Abstract
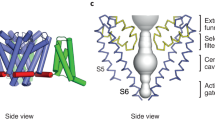
The complete amino acid sequence of a sodium channel from squid Loligo bleekeri has been deduced by cloning and sequence analysis of the complementary DNA. A unique feature of the squid sodium channel is the 1,522 residue sequence, approximately three-fourths of those of the rat sodium channels I, II and III. On the basis of the sequence, and in comparison with those of vertebrate sodium channels, we have proposed a tertiary structure model of the sodium channel where the transmembrane segments are octagonally aligned and the four linkers of S5–6 between segments S5 and S6 play a crucial role in the activation gate, voltage sensor and ion selective pore, which can slide, depending on membrane potentials, along inner walls consisting of alternating segments S2 and S4. The proposed octagonal structure model is contrasted with that of Noda et al. (Nature 320; 188–192, 1986). The octagonal structure model can explain the gating of activation and inactivation, and ion selectivity, as well as the action mechanism of both tetrodotoxin (TTX) and α-scorpion toxin (ScTX), and can be applied not only to the sodium channel, but also to the calcium channel, potassium channel and cGMP-gated channel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, P.A.V. 1987. Properties and pharmacology of a TTXinsensitive Na+ current in neurones of the jellyfish Cyanea capillata. J. Exp. Biol. 133:231–248
Anderson, P.A.V., Holman, M.A., Greenberg, R.M. 1993. Deduced amino acid sequence of a putative sodium channel from the scyphozoan jellyfish Cyanea capillata. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:7419–7423
Armstrong, C.M., Bezanilla, F. 1974. Charge movement associated with the opening and closing of the activation gates of the Na channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 63:533–552
Armstrong, C.M., Bezanilla, F. 1977. Inactivation of the sodium channel. II. Gating current experiments. J. Gen. Physiol. 70:567–590
Auld, V.J., Goldin, A.L., Krafte, D.S., Catterall, W.A., Lester, H.A., Davidson, N., Dunn, R.J. 1990. A neutral amino acid change in segment IIS4 dramatically alters the gating properties of the voltage-dependent sodium channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:323–327
Baker, P.F., Hodgkin, A.L., Ridgway, E.B. 1971. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J. Physiol. 218:709–755
Bezanilla, F., Armstrong, C.M. 1972. Negative conductance caused by entry of sodium and cesium ions into the potassium channels of squid axons. J. Gen. Physiol. 60:588–608
Bezanilla, F. 1985. Gating of sodium and potassium channels. J. Membrane Biol. 88:97–111
Biel, M., Altenhofen, W., Hullin, R., Ludwig, J., Freichel, M., Flockerzi, V., Dascal, N., Kaupp, U.B., Hofmann, F. 1993. Primary structure and functional expression of a cyclic nucleotide-gated channel from rabbit aorta. FEBS Lett. 329:134–138
Butler, A., Wei, A., Baker, K., Salkoff, L. 1989. A family of putative potassium channel genes in Drosophila. Science 243:943–947
Catterall, W.A., 1979. Binding of scorpion toxin to receptor sites associated with sodium channels in frog muscle. Correlation of voltage-dependent binding with activation. J. Gen. Physiol. 74:375–391
Catterall, W.A., Beneski, D.A. 1981. Biochemical and allosteric properties of neurotoxin receptor site associated with voltage-sensitive sodium channels, in Nerve membrane. In: Biochemistry and function of channel proteins. G. Matsumoto, M. Kotani, editors, pp. 3–11. The University of Tokyo, Tokyo
Catterall, W.A. 1986. Voltage-dependent gating of sodium channels: correlating structure and function. TINS 9:7–10
Chabala, L.D., Urban, B.W., Weiss, L.B., Green, W.N., Andersen, O.S. 1991. Steady-state gating of batrachotoxin-modified sodium channels. Variability and electrolyte-dependent modulation. J. Gen. Physiol. 98:197–224
Chirgwin, J.M., Przybyla, A.E., MacDonald, R.J., Rutter, W.J. 1979. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry 18:5294–5299
Conn, E.E., Stump, K.P., Bruening, G., Doi, R.H. 1987. Outlines of biochemistry, Fifth edition. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Dhallan, R.S., Yau, K.-W., Schrader, K.A., Reed, R.R. 1990. Primary structure and functional expression of a cyclic nucleotide-activated channel from olfactory neurons. Nature 347:184–187
Durell, S.R., Guy, H.R. 1992. Atomic scale structure and functional models of voltage-gated potassium channels. Biophys. J. 62:238–250
Frech, G.C., VanDongen, A.M.J., Schuster, G., Brown, A.M., Joho, R.H. 1989. A novel potassium channel with delayed rectifier properties isolated from rat brain by expression cloning. Nature 340:642–645
French, R.J., Wells, J.B. 1977. Sodium ions as blocking agents and charge carriers in the potassium channel of the squid giant axon. J. Gen. Physiol. 70:707–724
Gellens, M.E., George, A.L., Jr., Chen, L., Chahine, M., Horn, R., Barchi, R.L., Kallen, R.G. 1992. Primary structure and functional expression of the human cardiac tetrodotoxin-insensitive voltagedependent sodium channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:554–558
Guy, H.R., Seetharamulu, P. 1986. Molecular model of the action potential sodium channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:508–512
Heinemann, S.H., Terlau, H., Stühmer, W., Imoto, K., Numa, S. 1992. Calcium channel characteristics conferred on the sodium channel by single mutations. Nature 356:441–443
Hille, B. 1992. Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes, Second edition. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA
Hironaka, T., Narahashi, T. 1977. Cation permeability ratio of sodium channels in normal and grayanotoxin-treated squid axon membranes. J. Membrane Biol. 31:359–381
Ho, K., Nichols, C.G., Lederer, W.J., Lytton, J., Vassilev, P.M., Kanazirska, M.V., Hebert, S.C. 1993. Cloning and expression of an inwardly rectifying ATP-regulated potassium channel. Nature 362:31–38
Hodgkin, A.L., Huxley, A.F. 1952. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 117:500–544
Hubbard, S.C., Ivatt, R.J. 1981. Synthesis and processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 50:555–583
Ichikawa, M., Urayama, M., Matsumoto, G. 1991. Anticalmodulin drugs block the sodium gating current of squid giant axons. J. Membrane Biol. 120:211–222
Ito, H., Morton, T.H., Vodyanoy, V. 1989. Small odorant molecules affect steady state properties of monolayers. Thin solid Films 180:1–13
Jan, L.Y., Jan, Y.N. 1990. A superfamily of ion channels. Nature 345:672
Kaupp, U.B., Niidome, T., Tanabe, T., Terada, S., Bönigk, W., Stühmer, W., Cook, N.J., Kangawa, K., Matsuo, H., Hirose, T., Miyata, T., Numa, S. 1989. Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of the rod photoreceptor cyclic GMPgated channel. Nature 342:762–766
Kayano, T., Noda, M., Flockerzi, V., Takahashi, H., Numa, S. 1988. Primary structure of rat brain sodium channel III deduced from the cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett. 228:187–194
Keynes, R.D., Greeff, N.G., Forster, I.C., Bekkers, J.M. 1991. The effect of tetrodotoxin on the sodium gating current in the squid giant axon. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 246:135–140
Khodorov, B.I. 1978. Chemicals as tools to study nerve fiber sodium channels; effects of batrachotoxin and some anesthetics. In: Membrane Transport Processes. D.C. Tosteson, Y.A. Ovchirrikov, R. Latorre. editors. Raven, New York
Kim, M.-S., Morii, T., Sun, L.-X., Imoto, K., Mori, Y. 1993. Structural determinants of ion selectivity in brain calcium channel. FEBS Lett. 318:145–148
Krapivinsky, G., Gordon, E.A., Wickman, K., Velimirović, B., Krapivinsky, L., Clapham, D.E., 1995. The G-protein-gated atrial K+ channel IKACh is a heteromultimer of two inwardly rectifying K+ channel proteins. Nature 374:135–141
Kubo, Y., Baldwin, T.J., Jan, Y.N., Jan, L.Y. 1993a. Primary structure and functional expression of a mouse inward rectifier potassium channel. Nature 362:127–133
Kubo, Y., Reuveny, E., Slesinger, P.A., Jan, Y.N., Jan, L.Y. 1993b. Primary structure, functional expression of a rat G-proteincoupled muscarinic potassium channel. Nature 364:802–806
Kyte, J., Doolittle, R.F. 1982. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J. Mol. Biol. 157:105–132
Landowne, D. 1993. Measuring nerve excitation with polarized light. Jap. J. Physiol. 43:7–11
Lehmann-Horn, F., Iaizzo, P.A., Hatt, H., Franke, Ch. 1991. Altered gating and conductance of Na+ channels in hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Pfluegers Arch 418:297–299
Lewin, B. 1994. The apparatus for nuclear splicing. In: Genes, V. pp. 911–940. Oxford University, Oxford
Ludwig, J., Margalit, T., Eismann, E., Lancet, D., Kaupp, U.B. 1990. Primary structure of cAMP-gated channel from bovine olfactory epithelium. FEBS Lett. 270:24–29
MacKinnon, R., Yellen, G. 1990. Mutations affecting TEA blockade and ion permeation in voltage-activated K+ channels. Science 250:276–279
Mathur, R., Zheng, J., Yan, Y., Sigworth, F.J. 1995. Role of the S3-S4 linker in activation of Shaker K+ channels. Biophys. J. 68:A32
McClatchey, A.I., Van den Bergh, P., Pericak-Vance, M.A., Raskind, W., Verellen, C., Mckenna-Yasek, D., Rao, K., Haines, J.L., Bird, T., Brown, R.H., Jr., Gusella, J.F. 1992. Temperature-sensitive mutations in the III–IV cytoplasmic loop region of the skeletal muscle sodium channel gene in paramyotonia congenita. Cell 68:769–774
McCormack, K., Tanouye, M.A., Iverson, L.E., Lin, J.-W., Ramaswami, M., McCormack, T., Campanelli, J.T., Mathew, M.K., Rudy, B. 1991. A role for hydrophobic residues in the voltagedependent gating of Shaker K+ channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:2931–2935
Mikami, A., Imoto, K., Tanabe, T., Niidome, T., Mori, Y., Takeshima, H., Narumiya, S., Numa, S. 1989. Primary structure and functional expression of the cardiac dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel. Nature 340:230–233
Miller, I.R. 1993. Mechanism of channel opening and closing: a hypothesis. Bioelectrochem. Bioenergetics 31:323–328
Moorman, J.R., Kirsch, G.E., Brown, A.M., Joho, R.H. 1990. Changes in sodium channel gating produced by point mutations in a cytoplasmic linker. Science 250:688–691
Mori, Y., Friedrich, T., Kim, M.-S., Mikami, A., Nakai, J., Ruth, P., Bosse, E., Hofmann, F., Flockerzi, V., Furuichi, T., Mikoshiba, K., Imoto, K., Tanabe, T., Numa, S. 1991. Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of a brain calcium channel. Nature 350:398–402
Nakayama, H., Hatanaka, Y., Yoshida, E., Oka, K., Takanohashi, M., Amano, Y., Kanaoka, Y. 1992. Photolabeled sites with a tetrodotoxin derivative in the domain III and IV of the electroplax sodium channel. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 184:900–907
Niidome, T., Kim, M.-S., Friedrich, T., Mori, Y. 1992. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel calcium channel from rabbit brain. FEBS Lett. 308:7–13
Noda, M., Shimizu, S., Tanabe, T., Takai, T., Kayano, T., Ikeda, T., Takahashi, H., Nakayama, H., Kanaoka, Y., Minamino, N., Kangawa, K., Matsuo, H., Raftery, M.A., Hirose, T., Inayama, S., Hayashida, H., Miyata, T., Numa, S. 1984. Primary structure of Electrophorus electricus sodium channel deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature 312:121–127
Noda, M., Ikeda, T., Kayano, T., Suzuki, H., Takeshima, H., Kurasaki, M., Takahashi, H., Numa, S. 1986. Existence of distinct sodium channel messenger RNAs in rat brain. Nature 320:188–192
Noda, M., Suzuki, H., Numa, S., Stühmer, W. 1989. A single point mutation confers tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin insensitivity on the sodium channel II. FEBS Lett. 259:213–216
Pittler, S.J., Lee, A.K., Altherr, M.R., Howard, T.A., Seldin, M.F., Hurwitz, R.L., Wasmuth, J.J., Baehr, W. 1992. Primary structure and chromosomal localization of human and mouse rod photoreceptor cGMP-gated cation channel. J. Biol. Chem. 267:6257–6262
Planells-Cases, R., Ferrer-Montiel, A.V., Patten, C.D., Montal, M. 1995. The S2 and S3 transmembrane segments are additional components of the voltage sensor in voltage-gated potassium channels. Biophys. J. 68:A34
Ptáček, L.J., George, A.L., Jr., Griggs, R.C., Tawil, R., Kallen, R.G., Barchi, R.L., Robertson, M., Leppert, M.F. 1991. Identification of a mutation in the gene causing hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Cell 67:1021–1027
Pusch, M., Noda, M., Stühmer, W., Numa, S., Conti, F. 1991. Single point mutations of the sodium channel drastically reduce the pore permeability without preventing its gating. Eur. Biophys. J. 20:127–133
Rogart, R.B., Cribbs, L.L., Muglia, L.K., Kephart, D.D., Kaiser, M.W. 1989. Molecular cloning of a putative tetrodotoxin-resistant rat heart Na+ channel isoform. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:8170–8174
Rosenthal, J.J.C., Gilly, W.F. 1993. Amino acid sequence of a putative sodium channel expressed in the giant axon of the squid Loligo opalescens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 90:10026–10030
Saiki, R.K., Scharf, S., Faloona, F., Mullis, K.B., Horn, G.T., Erlich, H.A., Arnheim, N. 1985. Enzymatic amplification of β- globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science 230:1350–1354
Saiki, R.K., Gelfand, D.H., Stoffel, S., Scharf, S.J., Higuchi, R., Horn, G.T., Mullis, K.B., Erlich, H.A. 1988. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239:487–491
Salkoff, L., Butler, A., Wei, A., Scavarda, N., Giffen, K., Ifune, C., Goodman, R., Mandel, G. 1987. Genomic organization and deduced amino acid sequence of a putative sodium channel gene in Drosophila. Science 237:744–749
Satin, J., Kyle, J.W., Chen, M., Bell, P., Cribbs, L.L., Fozzard, H.A., Rogart, R.B. 1992. A mutant of TTX-resistant cardiac sodium channels with TTX-sensitive properties. Science 256:1202–1205
Sato, C., Matsumoto, G. 1992a. Primary structure of squid sodium channel deduced from the complementary DNA sequence. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 186:61–68
Sato, C., Matsumoto, G. 1992b. Proposed tertiary structure of the sodium channel. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 186:1158–1167
Sato, C., Hirota, K., Matsumoto, G. 1995. Neuronal specificity of sub-type SQSC1 of squid putative sodium channel. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 206:807–813
Stocker, M., Stühmer, W., Wittka, R., Wang, X., Müller, R., Ferrus, A., Pongs, O. 1990. Alternative Shaker transcripts express either rapidly inactivating or noninactivating K+ channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:8903–8907
Stühmer, W., Conti, F., Suzuki, H., Wang, X., Noda, M., Yahagi, N., Kubo, H., Numa, S. 1989. Structural parts involved in activation and inactivation of the sodium channel. Nature 339:597–603
Tanabe, T., Takeshima, H., Mikami, A., Flockerzi, V., Takahashi, H., Kangawa, K., Kojima, M., Matsuo, H., Hirose, T., Numa, S. 1987. Primary structure of the receptor for calcium channel blockers from skeletal muscle. Nature 328:313–318
Tang, S., Mikala, G., Bahinski, A., Yatani, A., Varadi, G., Schwartz, A. 1993. Molecular localization of ion selectivity sites within the pore of a human L-type cardiac calcium channel. J. Biol. Chem. 268:13026–13029
Tejedor, F.J., Catterall, W.A. 1988. Site of covalent attachment of α-scorpion toxin derivatives in domain I of the sodium channel α subunit. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci USA 85:8742–8746
Tempel, B.L., Papazian, D.M., Schwarz, T.L., Jan, Y.N., Jan, L.Y. 1987. Sequence of a probable potassium channel component encoded at Shaker Locus of Drosophila. Science 237:770–775
Tempel, B.L., Jan, Y.N., Jan, L.Y. 1988. Cloning of a probable potassium channel gene from mouse brain. Nature 332:837–839
Terlau, H., Heinemann, S.H., Stühmer, W., Pusch, M., Conti, F., Imoto, K., Numa, S. 1991. Mapping the site of block by tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin of sodium channel II. FEBS Lett. 293:93–96
Thomsen, W.J., Catterall, W.A. 1989. Localization of the receptor site for α-scorpion toxins by antibody mapping: Implications for sodium channel topology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:10161–10165
Triglia, T., Peterson, M.G., Kemp, D.J. 1988. A procedure for in vitro amplification of DNA segments that lie outside the boundaries of known sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 16:8186
Trimmer, J.S., Cooperman, S.S., Tomiko, S.A., Zhou, J., Crean, S.M., Boyle, M.B., Kallen, R.G., Sheng, Z., Barchi, R.L., Sigworth, F.J., Goodman, R.H., Agnew, W.S., Mandel, G. 1989. Primary structure and functional expression of a mammalian skeletal muscle sodium channel. Neuron 3:33–49
Trimmer, J.S., Agnew, W.S. 1989. Molecular diversity of voltagesensitive Na channels. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 51:401–418
Trudeau, M.C., Warmke, J.W., Ganetzky, B., Robertson, G.A. 1995. H-erg, a member of the eag family of K+ channels, encodes an inward rectifier. Biophys. J. 68:A32
Tsuji, K., Kawanishi, T., Handa, S., Kamano, H., Iwasa, J., Seyama, I. 1991. Effect of structural modification of several groups on the D-ring of grayanotoxin on its depolarization potency in squid giant axon. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 257:788–794
Tsukita, S., Tsukita, S., Kobayashi, T., Matsumoto, G. 1986. Subaxolemmal cytoskeleton in squid giant axon. II. Morphological identification of microtubule-and microfilament-associated domains of axolemma. J. Cell Biol. 102:1710–1725
Vale, R.D., Schnapp, B.J., Reese, T.S., Sheetz, M.P. 1985. Movement of organelles along filaments dissociated from the axoplasm of the squid giant axon. Cell 40:449–454
Vassilev, P.M., Scheuer, T., Catterall, W.A. 1988. Identification of an intracellular peptide segment involved in sodium channel inactivation. Science 241:1658–1661
Warmke, J.W., Ganetzky, B. 1994. A family of potassium channel genes related to eag in Drosophila and mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 91:3438–3442
Waugh, R.E., Hochmuth, R.M. 1987. Mechanical equilibrium of thick, hollow, liquid membrane cylinders. Biophys. J. 52:391–400
Waugh, R.E., Song, J., Svetina, S., Žekš, B. 1992. Local and nonlocal curvature elasticity in bilayer membranes by tether formation from lecithin vesicles. Biophys. J. 61:974–982
Wei, A., Covarrubias, M., Butler, A., Baker, K., Pak, M., Salkoff, L. 1990. K+ current diversity is produced by an extended gene family conserved in Drosophila and mouse. Science 248:599–603
West, J.W., Numann, R., Murphy, B.J., Scheuer, T., Catterall, W.A. 1991. A phosphorylation site in the Na+ channel required for modulation by protein kinase C. Science 254:866–868
West, J.W., Patton, D.E., Scheuer, T., Wang, Y., Goldin, A.L., Catterall, W.A. 1992. A cluster of hydrophobic amino acid residues required for fast Na+-channel inactivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 89:10910–10914
Yellen, G., Jurman, M.E., Abramson, T., MacKinnon, R. 1991. Mutations affecting internal TEA blockade identify the probable poreforming region of a K+ channel. Science 251:939–942
Yokoyama, S., Imoto, K., Kawamura, T., Higashida, H., Iwabe, N., Miyata, T., Numa, S. 1989. Potassium channels from NG108–15 neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells. Primary structure and functional expression from cDNAs. FEBS Lett. 259:37–42
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors would like to express our cordial acknowledgments to Dr. Hideo Tani (Kowa) and Drs. Masahiko Fujino and Haruo Onda (Takeda Pharmaceutical) for their kind support for us to utilize their experimental facilities for DNA cloning and as well as for their stimulating and helpful discussions. We also thank Drs. Toshio Iijima, Michinori Ichikawa, Kiyonori Hirota, Messrs. Tadashi Kimura and Osamu Shono and all our colleagues (Supermolecular Science Division, Electrotechnical Laboratory) for their kind support to collect and isolate optic lobes from live squid. We greatly thank Professors Takuji Takeuchi (University of Tohoku) and David Landowne (University of Miami) for their illuminating discussions and valuable comments.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, C., Matsumoto, G. Sodium channel functioning based on an octagonal structure model. J. Membarin Biol. 147, 45–70 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235397
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235397