Abstract
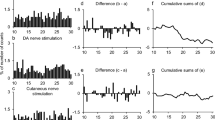
The possibility was investigated that stimulation of high-threshold afferents in the common peroneal nerve (CPN) evokes excitation of quadriceps (Q) motoneurones in humans. Effects of conditioning stimuli at motor threshold (1×MT) and at higher intensities were compared on both the Q H-reflex and the post-stimulus time histogram (PSTH) of individual motor units. At 1×MT, CPN stimulation evokes a facilitation, which has been shown to be caused by an interneuronally mediated group I excitation. Increasing the CPN stimulus intensity above 2×MT caused this early excitation to increase and a later facilitation to appear both in the H-reflex and in the PSTH of single units. The later excitation had its threshold between 2 and 3×MT, and it appeared 4–8 ms after the group I-induced excitation. The higher threshold and the longer latency suggest that this excitation is evoked by afferents with a smaller diameter than group I afferents, and group II afferents meet this criterion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cavallari P, Edgley SA, Jankowska E (1987) Post-synaptic actions of midlumbar interneurones on motoneurones of hind-limb muscles in the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 389:675–689
Corna S, Grasso M, Nardone A, Schiepatti M (1995) Selective depression of medium-latency leg and foot muscle responses to stretch by an α2-agonist in humans. J Physiol (Lond) 484:803–809
Dietz V (1992) Human neuronal control of automatic functional movements: interaction between central programs and afferent input. Physiol Rev 72:33–69
Eccles RM, Lundberg A (1959) Synaptic actions in motoneurones by afferents which may evoke the flexion reflex. Arch Ital Biol 97:199–221
Edgley SA, Jankowska E (1987a) Field potentials generated by group I and II muscle afferents in the middle lumbar segments of the cat spinal cord. J Physiol (Lond) 385:393–413
Edgley SA, Jankowska E (1987b) An interneuronal relay for group I and II muscle afferents in the midlumbar segments of the cat spinal cord. J Physiol (Lond) 389:647–674
Forget R, Pantieri R, Pierrot-Deseilligny E, Shindo M, Tanaka R (1989) Facilitation and quadriceps motoneurones by group I afferents from pretibial flexors in man. 1. Possible interneuronal pathway. Exp Brain 78:10–20
Fournier E, Meunier S, Pierrot-Deseilligny E, Shindo M (1986) Evidence for interneuronally mediated Ia excitatory effects to human quadriceps motoneurones. J Physiol (Lond) 377:143–169
Gracies JM, Pierrot-Deseilligny E, Robain G (1994) Evidence for further recruitment of group I fibres with high stimulus intensities when using surface electrodes in man. EEG Clin Neurophysiol 93:353–357
Hultborn H, Meunier S, Morin C, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (1987) Assessing changes in presynaptic inhibition of Ia fibres: a study in man and the cat. J Physiol (London) 389:729–756
Kernell D, Hultborn H (1990) Synaptic effects on recruitment gain: a mechanism of importance for the input-output relations of motoneurone pools? Brain Res 507:176–179
Lundberg A, Malmgren K, Schomburg ED (1987a) Reflex pathways from group II muscle afferents. 1. Distribution and linkage of reflex actions to alpha-motoneurones. Exp Brain Res 65:271–281
Lundberg A, Malmgren K, Schomburg ED (1987b) Reflex pathways from group II muscle afferents. 2. Functional characteristics of reflex pathways to α-motoneurones. Exp Brain Res 65:282–293
Lundberg A, Malmgren K, Schomburg ED (1987c) Reflex pathways from group II muscle afferents. 3. Secondary spindle afferents and the FRA: a new hypothesis. Exp Brain Res 65:294–306
Matthews PBC (1972) Mammalian muscle spindles and their central action. Arnold, London
Meunier S, Pierrot-Deseilligny E, Simonetta-Moreau M (1993) Pattern of monosynaptic heteronymous Ia connections in the human lower limb. Exp Brain Res 96:533–544
Meunier S, Pierrot-Deseilligny E, Simonetta-Moreau M (1994) Pattern of heteronymous recurrent inhibition in the human lower limb. Exp Brain Res 102:149–159
Nielsen J, Kagamihara Y (1993) Differential projection of the sural nerve of early and late recruited human tibialis anterior motor units: change of recruitment gain. Acta Physiol Scand 147:385–401
Rossi A, Mazzocchio R (1991) Presence of homonymous recurrent inhibition in motoneurones supplying different lower limb muscles in humans. Exp Brain Res 84:367–373
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marque, P., Pierrot-Deseilligny, E. & Simonetta-Moreau, M. Evidence for excitation of the human lower limb motoneurones by group II muscle afferents. Exp Brain Res 109, 357–360 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231793
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231793