Conclusions
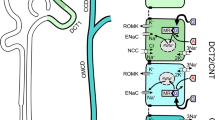
The model for the adrenal steroid action on Na transport in tight epithelia as depicted in Fig. 3A and B dissociates two phases: an early phase during which the pre-existing Na transport machinery is activated and a late phase during which the transport capacity of the machinery is increased. These two sequential phases have been distinguished based on differences in functional aspects of the induced transport, on selective effects of agents interfering with transcriptional regulation and on a correlation of the late response phase with an increase in transport protein synthesis and expression [26, 45, 46, 98, 99, 124]. These observations suggest that a bimodal stimulation of Na transport could involve two different gene networks which are directly (in the physiological meaning) and independently stimulated by the action of the hormone-receptor complex and the following “molecular” cascades (see section Molecular and Physiological Cascades). The relatively clear temporal dissociation of the responses found in experimental situations is probably the consequence of inherent properties of the two networks. Indeed, to generate rapid functional changes, the genes involved in the early response must encode products which have relatively short half-lifes at the mRNA and protein levels. In contrast, the constitutive elements of the Na transport machinery that are increased during the late phase of adrenal steroid action have, as shown for the Na,K-ATPase [82], relatively long half-lifes. Consequently, even though changes in transcription may take place early in the course of the hormonal treatment, they impact on protein synthesis and pools only slowly and after a substantial lag period.
On the one hand, ongoing research will soon provide more information on the nature, time course and hormone/receptor specificity of adrenal-steroid-regulated genes. On the other hand, the availability of new technical and molecular tools to study the proteins of the Na transport machinery greatly increases the possibilities for studying its regulation by adrenal steroids. Consequently, it will be a fascinating challenge to relate the data emerging from both approaches, and it appears that only a combination of methods and tools will allow to progressively fill the gap of understanding which still lies between the transcriptional effects and the transport regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, A.J., Danielsen, M., Robins, D.M. 1992. Androgen-specific gene activation via a consensus glucocorticoid response element is determined by interaction with nonreceptor factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:11660–11663
Allan, G.F., Tsai, S.Y., Tsai, M.J., Omalley, B.W. 1992. Ligand-dependent conformational changes in the progesterone receptor are necessary for events that follow DNA binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:11750–11754
Arriza, J.L., Simerly, R.B., Swanson, L.W., Evans, R.M. 1988. The neuronal mineralocorticoid receptor as a mediator of glucocorticoid response. Neuron 1:887–900
Asher, C., Eren, R., Kahn, L., Yeger, O., Garty, H. 1992. Expression of the amiloride-blockable Na+ channel by RNA from control versus aldosterone-stimulated tissue. J. Biol. Chem. 267:16061–16065
Asher, C., Garty, H. 1988. Aldosterone increases the apical Na+ permeability of toad bladder by two different mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:7413–7417
Asher, C., Singer, D., Eren, R., Yeger, O., Dascal, N., Garty, H. 1992. NaCl-dependent expression of amiloride-blockable Na+ channel in Xenopus oocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 262:G244-G298
Barlet-Bas, C., Cheval, L., Feraille, E., Marsy, S., Doucet, A. 1991. Regulation of tubular Na-K-ATPase. In: Nephrology. M. Hatano, editor. pp. 419–434. Springer-Verlag, Tokyo
Barlet-Bas, C., Khadoury, C., Marsy, S., Doucet, A. 1988. Sodium-independent in vitro induction of Na+,K+-ATPase by aldosterone in renal target cells: Permissive effect of triiodothyronine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:1707–1711
Bastl, C.P., Hayslett, J.P. 1992. The cellular action of aldosterone in target epithelia. Kidney Int. 42:250–264
Bastl, C.P., Schulman, G., Cragoe, E.J. 1992. Glucocorticoids inhibit colonic aldosterone-induced conductive Na+ absorption in adrenalectomized rat. Am. J. Physiol. 263:F443-F452
Baumann, H., Paulsen, K., Kovacs, H., Berglund, H., Wright, A.P.H., Gustafsson, J.A., Hard, T. 1993. Refined solution structure of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain. Biochemistry 32:13463–13471
Beekman, J.M., Allan, G.F., Tsai, S.Y., Tsai, M.J., O'Malley, B.W. 1993. Transcriptional activation by the estrogen receptor requires a conformational change in the ligand binding domain. Mol. Endocrinol. 7:1266–1274
Benos, D.J., Saccomani, G., Brenner, B.M., Sariban-Sohraby, S. 1986. Purification and characterization of the amiloride-sensitive sodium channel from A6 cultured cells and bovine renal papilla. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:8525–8529
Beron, J., Verrey, F. 1994. Aldosterone induces early activation and late accumulation of Na,K-ATPase at surface of A6 cells. Am. J. Physiol. 266:C1728-C1290
Blazer-Yost, B.L., Fesseha, Y., Cox, M. 1992. Aldosterone-mediated Na+ transport in renal epithelia—Time-course of induction of a potential regulatory component of the conductive Na+ channel. Biochem. Int. 26:887–897
Bocquel, M.T., Kumar, V., Stricker, C., Chambon, P., Gronenmeyer, H. 1989. The contribution of the N- and C-terminal regions of steroid receptors to activation of the transcription is both receptor and cell specific. Nucl. Acids Res. 17:2581–2595
Bourgeois, S., Gruol, D.J., Newby, R.F., Rajah, F.M. 1993. Expression of an MDR gene is associated with a new form of resistance to dexamethasone-induced apoptosis. Mol. Endocrinol. 7:840–851
Bowen, J.D., McDonough, A.A. 1987. Pretranslational regulation of Na+-K+-ATPase in cultured canine kidney cells by low K. Am. J. Physiol. 252:C179-C189
Brem, A.S., Morris, D.J. 1993. Interactions between glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids in the regulation of renal electrolyte transport. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 97:C1-C5
Broillet, M.C., Berger, A., Horisberger, J.D. 1993. Early effect of aldosterone on the basolateral potassium conductance of A6 cells. Pfluegers Arch. 424:91–93
Burns, K., Duggan, B., Atkinson, E.A., Famulski, K.S., Nemer, M., Bleackley, R.C., Michalak, M. 1994. Modulation of gene expression by calreticulin binding to the glucocorticoid receptor. Nature 367:476–480
Canessa, C.M., Horisberger, J.D., Rossier, B.C. 1993. Epithelial sodium channel related to proteins involved in neurodegeneration. Nature 361:467–470
Canessa, C.M., Schild, L., Buell, G., Thorens, B., Gautschi, I., Horisberger, J.D., Rossier, B.C. 1994. Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits. Nature 367:463–467
Chuard, F., Durand, J. 1992. Coupling between the intracellular pH and the active transport of sodium in an epithelial cell line from Xenopus laevis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 102:7–14
Clore, J., Schoolwerth, A., Watlington, C.O. 1992. When is cortisol a mineralocorticoid. Kidney Int. 42:1297–1308
Coupaye-Gerard, B., Kim, H.J., Singh, A., Blazer-Yost, B.L. 1994. Differential effects of brefeldin-a on hormonally regulated Na+ transport in a model renal epithelial cell line. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Biomembr. 1190:449–456
Dahlman-Wright, K., Almlof, T., McEwan, I.J., Gustafsson, J.A., Wright, A.P.H. 1994. Delineation of a small region within the major transactivation domain of the human glucocorticoid receptor that mediates transactivation of gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:1619–1623
Dauvois, S., White, R., Parker, M.G. 1993. The antiestrogen ICI 182780 disrupts estrogen receptor nucleocytoplasmic shuttling. J. Cell Sci. 106:1377–1388
Dedhar, S., Rennie, P.S., Shago, M., Hagesteijn, C.Y.L., Yang, H.L., Filmus, J., Hawley, R.G., Bruchovsky, N., Cheng, H., Matusik, R.J., Giguere, V. 1994. Inhibition of nuclear hormone receptor activity by calreticulin. Nature 367:480–483
DeKloet, E.R., Sutanto, W., Vandenberg, D.T.W.M., Carey, M.P., Vanhaarst, A.D., Hornsby, C.D., Meijer, O.C., Rots, N.Y., Oitzl, M.S. 1993. Brain mineralocorticoid receptor diversity-functional implications. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 47:183–190
Denault, D., Rusvai, E., Chen, W.R., Fejes-Tóth, G., Náray-Fejes-Tóth, A. 1993. Aldosterone-induced proteins and mRNAs in cortical collecting duct (CCD) cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 4:437 (Abstr.)
Djouadi, F., Wijkhuisen, A., Bastin, J. 1992. Coordinate development of oxidative enzymes and Na-K-ATPase in thick ascending limb—role of corticosteroids. Am. J. Physiol. 263:F237-F242
Doucet, A., Barlet-Bas, C. 1989. Involvement of Na+,K+-ATPase in antinatriuretic action of mineralocorticoids in mammalian kidney. Curr. Top. Membr. Transp. 34:185–208
Duncan, R.L., Grogan, W.M., Kramer, L.B., Watlington, C.O. 1988. Corticosterone's metabolite is an agonist for Na+ transport stimulation in A6 cells. Am. J. Physiol. 255:F736-F748
Edelman, I.S., Bogoroch, R., Porter, G.A. 1963. On the mechanism of action of aldosterone on sodium transport: the role of protein synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 50:1169–1177
ElMernissi, G., Barlet-Bas, C., Khadouri, C., Cheval, L., Marsy, S., Doucet, A. 1993. Short-term effect of aldosterone on vasopressin-sensitive adenylate cyclase in rat collecting tubule. Am. J. Physiol. 264:F821-F826
Evans, R.M. 1988. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science 240:889–895
Falvey, E., Schibler, U. 1991. How are the regulators regulated? FASEB J. 5:309–314
Farman, N., Bonvalet, J.P., Seckl, J.R. 1994. Aldosterone selectively increases Na+-K+-ATPase alpha(3)-subunit mRNA expression in rat hippocampus. Am. J. Physiol. 266:C423-C428
Fromm, M., Schulzke, J.D., Hegel, U. 1993. Control of electrogenic Na+ absorption in rat late distal colon by nanomolar aldosterone added in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. 264:E68-E73
Fujii, Y., Takemoto, F., Katz, A.I. 1990. Early effects of aldosterone on Na-K pump in rat cortical collecting tubules. Am. J. Physiol. 259:F40-F45
Funder, J.W. 1993. Aldosterone action. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 55:115–130
Funder, J.W. 1993. Mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, receptors and response elements. Science 259:1132–1133
Gaeggeler, H.P., Duperrex, H., Hautier, S., Rossier, B.C. 1993. Corticosterone induces 11beta-HSD and mineralocorticoid specificity in an amphibian urinary bladder cell line. Am. J. Physiol. 264:C317-C322
Garty, H. 1986. Mechanism of aldosterone action in tight epithelia. J. Membrane Biol. 90:193–205
Garty, H. 1994. Molecular properties of epithelial, amilorideblockable Na+ channels. FASEB J. 8:522–528
Garty, H., Edelman, I.S. 1983. Amiloride-sensitive trypsinisation of apical sodium channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 81:785–803
Garty, H., Peterson-Yantorno, K., Asher, C., Civan, M.M. 1994. Effects of corticoid agonists and antagonists on apical Na+ permeability of toad urinary bladder. Am. J. Physiol. 266:F108-F116
Geering, K., Claire, M., Gaeggeler, H.P., Rossier, B.C. 1985. Receptor occupancy vs. induction of Na+-K+-ATPase and Na+ transport by aldosterone. Am. J. Physiol. 248:C102-C108
Geering, K., Gaeggeler, H.P., Rossier, B.C. 1984. Effects of thyromimetic drugs on aldosterone-dependent sodium transport in the toad bladder. J. Membrane Biol. 77:15–23
Geering, K., Girardet, M., Bron, C., Kraehenbuhl, J.P., Rossier, B.C. 1982. Hormonal regulation of (Na+,K+)-ATPase biosynthesis in the toad bladder. J. Biol. Chem. 257:10388–10343
Guiochon-Mantel, A., Milgrom, E. 1993. Cytoplasmic nuclear trafficking of steroid hormone receptors. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 4:322–328
Guyton, A.C. 1991. Blood pressure control—special role of the kidneys and body fluids. Science 252:1813–1816
Halm, D.R., Troutman-Halm, S. 1994. Aldosterone stimulates K secretion prior to onset of Na absorption in guinea pig distal colon. Am. J. Physiol. 266:C552-C558
Harvey, B.J., Thomas, S.R., Ehrenfeld, J. 1988. Intracellular pH controls cell membrane Na+ and K+ conductances and transport in frog skin epithelium. J. Gen. Physiol. 92:767–791
Hinton, C.F., Eaton, D.C. 1989. Expression of amilorideblockable sodium channels in Xenopus oocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 257:C825-C829
Horisberger, J.D. 1992. Early effects of aldosterone on apical and basolateral membrane conductances of TBM cells. Am. J. Physiol. 263:C384-C388
Hsu, S.C., Qi, M., Defranco, D.B. 1992. Cell cycle regulation of glucocorticoid receptor function. EMBO J. 11:3457–3468
Hutchison, K.A., Dittmar, K.D., Czar, M.J., Pratt, W.B. 1994. Proof that hsp70 is required for assembly of the glucocorticoid receptor into a heterocomplex with hsp90. J. Biol. Chem. 269:5043–5049
Inoue, S., Orimo, A., Hosoi, T., Kondo, S., Toyoshima, H., Kondo, T., Ikegami, A., Ouchi, Y., Orimo, H., Muramatsu, M. 1993. Genomic binding-site cloning reveals an estrogen-responsive gene that encodes a RING finger protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:11117–11121
Ivarie, R.D., Baxter, J.D., Morris, J.A. 1981. Interaction of thyroid and glucocorticoid hormones in rat pituitary tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 256:4520–4528
Johnson, J.P. 1992. Cellular mechanisms of action of mineralocorticoid hormones. Pharmacol. Ther. 53:1–29
Jorkasky, D., Cox, M., Feldman, G.M. 1985. Differential effects of corticosteroids on Na+ transport in rat distal colon in vitro. A. J. Physiol. 248:G424-G431
Kaissling, B., Le Hir, M. 1991. Aldosterone: influence on distal tubule cell structure. In: Aldosterone: Fundamental Aspects, Colloque INSERM Vol 215. J.-P. Bonvalet, N. Farman, M. Lombès, and M.E. Rafestin-Oblin, editors. pp. 175–185. John Libbey Eurotext, Paris
Kang, K.I., Devin, J., Cadepond, F., Jibard, N., Guiochonmantel, A., Baulieu, E.E., Catelli, M.G. 1994. In vivo functional protein protein interaction-nuclear targeted hsp90 shifts cytoplasmic steroid receptor mutants into the nucleus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:340–344
Kemendy, A.E., Kleyman, T.R., Eaton, D.C. 1992. Aldosterone alters the open probability of amiloride-blockable sodium channels in A6 epithelia. Am. J. Physiol. 263:C825-C837
Kenouch, S., AlFaidy, N., Bonvalet, J.P., Farman, N. 1994. Expression of 11 beta-OHSD along the nephron of mammals and humans. Steroids 59:100–104
Lanz, R.B., Hug, M, Gola, M., Tallone, T., Wieland, S., Rusconi, S. 1994. Active, interactive, and inactive steroid receptor mutants. Steroids 59:148–152
Laplace, J.R., Husted, R.F., Stokes, J.B. 1992. Cellular responses to steroids in the enhancement of Na+ transport by rat collecting duct cells in culture-differences between glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid hormones. J. Clin. Invest. 90:1370–1378
Legoff, P., Montano, M.R., Schodin, D.J., Katzenellenbogen, B.S. 1994. Phosphorylation of the human estrogen receptor—identification of hormone-regulated sites and examination of their influence on transcriptional activity. J. Biol. Chem. 269:4458–4466
Liang, P., Pardee, A.B. 1992. Differential display of eukariotic messenger RNA by means of the polymerase chain reaction. Science 257:967–971
Lombés, M., Oblin, M.E., Gasc, J.M., Baulieu, E.E., Farman, N., Bonvalet, J.P. 1992. Immunohistochemical and biochemical evidence for a cardiovascular mineralocorticoid receptor. Circ. Res. 71:503–510
Luisi, B.F., Xu, W.X., Otwinowski, Z., Freedman, L.P., Yamamoto, K.R., Sigler, P.B. 1991. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature 352:497–505
Marunaka, Y., Eaton, D.C. 1991. Effects of vasopressin and cAMP on single amiloride-blockable Na channels. Am. J. Physiol. 260:C1071-C1084
Marver, D., Stewart, J., Funder, J., Feldman, D., Edelman, I.S. 1974. Renal aldosterone receptors: studies with [3H]aldosterone and the antimineralocorticoid [3H]spironolactone (SC-26304). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 71:1431–1435
Meyer, M.E., Pornon, A.J., Ji, J., Bocquel, M.T., Chambon, P., Gronemeyer, H. 1990. Agonistic and antagonistic activities of RU486 on the functions of the human progesterone receptor. EMBO J. 9:3923–3932
Morris, D.J., Souness, G.W. 1992. Protective and specificity-conferring mechanisms of mineralocorticoid action. Am. J. Physiol. 263:F759-F768
Muchardt, C., Yaniv, M. 1993. A human homologue of saccharomyces-cerevisiae SNF2/SWI2 and drosophila-brm genes potentiates transcriptional activation by the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 12:4279–4290
Náray-Fejes-Tóth, A., Fejes-Tóth, G. 1990. Glucocorticoid receptors mediate mineralocorticoid-like effects in cultured collecting duct cells. Am. J. Physiol. 259:F672-F678
Náray-Fejes-Tóth, A., Rusvai, E., Fejes-Tóth, G. 1994. Mineralocorticoid receptors and 11 beta-steroid dehydrogenase activity in renal principal and intercalated cells. Am. J. Physiol. 266:F76-F80
Oberleithner, H., Vogel, U., Kersting, U., Steigner, W. 1990. Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. II. Aldosterone stimulates Na+/H+ and Cl−/HCO −3 exchange. Pfluegers Arch. 416:533–539
O'Neil, R.G. 1989. Modulation of Na+,K+-ATPase expression in renal collecting duct. Curr. Top. Membr. Transp. 34:209–228
Paccolat, M.P., Geering, K., Gaeggeler, H.P., Rossier, B.C. 1987. Aldosterone regulation of Na+ transport and Na+-K+-ATPase in A6 cells: role of growth conditions. Am. J. Physiol. 252:C468-C476
Palmer, L.G. 1992. Epithelial Na channels—Function and diversity. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 43:51–66
Palmer, L.G., Antonian, L., Frindt, G. 1993. Regulation of the Na-K pump of the rat cortical collecting tubule by aldosterone. J. Gen. Physiol. 102:43–57
Palmer, L.G., Corthesy-Theulaz, I., Gaeggeler, H.P., Kraehenbuhl, J.P., Rossier, B.C. 1990. Expression of epithelial Na channels in Xenopus oocytes. J. Gen. Physiol. 96:23–46
Palmer, L.G., Edelman, I.S. 1981. Control of apical sodium permeability in the toad urinary bladder by aldosterone. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 372:1–14
Pácha, J., Frindt, G., Antonian, L., Silver, R.B., Palmer, L.G. 1993. Regulation of Na channels of the rat cortical collecting tubule by aldosterone. J. Gen. Physiol. 102:25–42
Pearce, D., Yamamoto, K.R. 1993. Mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptor activities distinguished by nonreceptor factors at a composite response element. Science 259:1161–1165
Pellanda, A.M., Gaeggeler, H.P., Horisberger, J.D., Rossier, B.C. 1992. Sodium-independent effect of aldosterone on initial rate of ouabain binding in A6 cells. Am. J. Physiol. 262:C899-C906
Petzel, D., Ganz, M.B., Nestler, E.J., Lewis, J.J., Goldenring, J., Akcicek, F., Hayslett, J.P. 1992. Correlates of aldosterone-induced increases in Ca- (2+)i and Isc suggest that Ca- (2+)i is the second messenger for stimulation of apical membrane conductance. J. Clin. Invest. 89:150–156
Power, R.F., Mani, S.K., Codina, J., Conneely, O.M., Omalley, B.W. 1991. Dopaminergic and ligand-independent activation of steroid hormone receptors. Science 254:1636–1639
Pratt, W.B. 1993. The role of heat shock proteins in regulating the function, folding, and trafficking of the glucocorticoid receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 268:21455–21458
Rafestin-Oblin, M.E., Lombés, M., Couette, B., Baulieu, E.E. 1992. Difference between aldosterone and its antagonists in binding kinetics and ligand-induced hsp90 release from mineralocorticosteroid receptor. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 41:815–821
Ray, A., Prefontaine, K.E. 1994. Physical association and functional antagonism between the p65 subunit of transcription factor NF-kappa B and the glucocorticoid receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:752–756
Rayson, B.M. 1991. [Ca2+]i regulates transcription rate of the Na+/K+-ATPase-alphal subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 266:21335–21338
Rokaw, M.D., Palevsky, P.M., Johnson, J.P. 1993. Aldosterone (aldo) stimulates protein lipidation and G-protein (GP) synthesis in A6 cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 4:446 (Abstr.)
Rossier, B.C., Canessa, C.M., Schild, L., Horisberger, J.D. 1994. Epithelial sodium channels. Curr. Opinion Nephrol. Hypertension 3:487–496
Rossier, B.C., Paccolat, M.-P., Verrey, F., Kraehenbuhl, J.P., Geering, K. 1985. Mechanism of action of aldosterone: A pleiotropic response. In: Hormones and Cell Regulation Vol. 9, J.E. Dumont, B. Hamprecht and J. Nunez, editors. pp. 209–225. INSERM, Paris
Rossier, B.C., Palmer, L.G. 1992. Mechanisms of aldosterone action on sodium and potassium transport. In: The Kidney: Physiology and Pathophysiology (2nd ed.). D.W. Seidin and G. Giebisch, editors. pp. 1373–1405. Raven, New York
Rupprecht, R., Arriza, J.L., Spengler, D., Reul, J.M.H.M., Evans, R.M., Holsboer, F., Damm, K. 1993. Transactivation and synergistic properties of the mineralocorticoid receptor—relationship to the glucocorticoid receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 7:597–603
Rupprecht, R., Reul, J.M.H.M., Vansteensel, B., Spengler, D., Soder, M., Berning, B., Holsboer, F., Damm, K. 1993. Pharmacological and functional characterization of human mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptor ligands. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 247:145–154
Sabatini, S., Hartsell, A., Meyer, M., Kurtzman, N.A., Hierholzer, K. 1993. Corticosterone metabolism and membrane transport. Mineral Electrolyte Metab. 19:343–350
Sariban-Sohraby, S., Burg, M., Wiesmann, W.P., Chiang, P.K., Johnson, J.P. 1984. Methylation increases sodium transport into A6 apical membrane vesicles: possible mode of action of aldosterone action. Science 225:745–746
Sariban-Sohraby, S., Fisher, R.S., Abramow, M. 1993. Aldosterone-induced and GTP-stimulated methylation of a 90-kDa polypeptide in the apical membrane of A6 epithelia. J. Biol. Chem. 268:26613–26617
Schafer, J.A., Hawk, C.T. 1992. Regulation of Na+ channels in the cortical collecting duct by AVP and mineralocorticoids. Kidney Int. 41:255–268
Schmidt, T.J., Husted, R.F., Stokes, J.B. 1993. Steroid hormone stimulation of Na+ transport in A6 cells is mediated via glucocorticoid receptors. Am. J. Physiol. 264:C875-C884
Schwabe, J.W.R., Chapman, L., Finch, J.T., Rhodes, D. 1993. The crystal structure of the estrogen receptor DNA-binding domain bound to DNA—how receptors discriminate between their response elements. Cell 75:567–578
Smith, D.F., Toft, D.O. 1993. Minireview—steroid receptors and their associated proteins. Mol. Endocrinol. 7:4–11
Smith, P.R., Saccomani, G., Joe, E.H., Angelides, K.J., Benos, D.J. 1991. Amiloride-sensitive sodium channel is linked to the cytoskeleton in renal epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:6971–6975
Spooner, P.M., Edelman, I.S. 1975. Further studies on the effect of aldosterone on electrical resistance of toad bladder. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 405:304–314
Stanton, B.A. 1986. Regulation by adrenal corticosteroids of sodium and potassium transport in loop of Henle and distal tubule of rat kidney. J. Clin. Invest. 78:1612–1620
Steinmetz, P.R. 1993. The reductionist approach to urinary acidification: scalar similarities. News Physiol. Sci. 8:282–286
Stewart, P.M., Wallace, A.M., Valentino, R., Burt, D., Shackleton, C.H.L., Edwards, C.R.W. 1987. Mineralocorticoid activity of licorice: 11-Beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency comes of age. Lancet 2:821–824
Stoos, B.A., Náray-Fejes-Tóth, A., Carretero, O.A., Ito, S., Fejes-Tóth, G. 1991. Characterization of a mouse cortical collecting duct cell line. Kidney Int. 39:1168–1175
Szerlip, H., Palevsky, P., Cox, M., Blazer-Yost, B. 1991. Relationship of the aldosterone-induced protein, gP70, to the conductive Na+ channel. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2:1108–1114
Tang, M.J., McDonough, A.A. 1992. Low K+ increases Na+-K+-ATPase alpha-subunit and beta-subunit messenger RNA and protein abundance in cultured renal proximal tubule cells. Am. J. Physiol. 263:C436-C442
Truscello, A., Gäggeler, H.P., Rossier, B.C. 1986. Thyroid hormone antagonizes an aldosterone-induced protein: a candidate mediator for the late mineralocorticoid response. J. Membrane Biol. 89:173–183
Truscello, A., Geering, K., Gaeggeler, H.P., Rossier, B.C. 1983. Effect of butyrate on histone deacetylation and aldosteronedependent Na+ transport in the toad bladder. J. Biol. Chem. 258:3388–3395
Truss, M., Bartsch, J., Hache, R.S.G., Beato, M. 1993B. Chromatin structure modulates transcription factor binding to the mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) promoter. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 47:1–10
Truss, M., Beato, M. 1993. Steroid hormone receptors—interaction with deoxyribonucleic acid and transcription factors. Endocr. Rev. 14:459–479
Tsukiyama, T., Becker, P.B., Wu, C. 1994. ATP-dependent nucleosome disruption at a heat-shock promoter mediated by binding of GAGA transcription factor. Nature 367:525–532
Tully, D.B., Allgood, V.E., Cidlowski, J.A. 1994. Modulation of steroid receptor-mediated gene expression by vitamin B-6. FASEB J. 8:343–349
Ueda, K., Okamura, N., Hirai, M., Tanigawara, Y., Saeki, T., Kioka, N., Komano, T., Hori, R. 1992. Human p-glycoprotein transports Cortisol, aldosterone, and dexamethasone, but not progesterone. J. Biol. Chem. 267:24248–24252
Verrey, F. 1990. Regulation of gene expression by aldosterone in tight epithelia. Semin. Nephrol. 10:410–420
Verrey, F. 1994. Antidiuretic hormone action in A6 cells: Effect on apical Cl and Na conductances and synergism with aldosterone for NaCl reabsorption. J. Membrane Biol. 138:65–76
Verrey, F., Digicaylioglu, M., Bolliger, U. 1993. Polarized membrane movements in A6 kidney cells are regulated by aldosterone and vasopressin/vasotocin. J. Membrane Biol. 133:213–226
Verrey, F., Kairouz, P., Schaerer, E., Fuentes, P., Geering, K., Rossier, B.C., Kraehenbuhl, J.P. 1989. Primary sequence of Xenopus laevis Na+-K+-ATPase and its localization in A6 kidney cells. Am. J. Physiol. 256:F1034–F1043
Verrey, F., Kraehenbuhl, J.P., Rossier, B.C. 1989. Aldosterone induces a rapid increase in the rate of Na,K-ATPase gene transcription in cultured kidney cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 3:1369–1376
Verrey, F., Schaerer, E., Zoerkler, P., Paccolat, M.-P., Geering, K., Kraehenbuhl, J.P., Rossier, B.C. 1987. Regulation by aldosterone of Na+,K+-ATPase mRNAs, protein synthesis, and sodium transport in cultured kidney cells. J. Cell Biol. 104:1231–1237
Vilella, S., Guerra, L., Helmle-Kolb, C., Murer, H. 1992. Aldosterone actions on basolateral Na+/H+ exchange in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Pfluegers Arch. 422:9–15
Wade, J.B., Stanton, B.A., Field, M.J., Kashgarian, M., Giebisch, G. 1990. Morphological and physiological response: time course and sodium dependence. Am. J. Physiol. 259:F88-F94
Walker, B.R., Campbell, J.C., Williams, B.C., Edwards, C.R.W. 1992. Tissue-specific distribution of the NAD+-dependent isoform of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Endocrinology 131:970–972
Wang, Z., Brown, D.D. 1991. A gene expression screen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:11505–11509
Watlington, C.O., Perkins, F.M., Muson, P.J., Handler, J.S. 1982. Aldosterone and corticosterone binding and effects on Na+ transport in cultured kidney cells. Am. J. Physiol. 242:F610-F619
Wehling, M. 1994. Novel aldosterone receptors—specificity-conferring mechanism at the level of the cell membrane. Steroids 59:160–163
Welling, P.A., Caplan, M., Sutters, M., Giebisch, G. 1993. Aldosterone-mediated Na/K-ATPase expression is alpha(1) isoform specific in the renal cortical collecting duct. J. Biol. Chem. 268:23469–23476
Wiener, H., Nielsen, J.M., Klaerke, D.A., Jørgensen, P.L. 1993. Aldosterone and thyroid hormone modulation of alpha-1-messenger RNA, beta-1-messenger RNA, and Na,K-pump sites in rabbit distal colon epithelium—Evidence for a novel mechanism of escape from the effect of hyperaldosteronemia. J. Membrane Biol. 133:203–211
Wills, N.K., Purcell, R.K., Clausen, C., Millinoff, L.P. 1993. Effects of aldosterone on the impedance properties of cultured renal amphibian epithelia. J. Membrane Biol. 133:17–27
Wolffe, A.P. 1994. Transcription—in tune with the histones. Cell 77:13–16
Wright, A.P.H., Zilliacus, J., McEwan, I.J., Dahlman-Wright, K., Almlof, T., Carlstedt-Duke, J., Gustafsson, J.A. 1993. Structure and function of the glucocorticoid receptor. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 47:11–19
Yamamoto, K., Ikeda, U., Seino, Y., Tsuruya, Y., Oguchi, A., Okada, K., Ishikawa, S.E., Saito, T., Kawakami, K., Hara, Y., Shimada, K. 1993. Regulation of Na,K-adenosine triphosphatase gene expression by sodium ions in cultured neonatal rat cardiocytes. J. Clin. Invest. 92:1889–1895
Yoshinaga, S.K., Peterson, C.L., Herskowitz, I., Yamamoto, K.R. 1992. Roles of SWI1, SWI2, and SWI3 proteins for transcriptional enhancement by steroid receptors. Science 258:1598–1604
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
I wish to thank Bernard Rossier, Jörg Beron and Gillian Hayes for reading the manuscript, Bernard Rossier, Alex Puoti, Haim Garty and Anikó Náray-Fejes-Tóth for the communication of unpublished results, and Christian Gasser for the artwork. The laboratory of the author is supported by Grant 31-39499-93 from the Swiss National Science Foundation and by the Olga Mayenfisch Stiftung, Zürich.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verrey, F. Transcriptional control of sodium transport in tight epithelia by adrenal steroids. J. Membarin Biol. 144, 93–110 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232796
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232796