Summary
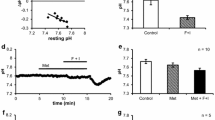
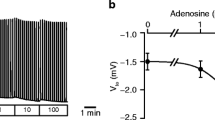
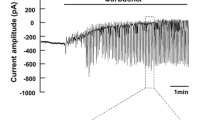
The regulation of intracellular pH (pH i ) in rat sublingual mucous acini was monitored using dual-wavelength microfluorometry of the pH-sensitive dye BCECF (2′,7′-biscarboxyethyl-5(6)-carboxyfluorescein). Acini attached to coverslips and continuously superfused with HCO −3 -containing medium (25 mm NaHCO3/5% CO2; pH 7.4) have a steady-state pH i of 7.25±0.02. Acid loading of acinar cells using the NH +4 /NH3 prepulse technique resulted in a Na+-dependent, MIBA-inhibitable (5-(N-methyl-N-isobutyl) amiloride, K i ∼ 0.42 μm) pH i recovery, the kinetics of which were not influenced by the absence of extracellular Cl−. The rate and magnitude of the pH i recovery were dependent on the extracellular Na+ concentration, indicating that Na+/H+ exchange plays a critical role in maintaining pH i above the pH predicted for electrochemical equilibrium. When the NH +4 /NH3 concentration was varied, the rate of pH i recovery was enhanced as the extent of the intracellular acidification increased, demonstrating that the activity of the Na+/H+ exchanger is regulated by the concentration of intracellular protons. Switching BCECF-loaded acini to a Cl−-free medium did not significantly alter resting pH i , suggesting the absence of Cl−/HCO −3 exchange activity. Muscarinic stimulation resulted in a rapid and sustained cytosolic acidification (t1/2 < 30 sec; 0.16 ± 0.02 pH unit), the magnitude of which was amplified greater than two-fold in the presence of MIBA (0.37±0.05 pH unit) or in the absence of extracellular Na+ (0.34±0.03 pH unit). The agonist-induced intracellular acidification was blunted in HCO −3 -free media and was inhibited by DPC (diphenylamine-2-carboxylate), an anion channel blocker. In contrast, the acidification was not influenced by removal of extracellular Cl−. The Ca2+ ionophore, ionomycin, mimicked the effects of stimulation, whereas preloading acini with BAPTA (bis-(o-aminophenoxy)-ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid) to chelate intracellular Ca2+ blocked the agonist-induced cytoplasmic acidification. The above results indicate that during muscarinic stimulation an intracellular acidification occurs which: (i) is partially buffered by increased Na+/H+ exchange activity; (ii) is most likely mediated by HCO −3 efflux via an anion channel; and (iii) requires an increase in cytosolic free [Ca2+].
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambudkar, I.S., Melvin, J.E., Baum, B.J. 1988. α1,-Adrenergic regulation of Cl− and Ca2+ movements in rat parotid acinar cells. Pfluegers Arch. 412:75–79
Aronson, P.S. 1985. Kinetic properties of the plasma membrane Na+-H+ exchanger. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 47:545–560
Boron, W.F. 1986. Intracellular pH regulation in epithelial cells. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 48:377–388
Boyarsky, G., Ganz, M.B., Sterzel, R.B., Boron, W.F. 1988. pH regulation in single glomerular mesangial cells. II. Na+-dependent and -independent Cl−-HCO −3 exchangers. Am. J. Physiol. 255:C857-C869
Cook, D.I., Day, M.L., Champion, M.P., Young, J.A. 1988. Ca2+ not cyclic AMP mediates the fluid secretory response to isoproterenol in the rat mandibular salivary gland: Whole-cell patch-clamp studies. Pfluegers Arch. 413:67–76
Cragoe, E.J., Jr., Woltersdorf, O.W., Jr., Bicking, J.B., Kwong, S.F., Jones, J.H. 1967. Pyrazine diuretics II. N-amidino-3-amino-5-substituted 6-halopyrazinecarboxyamides. J. Med. Chem. 10:66–75
Dissing, S., Nauntofte, B. 1990. Na+ transport properties of isolated parotid acini. Am. J. Physiol. 259:G1044-G1055
Foskett, J.K. 1990. [Ca2+] i modulation of Cl− content controls cell volume in single salivary acinar cells during fluid secretion. Am. J. Physiol. 259:C998-C1004
Foskett, J.K., Gunter-Smith, P.J., Melvin, J.E., Turner, R.J. 1989. Physiological localization of an agonist-sensitive pool of Ca2+ in parotid acinar cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:167–171
Foskett, J.K., Melvin, J.E. 1989. Activation of salivary secretion: Coupling of cell volume and [Ca2+]i in single cells. Science 244:1582–1585
Geibel, J., Giebisch, G., Boron, W.F. 1990. Angiotensin II stimulates both Na+-H+ exchange and Na+/HCO −3 cotransport in the rabbit proximal tubule. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:7917–7920
Grinstein, S., Rothstein, A. 1986. Mechanisms of regulation of the Na+/H+ exchanger. J. Membrane Biol. 90:1–12
Hart, D., Nord, E.P. 1991. Polarized distribution of Na+/H+ antiport and Na+/HCO −3 cotransport in primary cultures of renal inner medullary collecting duct cells. J. Biol. Chem. 266:2374–2382
Iwatsuki, N., Maruyama, Y., Matsumoto, O., Nishiyama, A. 1985. Activation of Ca2+-dependent Cl− and K+ conductances in rat and mouse parotid acinar cells. Jpn. J. Physiol. 35:933–944
Jentsch, T.J., Schwartz, P., Schill, B.S., Langner, B., Lepple, A.P., Keller, S.K., Wiederholt, M. 1986. Kinetic properties of the sodium bicarbonate (carbonate) symport in monkey kidney epithelial cells (BSC-1). J. Biol. Chem. 261:10673–10679
Kleyman, T.R., Cragoe, E.J., Jr. 1988. Amiloride and its analogs as tools in the study of ion transport. J. Membrane Biol. 105:1–21
Kopito, R.R. 1990. Molecular biology of the anion exchanger gene family. Int. Rev. Cytol. 123:177–199
Lau, K.R., Elliot, A.C., Brown, P.D. 1989. Acetylcholine-induced intracellular acidosis in rabbit salivary gland acinar cells. Am. J. Physiol. 256:C288-C295
Lee, S.I., Turner, R.J. 1991. Mechanisms of secretagogue-induced HCO −3 and Cl− loss from rat parotid acini. Am. J. Physiol. 261:G111-G118
Manganel, M., Turner, R.J. 1989. Agonist-induced activation of Na+/H+ exchange in rat parotid acinar cells. J. Membrane Biol. 111:191–198
Manganel, M., Turner, R.J. 1990. Agonist-induced activation of Na+/H+ exchange in rat parotid acinar cells is dependent on calcium but not on protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 265:4284–4289
Manganel, M., Turner, R.J. 1991. Rapid secretagogue-induced activation of Na+/H+ exchange in rat parotid acinar cells. J. Biol. Chem. 266:10182–10189
Martinez, J.R., Cassity, N. 1986. 36Cl fluxes in dispersed rat submandibular acini: Effects of Ca2+ emission and of the ionophore A23187. Pfluegers Arch. 407:615–619
Maruyama, Y., Gallacher, D.V., Peterson, O.H. 1983. Voltage and Ca2+ activated K+ channel in basolateral acinar cell membranes of mammalian salivary glands. Nature 302:827–829
Melvin, J.E., Kawaguchi, M., Baum, B.J., Turner, R.J. 1987. A muscarinic agonist-stimulated chloride efflux pathway is associated with fluid secretion in rat parotid acinar cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 145:754–759
Melvin, J.E., Koek, L., Zhang, G.H. 1991. A capacitative Ca2+ influx is required for sustained fluid secretion in sublingual mucous acini. Am. J. Physiol. 261:G1043-G1050
Melvin, J.E., Moran, A., Turner, R.J. 1988. The role of HCO −3 and Na+/H+ exchange in the response of rat parotid acinar cells to muscarinic stimulation. J. Biol. Chem. 263:19564–19569
Melvin, J.E., Turner, R.J. 1992. Cl− fluxes related to fluid secretion by rat parotid: Involvement of Cl−/HCO3-exchange. Am. J. Physiol. 262:G393-G398
Merritt, J.E., Rink, T.J. 1987. Regulation of cytosolic free calcium in fura-2 loaded rat parotid acinar cells. J. Biol. Chem. 262:17362–17369
Moolenaar, W.H. 1986. Effects of growth factors on intracellular pH regulation. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 48:363–376
Nauntofte, B., Dissing, S. 1987. Stimulation induced changes in cytosolic calcium in rat parotid acini. Am. J. Physiol. 253:G290-G297
Nauntofte, B., Dissing, S. 1988. K+ transport and membrane potentials in isolated rat parotid acini. Am. J. Physiol. 255:C508-C518
Nauntofte, B., Poulsen, J.H. 1986. Effects of Ca2+ and furosemide on Cl−, transport and O2 uptake in parotid acini. Am. J. Physiol. 251:C175-C185
Novak, I., Young, J.A. 1986. Two independent anion transport systems in rabbit mandibular salivary glands. Pfluegers Arch. 407:649–656
Petersen, O.H., Gallacher, D.V. 1988. Electrophysiology of pancreatic and salivary acinar cells. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 50:65–80
Pirani, D., Evans, A.R., Cook, D.I., Young, J.A. 1987. Intracellular pH in rat mandibular salivary gland: The role of Na-H and Cl-HCO3 antiports in secretion. Pfluegers Arch. 408:178–184
Putney, J.W., Jr. 1976. Biphasic modulation of potassium release in rat parotid gland by carbachol and phenylephrine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 198:375–384
Reinertsen, K.V., Tonnessen, T.I., Jacobsen, J., Sandvig, K., Olsnes, S. 1988. Role of chloride/bicarbonate antiport in the control of cytosolic pH. J. Biol. Chem. 263:11117–11125
Roos, A., Boron, W.F. 1981. Intracellular pH. Physiol. Rev. 61:296–434
Sardet, C., Franchi, A., Pouyssegur, J. 1989. Molecular cloning, primary structure, and expression of the human growth factor-activatable Na+/H+ antiporter. Cell 56:271–280
Silva, P.J., Staff, J., Field, J., Fine, L., Forrest, J.N., Epstein, F.H. 1977. Mechanism of active chloride secretion by shark rectal gland: Role of Na+, K+ ATPase in chloride transport. Am. J. Physiol. 233:F298-F306
Soltoff, S.P., McMillian, M.K., Cantley, L.C., Cragoe, E.J., Jr., Talamo, B.R. 1989. The effects of muscarinic, alpha-adrenergic, and substance P agonists and ionomycin on ion transport mechanisms in the rat parotid acinar cell. J. Gen. Physiol. 93:285–319
Star, R.A., Burg, M.B., Knepper, M.A. 1985. Bicarbonate secretion and chloride absorption by rabbit cortical collecting ducts. J. Clin. Invest. 76:1123–1130
Stewart, M.C., Seo, Y., Case, M.R. 1989. Intracellular pH during secretion in the perfused rabbit mandibular salivary gland measured by 31P NMR spectroscopy. Pfluegers Arch. 414:200–207
Thomas, J.A., Buchsbaum, R.N., Zimniak, A., Racker, E. 1979. Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ. Biochemistry 18:2210–2218
Townsley, M.C., Machen, T.E. 1989. Na-HCO3 cotransport in rabbit parietal cells. Am. J. Physiol. 257:G350-G356
Turner, R.J. 1992. Ion transport related to fluid secretion in salivary glands. In: The Biology of the Salivary glands. K. Vergona, editor. Telford, Caldwell (NJ) (in press)
Turner, R.J., George, J.N. 1988. Cl−-HCO −3 exchange is present with Na+-K+-Cl− cotransport in rabbit parotid acinar basolateral membrane. Am. J. Physiol. 254:C391–396
Turner, R.J., George, J.N., Baum, B.J. 1986. Evidence for a Na+/K+/Cl− cotransport system in basolateral membrane vesicles from rabbit parotid. J. Membrane Biol. 94:143–152
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors would like to thank Drs. P.A. Knauf and L.A. Tabak for their helpful comments during the preparation of this manuscript and L. Koek for technical assistance. This work was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health, R01 DE08921 and P50 DE07003 (JEM).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G.H., Cragoe, E.J. & Melvin, J.E. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH in rat sublingual mucous acini at rest and during muscarinic stimulation. J. Membarin Biol. 129, 311–321 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232912
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232912