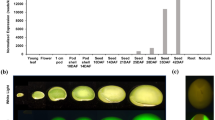
Summary
The 5′ and 3′ flanking regions of the soybean glycinin gene, Gy1, responsible for expression in seeds, were analyzed by quantitative transient expression assay. The construct containing the β-glucuronidase (uidA) reporter gene under the control of the 1.12 kb Gy1 promoter and 0.74 kb Gy1 terminator was introduced into immature soybean seeds and leaves by particle bombardment. To normalize the variability of introduction efficiency, a second reporter gene, firefly luciferase, was cobombarded as an internal standard, and relative activities (GUS/luciferase) were measured. There was a seed-specific β-glucuronidase (GUS) expression, as observed by X-Gluc staining. Compared with the nopaline synthase gene (nos) terminator, the Gy1 terminator enhanced the level of expression in immature seeds, indicating that the terminator region of the glycinin gene is involved in the activation of the gene expression in these seeds. To identify cis-regulatory elements in the glycinin gene upstream sequence, deleted derivatives of the promoter were fused to the luciferase reporter gene. The expression could be measured with a higher accuracy, and constructs were introduced with the internal reporter uidA gene into immature seeds. The results suggest the presence of a positive regulatory element in the −620 to −−380 region of the Gy1 promoter. A deletion which eliminates the legumin box with its RY element led to increased relative activity, suggesting that this box is negatively regulating expression of the seed storage protein gene. Analysis of mutant promoters also suggest that the RY element involves negative regulation in seeds. This quantitative transient expression assay using particle bombardment provides a reliable system for the study of seed-specific gene expression in soybeans.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GUS:
-
β-glucuronidase
- Gy1 :
-
glycinin AlaB2 gene
- CaMV:
-
cauliflower mosaic virus
- nos :
-
nopaline synthase gene
- uidA :
-
β-glucuronidase gene
- X-Gluc:
-
5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl glucuronide
References
Baumlein H, Boerjan W, Nagy I, Panitz R, Inze D, Wobus U (1991) Mol Gen Gent 225:121–128
Baumlein H, Nagy I, Villarroel R, Inze D, Wobus U (1992) The Plant J 2:233–239
Bradford MM (1976) Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bruce WB, Quail PH (1990) The Plant Cell 2:1081–1089
Bustos MM, Begum D, Kalkan FA, Battraw MJ, Hall TC (1991) The EMBO J 10:1469–1479
Callis J, Fromm M, Walbot V (1987) Genes & Development 1:1183–1200
Chamberland S, Daigle N, Bernier F (1992) Plant Mol Biol 19:937–949
Dehneke J, Gossele V, Botterman J, Cornelissen M (1989) Methods Mol Cell Biol 1:19–27
Fujiwara T, Beachy RN (1994) Plant Mol Biol 24:261–272
Gidoni D, Bond-Nutter D, Brosio P, Jones J, Bedbrook J, Dunsmuir P (1988) Mol Gen Genet 211:507–514
Goldberg RB, Barker SJ, Perez-Grau L (1989) Cell 56:149–160
Hamilton DA, Roy M, Rueda J, Sindhu RK, Sanford J, Mascarenhas JP (1992) Plant Mol Biol 18:211–218
Higuchi R (1989) In: Erlich H (ed) PCR Technology, pp. 61–70, Stockton Press, New York
Hill JE, Breidenbach RW (1974) Plant Physiol 53:742–746
Iida A, Seki M, Kamada M, Yamada Y, Morikawa H (1990) Theor Appl Genet 80:813–816
Itoh Y, Kitamura Y, Arahira M, Fukazawa C (1993) Plant Mol Biol 21:973–984
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) The EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Lanahan MB, Ho T, Rodgers SW, Rodgers JC (1992) Plant Cell 4:203–211
Lelievre JM, Oliveira LO, Nielsen NC (1992) Plant Physiol 98:387–391
Morikawa H, Chiba K, Irifune K, Iida A, Seki M, Nishihara M, Tanaka T, Yamashita T, Asakura N (1994) In: Yang N-S, Christou P (eds) Particle bombardment technology for gene transter. W.H. Freeman and Co. Publishers, New York, pp. 52–59
Nielsen NC, Dickinson CD, Cho TJ, Thanh VH, Scallon BJ, Fischer RL, Sims TL, Drews GN, Goldberg RB (1989) The Plant Cell 1:313–328
Ow DW, Wood KV, DeLuca M, Wet JR, Helinski DR, Howell SH (1986) Science 234:856–859
Sims TL, Goldberg RB (1989) Nucl Acids Res 17:4386
Walling L, Drews GM, Goldberg RB (1986) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:2123–2127
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Widholm
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iida, A., Nagasawa, A. & Oeda, K. Positive and negative cis-regulatory regions in the soybean glycinin promoter identified by quantitative transient gene expression. Plant Cell Reports 14, 539–544 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231934
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231934