Abstract
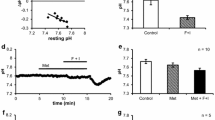
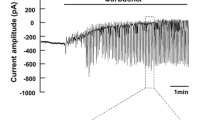
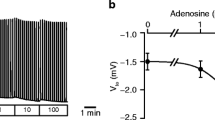
The actions of intracellular pH (pH i ) on Ca2+dependent Cl− channels were studied in secretory epithelial cells derived from human colon carcinoma (T84) and in isolated rat parotid acinar cells. Channel currents were measured with the whole cell voltage clamp technique with pipette solutions of different pH. Ca2+dependent Cl− channels were activated by superfusing ionomycin to increase the intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+] i ) or by using pipette solutions with buffered Ca2+ levels. Large currents were activated in T84 and parotid cells by both methods with pH i levels of 7.3 or 8.3. Little or no Cl− channel current was activated with pH i at 6.4. We used on-cell patch clamp methods to investigate the actions of low pH i on single Cl− channel current amplitude in T84 cells. Lowering the pH i had little or no effect on the current amplitude of a 8 pS Cl− channel, but did reduce channel activity. These results suggest that cytosolic acidification may be able to modulate stimulus-secretion coupling in fluid-secreting epithelia by inhibiting the activation of Ca2+-activated Cl− channels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alton, E.W.F.W., Manning, S.D., Schlatter, P.J., Geddes, D.M., Williams, A.J. 1991. Characterization of a Ca2+-dependent anion channel from sheep tracheal epithelium incorporated into planar bilayers. J. Physiol. 443:137–159
Anderson, M.P., Shepard, D.N., Berger, H.A., Welsh, M.J. 1992. Chloride channels in the apical membrane of normal and cystic fibrosis airway and intestinal epithelia. Am. J. Physiol. 263:L1-L14
Anderson, M.P., Welsh., M.J. 1991. Calcium and cAMP activate different chloride channels in the apical membrane of normal and cystic fibrosis epithelia. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 88:6003–6007
Arreola, J., Melvin, J.E., Begenisich, T. 1995. Volume-sensitive chloride channels in rat parotid acinar cells. J. Physiol 484:677–687
Arreola, J., Melvin, J.E., Begenisich, T. (1993). Blockade of Ca2+dependent Cl− channels by low cytoplasmic pH in secretory epithelial cells. XXXII Congress of the International Union of Physiological Sciences:116
Bormann, J., Hamill, O.P., Sakmann, B. 1987. Mechanisms of anion permeation through channels gated by glycine and γ-aminobutyric acid in cultured spinal neurones. J. Physiol. 385:243–286
Cartwright, C.A., McRoberts, J.A., Mandel, K.G., Dharmsathophorn, K. 1985. Synergistic action of cyclic adenosine monophosphateand calcium-mediated chloride secretion in a colonic epithelial cell line. J. Clin. Invest. 76:1837–1842
Cliff, W.H., Frizzell, R.A. 1990. Separate Cl− conductances activated by cAMP and Ca2+ in Cl−-secreting epithelial cells. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 87:4956–4960
Dharmsathophorn, K., Cohn, J., Beuerlein, G. 1989. Multiple calciummediated effector mechanisms regulate chloride secretory responses in T84-cells. Am. J. Physiol. 256:C1224-C1230
Dharmsathophorn, K., McRoberts, J.A., Mandel, K.G., Tisdale, L.D., Masui, H. 1984. A human colonic tumor cell line that maintains vectorial electrolyte transport. Am. J. Physiol. 246:G204-G208
Dharmsathophorn, K., Pandol, S.J. 1986. Mechanism of chloride secretion induced by carbachol in a colonic epithelial cell line. J. Clin. Invest. 77:348–354
Elliot, A.C., Lau, K.R., Brown, P.D. 1991. The effects of Na+ replacement on intracellular pH and [Ca2+] in rabbit salivary gland acinar cells. J. Physiol. 444:419–439
Evans, M.G., Marty, A. 1986. Calcium-dependent chloride current in isolated cells from rat lachrimal glands. J. Physiol. 378:437–460
Fasolato, C., Pozzan, T. 1989. Effect of membrane potential on divalent cation transport catalyzed by the “electroneutral” ionophores A23187 and ionomycin. J. Biol. Chem. 264:19630–19636
Findlay, I., Petersen, O.H. 1985. Acethylcholine stimulates a Ca2+dependent Cl− conductance in mouse lachrymal acinar cells. Pfluegers Arch. 403:328–330
Frizzell, R.A., Halm, D.R. 1990. Chloride channels in epithelial cells. Currents Topics in Membranes and Transport 37:247–282
Grynkiewicz, G., Poenie, M., Tsien, R.Y. 1985. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J. Biol. Chem. 360:3440–3450
Halm, D.R., Frizzell, R.A. 1992. Anion permeation in an apical membrane chloride channel of a secretory epithelial cell. J. Gen. Physiol. 99:339–366
Hamill, O.P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., Sigworth, F.J. 1981. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pfluegers Arch. 391:85–100
Harrison, S.M., Bers, D.M. 1987. The effect of temperature and ionic strength on the apparent Ca-affinity of EGTA and the analogous Ca-chelators BAPTA and dibromo-BAPTA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 925:133–143
Hume, R.I., Thomas, S.A. 1989. A calciumand voltage-dependent chloride current in developing chick skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 417:241–261
Iwatsuki, N., Maruyama, Y., Matsumoto, O., Nishiyama, A. 1985. Activation of Ca2+-dependent Cl− and K+ conductances in rat and mouse parotid acinar cells. Jap. J. Physiol. 35:933–944
Lattanzio, F.A., Jr. 1990. The effects of pH and temperature on fluorescent calcium indicators and determined with chelex-100 and EDTA buffer systems. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 171:102–108
Lewis, R.S., Ross, P.E., Cahalan, M.D. 1993. Chloride channels activated by osmotic stress in T lymphocytes. J. Gen. Physiol. 101:801–826
Light, D.B., Schwiebert, E.M., Fejes-Toth, G., Naray-Fejes-Toth, A., Karlson, K.H., McCann, F.V., Stanton, B.A. 1990. Chloride channels in the apical membrane of cortical collecting duct cells. Am. J. Physiol. 258:F273-F280
Martinez., J.R., Cassity, N. 1985. Effects of 4,4′diisothiocyano-2,2′stilbene disulphonic acid and amiloride on salivary secretion by isolated, perfused rat submandibular glands. Arch. Oral Biol. 30:797–803
Melvin, I.E., Moran, A., Turner, R.J. 1988. The role of HCO −3 and Na+/H+ exchange in the response of rat parotid acinar cells to muscarinic stimulation. J. Biol. Chem. 263:19564–19569
Morris, A.P., Frizzell, R.A. 1993. Ca2+-dependent Cl− channels in undifferentiated human colonic cells (HT-29). I. Single-channel properties. Am. J. Physiol. 264:C968-C976
Novak, I., Young, J.A. 1986. Two independent anion transport systems in rabbit mandibular salivary glands. Pfluegers Arch. 407:649–656
Park, K., Brown, P.D. 1995. Intracellular pH modulates the activity of chloride channels in isolated lacrimal gland acinar cells. Am. J. Physiol. 268:C647-C650
Petersen, O.H. 1992. Stimulus-secretion coupling: cytoplasmic calcium signals and the control of ion channels in exocrine acinar cells. J. Physiol. 448:1–51
Pirani, D., Evans, A.R., Cook, D.I., Young, J.A. 1987. Intracellular pH in the rat mandibular salivary gland: the role of Na-H and C1-HCO3 antiports in secretion. Pfluegers Arch. 408:178–184
Reinhardt, R., Bridges, R.T., Rummel, W., Lindemann, B. 1987. Properties of an anion selective channel from rat colonic enterocytes plasma membranes reconstituted into planar lipid bilayers. J. Membrane Biol. 95:47–54
Sheppard, D.A., Welsh, M.J. 1992. Effect of ATP-sensitive K+ channel regulators on cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator chloride currents. J. Gen. Physiol. 100:573–591
Tabcharani, J.A., Low, W., Elie, D., Hanrahan, J.W. 1990. Lowconductance chloride channel activated by cAMP in the epithelial cell line T84. FEBS Lett. 270:157–164
Thomas, J.A., Buchsbaum, R.N., Zimniak, A., Racker, E. 1979. Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ. Biochemistry. 18:2210–2218
Tsien, R., Pozzan, T. 1989. Measurements of cytosolic free Ca2+ with Quin 2. Methods in Enzymol. 172:230–262
Turner, R.J. 1993. Ion transport related to fluid secretion in salivary glands. In: Biology of the Salivary Glands. K. DobrosielskiVergona, editor, pp. 105–127. CRC Press, New York
Wagner, J.A., Cozens, A.L., Schulman, H., Gruenert, D.C., Stryer, L., Gardner, P. 1991. Activation of chloride channels in normal and cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells by multifunctional calcium/ calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Nature 349:793–796
Wagner, J.A., McDonald, T.V., Nghiem, P.T., Lowe, A.W., Schulman, H., Gruenert, D.C., Stryer, L., Gardner, P. 1992. Antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator inhibit cAMP-activated but not calcium-activated chloride currents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:6785–6789
Worrell, R.T., Frizzell, R.A. 1991. CaMKII mediates stimulation of chloride conductance by calcium in T84 cells. Am. J. Physiol. 260:C877-C882
Yellen, G. 1984. Ionic permeation and blockade in Ca2+-activated K+ channels of bovine chromaffin cells. J. Gen. Physiol. 84:157–186
Zhang, G.H., Cragoe Jr., E.J., Melvin, J.E. 1992. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH in rat sublingual mucous acini at rest and during muscarinic stimulation. J. Membrane Biol. 129:311–321
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors thank Mrs. L. Koek for taking care of T84 cells culture. We are grateful to Dr. Tom Gunther for providing fura-2 Kd values at pH levels of 6.4 and 8.3. We thank Dr. Sherrill Spires for a critical reading of the manuscript. This research was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health DE09692.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arreola, J., Melvin, J.E. & Begenisich, T. Inhibition of Ca2+-dependent Cl− channels from secretory epithelial cells by low internal pH. J. Membarin Biol. 147, 95–104 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235400
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235400