Summary
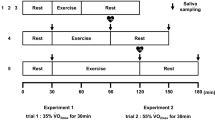
Two experiments were performed to examine salivary immunoglobulin A (s-IgA) responses to varying levels of exercise intensity and duration. For experiment 1, 9 college men (mean age, SD=23.56, 1.64 years) completed treadmill runs of 15, 30, and 45 min at approximately 60% of maximum oxygen consumption (VO2max). For experiment 2, 9 other college men (mean age, SD=23.67, 2.0 years) ran for 20 min at approximately 50, 65 and 80% of VO2max. Unstimulated salivary samples were collected before, and immediately, 1 and 2 h after the exercise. Samples were assayed for s-IgA using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Mean s-IgA levels did not change significantly (P>0.05) at any of the post-exercise collection times when compared to pre-exercise levels. The results of this investigation indicated that running at intensities of 50–80% of VO2max and for durations of 15–45 min did not affect s-IgA levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American College of Sports Medicine (1990) Position stand on the recommended quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness in healthy adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 22:265–274
Douglas DJ, Hanson PG (1978) Upper respiratory infections in the conditioned athlete. Med Sci Sports 10:55
Engvall E (1980) Enzyme immunoassay ELISA and EMIT. Methods Enzymol 70:419–438
Green RL, Kaplan SS, Rabin BS, Stanitski CL, Zdziarski U (1981) Immune function in marathon runners. Ann Allergy 47:73–75
Jemmott III, Borysenko JZ, Borysenko M, McClelland DC, Chapman R, Meyer D, Benson H (1983) Academia stress, power motivation and decrease in secretion rate of salivary immunoglobulin A. Lancet 1:1400–1402
Mackinnon L, Chick T, As A van, Tomasi T (1987) Decreased levels of secretory immunoglobulins following prolonged exercise. Adv Exp Med Biol 216A:869–876
Nieman DC, Johansen LM, Lee JW (1988) Infections episodes in runners before and after the Los Angeles marathon (abstract). Med Sci Sports Exerc 20:542
Peters EM, Bateman ED (1983) Ultramarathon running and upper respiratory tract infections. S Afr Med J 64:582–584
Portz W (1984) Running from infection. Running World 19:78–79
Rossen RD, Butler WT, Waldman RH, Alford RH, Homide RB, Togo Y, Kasel JA (1970)The proteins in nasal secretion. JAMA 211:1157–1161
Solomon GF, Amkraft AA, Kasper P (1974) Immunity, emotions and stress. Ann Clin Res 6:313–322
Tharp GP, Barnes M (1990) Reduction of immunoglobulin-A by swim training. Eur J Appl Physiol 60:61–64
Tomasi T (1969) The concept of local immunity and the secretory system. In: Dayton DH, Small PA, Chanock RM, Kaufman HE, Tomasi TB (eds) The secretory immunologic system. Proceedings on a conference on the secretory immunologic system. U.S. Department of Health, Education and Welfare, Washington, D.C. pp 3–10
Tomasi T (1976) The immune system of secretions. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, pp 6–110
Tomasi T, Trudeau FB, Czerwinski D, Erredge S (1982) Immune parameters in athletes before and after strenuous exercise. J Clin Immunol 2:173–178
Waldeman RH, Small PA, Rowe DS (1969) Utilization of the secretory immunologic system for protection against disease. In: Dayton DH, Small PA, Chanock RM, Kaufman HE, Tomasi TB (eds) The secretory immunologic system. Proceedings on a conference on the secretory immunologic system. U.S. Department of Health, Education and Welfare, Washington, D.C. pp 129–140
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McDowell, S.L., Chaloa, K., Housh, T.J. et al. The effect of exercise intensity and duration on salivary immunoglobulin A. Eur J Appl Physiol 63, 108–111 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235178
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235178