Summary
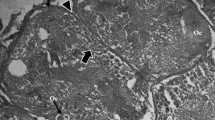
After hatching, the yolk syncytial layer of Salmo fario trutta may be subdivided into two zones, namely, the vitellolysis zone (containing numerous yolk platelets), and the cytoplasmic zone (where yolk platelets are rare). In the vitellolysis zone, two stages in the utilization of the yolk are observed:
-
1
The first stage, comprises the formation of yolk platelets from coalescent yolk by spherical cutting out and basal scission. This process seems to be achieved by the invagination of fibrillar elements into the coalescent yolk to form individual yolk platelets surrounded by a limiting membrane.
-
2
The second stage essentially consists of the extrusion or budding of yolk matter from a yolk platelet. Again, where the yolk matter leaves a platelet, fibrillar elements are evident and show an alkaline phosphatase activity. The platelets of the vitellolysis zone have a homogeneous content and variable diameter; they never acquire a heterogeneous and polymorphic aspect which could be interpreted as an intermediate stage in their degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amirante, G.A.: Immunochemical studies on rainbow trout lipovitellin. Acta Embryol. Exp. 373–383 (1972 Supp.)
Anderson, P.J.: Purification and quantitation of glutaraldehyde and its effect on several enzyme activities in skeletal muscle. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 15, 652–661 (1967)
Ando, K.: Ultracentrifugal analysis of yolk proteins in rainbow trout and their changes during development. Can. J. Biochem. 43, 373–379 (1965)
Ballard, W.W.: The role of the cellular envelope in the morphogenetic movements of teleost embryos. J. Exp. Zool. 161, 193–200 (1966a)
Ballard, W.W.: Origin of the hypoblast in Salmo. I. Does the blastodisc edge turn inward ? J. Exp. Zool. 161, 201–210 (1966b)
Ballard, W.W.: Item II. Outward movements of deep central cells. J. Exp. Zool. 161, 211–220 (1966c)
Ballard, W.W.: Normal embryonic stages for salmonid fishes, based on Salmo gairdneri (R.) and Salvelinus fontinalis (M.) J. Exp. Zool. 184, 7–26 (1973a)
Ballard, W.W.: Morphogenetic movements in Salmo gairdneri (R.) J. Exp. Zool. 184, 27–48 (1973b)
Ballard, W.W.: A new fate map for Salmo gairdneri. J. Exp. Zool. 184, 49–74 (1973c)
Ballard, W.W., Dodes, L.M.: The morphogenetic movements at the lower surface of the blastodisc in salmonid embryos. J. Exp. Zool. 168, 67–84 (1968)
Barka, T., Anderson, P.J.: Histochemical methods for acid phosphatase using hexazonium pararosanilin as coupler, J. Histochem. Cytochem. 10, 741–753 (1962)
Devillers, C.: Structural and dynamic aspects of the development of the teleostean egg. In: Advances in morphogenesis (M. Abercrombie and J. Brachet, eds.), pp. 379–428. New York: Academic Press 1961
Drochmans, P.: Morphologie du glycogène. Etude au microscope électronique de colorations négatives du glycogène. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 6, 141–163 (1962)
Ghinst, M. van der: Mise en évidence de ferments dans le syncytium vitellin de la truite. Bull. Hist. Phys. et Path. de Techn. Micros. 12, 257–258 (1935)
Gray, J.: The growth of fish. I. The relationship between embryo and yolk in Salmo fario. J. Exp. Biol. 4, 215–225 (1926)
Helminen, H.J., Ericsson, J.L.E.: On the mechanism of lysosomal enzyme secretion. Electron microscopic and histochemical studies on epithelial cells of the rat's ventral prostate lobe. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 33, 528–549 (1970)
Hugon, J., Borgers, M.: A direct lead method for the electron microscopic visualization of alkaline phosphatase activity. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 14, 429–431 (1966)
Jurand, A., Selman, G.G.: Yolk utilization in the notochord of newt as studied by electron microscopy. J. Embryol. Exptl. Morphol. 12, 43–53 (1964)
Kalt, R.K., Tandler, B.: A study of fixation of early amphibian embryos for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 36, 633–645 (1971)
Karasaki, S.: Studies on amphibian yolk. I. The ultrastructure of the yolk platelet. J. Cell Biol. 18, 135–151 (1963)
Kunz, Y.: Morphologische Studien über die embryonale und postembryonale Entwicklung bei Teleostiern mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Dottersystems und der Leber. Rev. Suisse Zool. 71, 445–525 (1964)
Lambson, R.O.: An electron microscopic study of the entodermal cells of the yolk sac of the chick during incubation and after hatching. Am. J. Anat. 129, 1–20 (1970)
Luft, J.H.: Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 9, 409–414 (1961)
Malcolm Love, R.: The chemical biology of fishes, pp. 60–128. New York: Academic Press 1970
McCay, C.M., Tunison, C.M., Crowell, M., Paul, H.: The calcium and phosphorus content of the body of the brook trout in relation to age, growth, and food. J. Biol. Chem. 114, 259–263 (1936)
Monneron, A., Bernhard, W.: Action de certaines enzymes sur des tissus inclus en épon. J. Microscopie 5, 697–714 (1966)
Nittinger, J.: Histologische und histochemische Untersuchungen über die Involution des Dottersacks bei Lebistes reticulatus Peters und Salmo irideus Gibb. Zool. Jb. Anat. Bd. 85, 245–325 (1967)
Philips, A.M., Podoliak, H.A., Dumas, R.F., Thoesen, R.W.: The nutrition of trout. Fish. Res. Bull. 22, 52–202 (1958)
Reynolds, E.S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963)
Richardson, K.C., Jarett, L., Finke, E.H.: Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 35, 313–323 (1960)
Smith, R.E., Farquhar, M.G.: Preparation of non-frozen sections for electron microscope cytochemistry. RCA Sci. Instr. News 10, 13–18 (1965)
Spurr, A.R.: A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 26, 31–43 (1969)
Tachibana, T.: Comparative ultrahistochemistry of the adepidermal granules of Salmo irideus, Lebistes reticulatus and Hynobius tokyoensis. Enzyme digestive experiment for the epoxy-embedded sections. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 23, 289–294 (1975)
Thiéry, J.-P.: Mise en évidence de polysaccharides sur coupes fines en microscopie électronique. J. Microscopie 6, 987–1017 (1967)
Trinkaus, J.-P.: A study of the mechanism of epiboly in the egg of Fundulus heteroclitus. J. Exp. Zool. 118, 269–319 (1951)
Trinkaus, J.-P.: Morphogenetic cell movements. In: Major problems of developmental biology (M. Locke, ed.), 25th Symp. soc. develop, biol., pp. 125–176. New York: Academic Press 1966
Trinkaus, J.-P.: The role of the periblast in Fundulus epiboly. Ontogenesis 2, 401–405 (1971)
Trinkaus, J.-P.: Surface activity and locomotion of Fundulus deep cells during blastula and gastrula stages. Develop. Biol. 30, 68–103 (1973)
Vernier, J.-M., Sire, M.-F.: Lipoprotéines de très basse densité et glycogène dans le syncytium vitellin. L'épithélium intestinal et le foie, aux stades précoces du développement embryonnaire chez la truite arc-en-ciel. Biol. cellulaire 29, 45–54 (1977a)
Vernier, J.-M., Sire, M.-F.: Plaquettes vitellines et activité hydrolasique acide au cours du développement embryonnaire de la truite arc-en-ciel. Etude ultrastructurale et biochimique. Biol. cellulaire 29, 99–112 (1977b)
Walzer, C., Schönenberger, N.: Ultrastructure and cytochemistry study of the yolk syncytial layer in the alevin of trout (Salmo fario trutta, L. and Salmo gairdneri, R.) after hatching. II. The cytoplasmic zone. Cell Tissue Res. 196, 75–93 (1979)
Ward, T.: The origin of protein and fatty yolk in Ranapipiens. Electronmicroscopical and cytochemical observation of young and mature oocytes. J. Cell Biol. 14, 309–341 (1962)
Williams, J.: Yolk utilization. In: The biochemistry of animal development (R. Weber, ed.), vol. 2, pp. 341–377. New York: Academic Press 1967
Yamagami, K.: Phosphorus metabolism in fish egg. I. Changes in the contents of some phosphorus compounds during early development of Oryzias latipes. Scient. Pap. Col. Gen. Educ. Univ. Tokyo 10, 99–108 (1960a)
Yamagami, K.: Item II. Transfer of some phosphorus compounds from egg yolk into embryonic tissues in Salmo irideus during development. Scient. Pap. Col. Gen. Educ. Univ. Tokyo 10, 325–336 (1960b)
Yamamoto, M.: Electron microscopy of fish development. V. The fine structure of the periblast in Oryzias latipes. J. Fac. Sci., Univ. Tokyo, Sec. IV 10, 483–490 (1967)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walzer, C., Schönenberger, N. Ultrastructure and cytochemistry study of the yolk syncytial layer in the alevin of trout (Salmo fario trutta L.) after hatching. Cell Tissue Res. 196, 59–73 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236348
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236348