-driven dorsal horn neurones in the lumbar spinal cord of the cat. Pain 2, 5–24 (1976)
Cowan, W.M., Woolsey, T.A., Wann, D.F., Dierker, M.L.: The computer analysis of Golgi-impregnated neurons. In: Golgi Centennial Symposium: Perspectives in Neurobiology (ed. M. Santini), pp. 81–85. New York: Raven Press 1975
Davenport, H.A., Combs, C.M.: Golgi's dichromate-silver method. 3. Chromating fluids. Stain Technol. 29, 165–173 (1954)
Egger, M.D., Wall, P.D.: The plantar cushion reflex circuit: an oligosynaptic cutaneous reflex. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 216, 483–501 (1971)
Fetz, E.: Pyramidal tract effects on interneurons in the cat lumbar dorsal horn. J. Neurophysiol. 31, 69–80 (1968)
Gelfan, S., Kao, G., Ruchkin, D.S.: The dendritic tree of spinal neurons. J. comp. Neurol. 139, 385–412 (1970)
Kelly, J.P., Van Essen, D.C.: Cell structure and function in the visual cortex of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 238, 515–547 (1974)
Kuypers, H.G.J.M., Tuerk, J.D.: The distribution of the cortical fibres within the nuclei cuneatus and gracilis of the cat. J. Anat. (Lond.) 98, 143–162 (1964)
Leontovich, T.A., Zhukova, G.P.: The specificity of the neuronal structure and topography of the reticular formation in the brain and spinal cord of carnivora. J. comp. Neurol. 121, 347–379 (1963)
Levick, W.R.: Form and function of cat retinal ganglion cells. Nature (Lond.) 254, 659–662 (1975)
Llinás, R., Hillman, D.E.: A multipurpose tridimensional reconstruction computer system for neuroanatomy. In: Golgi Centennial Symposium: Perspectives in Neurobiology (ed. M. Santini), pp. 71–79. New York: Raven Press 1975
Mannen, H.: Contribution to the morphological study of dendritic arborization in the brain stem. In: Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 21A: Correlative Neurosciences, Part A: Fundamental Mechanisms (eds. T. Tokizane, J.P. Schade), pp. 131–162. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1966
Pomeranz, B., Wall, P.D., Weber, W.V.: Cord cells responding to fine myelinated afferents from viscera, muscle and skin. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 199, 511–532 (1968)
Price, D.D., Mayer, D.J.: Physiological laminar organization of the dorsal horn of M. mulatta. Brain Res. 79, 321–325 (1974)
Pubols, B.H., Jr., Welker, W.I., Johnson, J.I., Jr.: Somatic sensory representation of forelimb in dorsal root fibers of raccoon, coatimundi and cat. J. Neurophysiol. 28, 312–341 (1965)
Puletti, F.: Cutaneous tactile units in cat. Physiologist 2, 96 (1959)
Proshansky, E., Egger, M.D.: Neuronal morphology of medial dorsal horn in kittens. Anat. Rec. 181, 453 (1975)
Proshansky, E., Egger, M.D.: Systematic differences in dendritic field size in cat dorsal horn. Anat. Rec. 184, 505–506 (1976)
Ramón-Moliner, E.: A chlorate-formaldehyde modification of the Golgi method. Stain Technol. 32, 105–116 (1957)
Ramón-Moliner, E.: An attempt at classifying nerve cells on the basis of their dendritic patterns. J. comp. Neurol. 119, 211–227 (1962)
Ramón-Moliner, E.: A source of error in the study of Golgi stained material. Arch. ital. Biol. 105, 139–148 (1967)
Ramón-Moliner, E., Nauta, W.J.H.: The isodendritic core of the brain stem. J. comp. Neurol. 126, 311–336 (1966)
Ramón y Cajal, S.: Histologie du Systeme Nerveux de L'homme et des Vertèbres, Vol. I. Madrid: Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas 1952
Réthelyi, M., Szentágothai, J.: Distribution and connections of afferent fibres in the spinal cord. In: Handbook of Sensory Physiology, Vol. II: Somatosensory System (ed. A. Iggo), pp. 207–252. New York: Springer 1973
Rexed, B.: The cytoarchitectonic organization of the spinal cord in the cat. J. comp. Neurol. 96, 415–495 (1952)
Scheibel, M.E., Scheibel, A.B.: Spinal motoneurons, interneurons and Renshaw cells. A Golgi study. Arch. ital. Biol. 104, 328–353 (1966)
Scheibel, M.E., Scheibel, A.B.: Terminal axonal patterns in cat spinal cord. II. The dorsal horn. Brain Res. 9, 32–58 (1968)
Scheibel, M.E., Scheibel, A.B.: A structural analysis of spinal interneurons and Renshaw cells. In: The Interneuron (ed. M.A. B. Brazier), pp. 159–208. Los Angeles: University of California Press 1969
Scheffé, H.: The Analysis of Variance. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1959
Sprague, J.M., Ha, H.: The terminal fields of dorsal root fibers in the lumbosacral spinal cord of the cat and the dendritic organization of the motor nuclei. In: Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 11: Organization of the Spinal Cord (eds. J.C. Eccles, J.P. Schade), pp. 120–154. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1964
Sterling, P., Kuypers, H.G.J.M.: Anatomical organization of the brachial spinal cord of the cat. I. The distribution of dorsal root fibers. Brain Res. 4, 1–15 (1967)
Szentágothai, J.: Neuronal synaptic arrangement in the substantia gelatinosa Rolandi. J. comp. Neurol. 122, 219–240 (1964)
Tapper, D.N., Brown, P.B., Moraff, H.: Functional organization of the cat's dorsal horn: connectivity of myelinated fiber systems of hairy skin. J. Neurophysiol. 36, 817–826 (1973)
Valverde, F.: The Golgi method. A tool for comparative structural analyses. In: Contemporary Research Methods in Neuroanatomy (eds. W.J.H. Nauta, S.O.E. Ebbesson), pp. 12–31. New York: Springer 1970
Wall, P.D.: The laminar organization of dorsal horn and effects of descending impulses. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 188, 403–423 (1967)
Wall, P.D.: Dorsal horn electrophysiology. In: Handbook of Sensory Physiology, Vol. II: Somatosensory System (ed. A. Iggo), pp. 253–270. New York: Springer 1973
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Proshansky, E., Egger, M.D. Dendritic spread of dorsal horn neurons in cats. Exp Brain Res 28, 153–166 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237093
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237093