Abstract
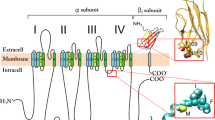
Voltage-sensitive Na channels from nerve and muscle are blocked by the guanidinium toxins tetrodotoxin (TTX) and saxitoxin (STX). Mutagenesis studies of brain RII channels have shown that glutamate 387 (E387) is essential for current block by these toxins. We demonstrate here that mutation of glutamate 403 (E403) of the adult skeletal muscle μI channel (corresponding to E387 of RII) also prevents current blockade by TTX and STX, and by neo-saxitoxin. However, the mutation fails to prevent blockade by the peptide neurotoxins, μ-conotoxin GIIIA and GIIIB; these toxins are thought to bind to the same or overlapping sites with TTX and STX. The E403Q mutation may have utility as a marker for exogenous Na channels in transgenic expression studies, since there are no known native channels with the same pharmacological profile.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnew, W.S. 1984. Voltage-regulated sodium channel molecules. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 46:517–530
Backx, P.H., Yue, D.T., Lawrence, J.H., Marban, E., Tomaselli, G.F. 1992. Molecular localization of an ion-binding site within the pore of mammalian sodium channels. Science 257:248–251
Barchi, R.L. 1985. Molecular characteristics of sodium channels in skeletal muscle. Curr Top. Membr. Transport 33:251–270
Blachly-Dyson, E., Peng, S., Colombini, M., Forte, M. 1990. Selectivity changes in site-directed mutants of the VDAC ion channel: Structural implications. Science 247:1233–1236
Catterall, W.A. 1988. Structure and function of voltage-sensitive ion channels. Science 242:50–61
Colman, A. 1984. Expression of exogenous DNA in Xenopus oocytes. In: Transcription and Translation. A Practical Approach. B.D. James and S.J. Higgins, editors, pp 49–69. IRL, Oxford
Cruz, L.J., Gray, W.R., Olivera, B.M., Zeikus, R.D., Kerr, L., Yoshikami, D., Moczydlowski, E. 1985. Conus geographus toxins that discriminate between neuronal and muscle sodium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 260:9280–9288
Cruz, L.J., Kupryszewski, G., LeCheminant, G.W., Gray, W.R., Olivera, B.M., Rivier, J. 1989. μ-Conotoxin GIIIA, a peptide lig and for muscle sodium channels: Chemical synthesis, radiolabeling, and receptor characterization. Biochemistry 28:3437–3442
Goldstein, S.A.N., Miller, C. 1992. A point mutation in a Shaker K+ channel changes its charybdotoxin binding site from low to high affinity. Biophys. J. 62:5–7
Heginbotham, L., MacKinnon, R. 1992. The aromatic binding site for tetraethylammonium ion on potassium channels. Neuron 8:483–491
Heinemann, S.H. Terlau, H., Stühmer, W.S., Imoto, K., Numa, S. 1992. Calcium channel characteristics conferred on the sodium channel by single mutations. Nature 356:441–443
Imoto, K., Busch, C., Sakmann, B., Mishina, M., Konno, T., Nakai, J., Bujo, H., Mori, Y., Fukuda, K., Numa, S. 1988. Rings of negatively charged amino acids determine the acetylcholine receptor channel conductance. Nature 335:645–648
Kao, C.Y. 1986. Structure-activity relations of tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin, and analogues. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 479:52–67
Lancelin, J.-M., Kohda, D., Tate, S., Yanagawa, Y., Abe, T., Satake, M., Inagaki, F. 1991. Tertiary structure of conotoxin GIIIA in aqueous solution. Biochemistry 30:6908–6916
Miller, C. 1991. 1990: Annus mirabilis of potassium channels. Science 252:1092–1096
Moczydlowski, E., Olivera, B.M., Gray, W.R., Strichartz, G.R. 1986. Discrimination of muscle and neuronal Na-channel subtypes by binding competition between [3H]saxitoxin and μ-conotoxins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:5321–5325
Moczydlowski, E., Uehara, A., Guo, X., Heiny, J. 1986. Isochannels and blocking modes of voltage-dependent sodium channels. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 479:269–292
Moczydlowski, E., Uehara, A., Hall, S. 1986. Blocking pharmacology of batrachotoxin-activated sodium channels. In: Ion Channel Reconstitution. C. Miller, editor, pp. 405–428. Plenum, New York
Noda, M., Suzuki, H., Numa, S., Stühmer, W. 1989. A single point mutation confers tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin insensitivity on the sodium channel II. FEBS Lett. 259:213–216
Ptacek, L.J., George, A.L., Griggs, R.C., Tawil, R., Kallen, R.G., Barchi, R.L., Robertson, M., Leppert, M.F. 1991. Identification of a mutation in the gene causing hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Cell 67:1021–1027
Pusch, M., Noda, M., Stühmer, W., Numa, S., Conti, F. 1991. Single point mutations of the sodium channel drastically reduce the pore permeability without preventing its gating. Eur. Biophys. J. 20:127–133
Rojas, C.V., Wang, J., Schwartz, L.S., Hoffman, E.P., Powell, B.R., Brown, R.H., Jr. 1991. A Met-to-Val mutation in the skeletal muscle Na+ channel α-subunit in hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Nature 354:387–389
Sarkar, G., Sommer, S.S. 1990. The “megaprimer” method of sitedirected mutagenesis. BioTechniques 8:404–407
Satin, J., Kyle, J.W., Chen, M., Bell, P., Cribbs, L.L., Fozzard, H.A., Rogart, R.B. 1992. A mutant of TTX-resistant cardiac sodium channels with TTX-sensitive properties. Science 256:1202–1205
Sato, K., Ishida, Y., Wakamatsu, K., R., Honda, H., Ohizumi, Y., Nakamura, H., Ohya, M., Lancelin, J.-M., Kohda, D., Inagaki, F. 1991. Active site of μ-conotoxin GIIIA, a peptide blocker of muscle sodium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 266:16989–16991
Schild, L., Moczydlowski, E. 1991. Competitive binding interaction between Zn2+ and saxitoxin in cardiac Na+ channels. Evidence for a sulfhydryl group in the Zn2+/saxitoxin binding site. Biophys. J. 59:523–537
Sigworth, F.J., Spalding, B.C. 1980. Chemical modification reduces the conductance of sodium channels in nerve. Nature 283:293–295
Spalding, B.C. 1980. Properties of toxin resistant sodium channels produced by chemical modification in frog skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 305:485–500
Stephan, M.M., Agnew, W.S. 1991. Voltage-sensitive Na+ channels: motifs, modes and modulation. Curr. Opinion in Cell Biol. 3:676–684
Stühmer, W., Methfessel, C., Sakmann, B., Noda, M., Numa, S. 1987. Patch clamp characterization of sodium channels expressed from rat brain cDNA. Eur. Biophys. J. 14:131–138
Terlau, H., Heinemann, S.H., Stühmer, W., Pusch, M., Conti, F., Imoto, K., Numa, S. 1991. Mapping the site of block by tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin of sodium channel II. FEBS Lett. 293:93–96
Trimmer, J.S., Agnew, W.S. 1989. Molecular diversity of voltage-sensitive Na channels. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 51:401–418
Trimmer, J.S., Cooperman, S.S., Tomiko, S.A., Zhou, J., Crean, S.M., Boyle, M.B., Kallen, R.G., Sheng, Z., Barchi, R.L., Sigworth, F.J., Goodman, R.H., Agnew, W.S., Mandel, G. 1989. Primary structure and functional expression of a mammalian skeletal muscle sodium channel. Neuron 3:33–49
Ukomadu, C., Zhou, J., Sigworth, F.J., Agnew, W.S. 1992. μI Na+ channels expressed transiently in human embryonic kidney cells: biochemical and biophysical properties. Neuron 8:663–676
Ulbricht, W., Wagner, H.-H., Schmidtmayer, J. 1986. Kinetics of TTX-STX block of sodium channels. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 479:68–83
Zhou, J., Potts, J.F., Trimmer, J.S., Agnew, W.S., Sigworth, F.J. 1991. Multiple gating modes and the effect of modulating factors on the μI sodium channel. Neuron 7:775–785
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stephan, M.M., Potts, J.F. & Agnew, W.S. The μI skeletal muscle sodium channel: Mutation E403Q eliminates sensitivity to tetrodotoxin but not to μ-conotoxins GIIIA and GIIIB. J. Membarin Biol. 137, 1–8 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234993
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234993