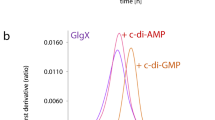
Summary
We have recently reported the existence of two forms of glycogen phosphorylase (1,4-α-D-glucan: orthophosphate-α-glucosyltransferase; EC 2.4.1.1) in Dictyostelium discoideum. During development the activity of the glycogen phosphorylase b form decreased as the activity of the a form increased. The total phosphorylase activity remained constant. The physical and kinetic properties of the Dictyostelium enzyme were similar to those of the mammalian enzyme. In mammals, cAMP regulates the conversion of the two forms by a cAMP dependent protein kinase (cAMPdPK). We report here that if cAMP is added to a single cell suspension, the Dictyostelium phosphorylase activity becomes independent of 5′AMP and a 104kd peptide appears. We also show the effect of several cAMP analogs on the phosphorylase activity in these single-cell suspensions. The cAMP analogs were selected on the basis of their affinities for the membrane-bound cAMP receptor or the cytoplasmic cAMPdPK. We found that relatively low levels, 100 μM, of cAMP or 2'd-cAMP added to aggregation-competent cells in shaking culture caused a loss of phosphorylase b activity and the appearance of phosphorylase a activity. The analog, 2'd-cAMP, has a high affinity for the cAMP receptor but a low affinity for the cAMPdPK. Two other analogs, Bt2-cAMP and 8-Br-cAMP, which have low affinities for the cAMP receptor but high affinities for the cAMPdPK, required high levels (500 μM) for ‘b’ to ‘a’ conversion. cDNAs to three cAMP-regulated genes-PL3, Dll, and D3-were used as controls in the above experiments. In order to determine if intracellular levels of cAMP were involved in the regulation of phosphorylase activity, both the phosphorylase and the PL3, D11 and D3 mRNA levels were examined in cells suspended in a glucose/albumin mixture - a medium in which adenylate cyclase is inhibited. Under these conditions, neither gene regulation nor a change in the phosphorylase b to a activity occurred in response to added extra cellular cAMP. The results suggest that an intracellular increase in cAMP is involved in the regulation of the two forms of glycogen phosphorylase in Dictyostelium.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGTA:
-
Ethyleneglycol-bis-(β-aminoethyl ether)
- N,N,N′:
-
N′-tetra acetic acid
- SDS:
-
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate
- PAGE:
-
Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
References
Loomis WF: Dictyostelium discoideum, A Development System, Academic Press, New York, 1975, pp 1–6
Wright BE, Dahlberg D: Cell wall synthesis in Dictyostelium discoideum II. Synthesis of soluble glycogen by a cytoplasmic enzyme. Biochemistry 6: 2074–2079, 1967
Wright BE, Simon W, Walsh BT: A kinetic model of metabolism essential to differentation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 60: 644–651, 1968
Konijn TM, Barkley D, Chang YY, Bonner J: Cyclic AMP-a naturally occurring acrasin in the cellular slime molds. Amer Natur 102: 225–233, 1968
Bonner JT, Barkley DS, Hall EM, Konijn TM, Mason NW, O'Keefe G, Wolfe PB: Acrasin, acrasinase, and the sensitivity to acrasin in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol 20: 72–87,1969
Rutherford CL, Vaughan RL, Cloutier MJ, Naranan V, Brickey DA, Ferris DK: Compartmentation in Dictyostelium. Ann Rev Microbiol 39: 271–298, 1985
Fisher EH, Kreb E: Conversion of phosphorylase ‘b’ to phosphorylase ‘a’ in muscle extracts. J Biol Chem 216: 121–133,1955
Cohen P: The role of cAMP dependent protein kinase in the regulation of glycogen metabolism in mammalian skeletal muscle. Curr Top Cell Regul 14: 117–197, 1978
Jones THD, Wright BE: Partial purification and characterization of glycogen, phosphorylase of Dictyostelium discoideum spores. J Bacteriol 104: 754–761, 1970
Firtel RA, Bonner JT: Developmental control of 1–4 glucanphosphorylase in the cellular slime mold, Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol 29: 85–103, 1972
Rutherford CL, Harris JF: Localization of glycogen phosphorylase in specific cell types of Dictyostelium discoideum. Arch Biochem Biophys 175: 453–462, 1976
Higgins RC, Dahmus ME: Glycogen phosphorylase synthesis in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem 257: 5068–5076,1982
Thomas DA, Wright BE: Glycogen phosphorylase in Dictyostelium discoideum. Part 1: Purification and properties of the enzyme. J Biol Chem 251: 1253–1257, 1976
Thomas DA, Wright BE: Glycogen phosphorylase in Dictyostelium discoideum. Part 2: Synthesis and degradation during differentiation. J Biol Chem 251: 1258–1263, 1976
Rahmsdorf HJ, Gerish G: Specific binding proteins for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP in Dictyosteliu, discoideum. Cell Differentiation 7: 249–258, 1978
Veron M, Patte JC: Intracellular cyclic AMP binding protein in Dictyostelium discoideum, differences in properties of the proteins from vegetative and differentiated cells. Dev Biol 63: 370–376, 1978
Takeuchi I, Sakai Y: Dedifferentiation of the disaggregated slug cell of the cellular slime mold, Dictyostelium discoideum. Develop Growth Differ 13: 201–210, 1971
Takemoto S, Okamoto K, Takeuchi I: The effects of cyclic AMP on disaggregation induced charges in activities of developmentally regulated enzymes in Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 80: 858–865, 1978
Okamoto K, Takeuchi I: Changes in activities of two developmentally regulated enzymes induced by disaggregation of the pseudoplasmodia Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 72: 739–746, 1976
Rutherford CL, Taylor RD, Frame LT, Auck RL: A cyclic AMP dependent protein kinase in Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 108: 1210–1220, 1982
de Gunzburg J, Veron A: A CAMP dependent protein kinase is present in differentiating Dictyostelium discoideum cells. EMBO J 9: 1063–1068, 1982
Leichtling BH, Majerfield IH, Coffman DS, Rickenberg HV: Identification of the regulatory subunit of a cAMP dependent protein kinase in Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 105: 949–955, 1982
Rutherford CL, Cloutier MJ: Identification of two forms of glycogen phosphorylase in Dictyostelium. Arch Biochem Biophys 250: 435–439, 1986
Cloutier MJ, Rutherford CL: Glycogen phosphorylase in Dictyostelium: Developmental regulation of two forms and their physical and kinetic properties. J Biol Chem 262: 1102–1106,1987
Pahlic M, Rutherford CL: Adenylate cyclase activity and cyclic AMP levels during the development of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem 254: 9703–9707, 1979
Kimmel AR: Different molecular mechanisms for CAMP regulation of gene expression during Dictyostelium discoideum development. Dev Biol 122: 163–171, 1987
Oyama M, Blumberg DD: Interaction of cAMP with the cell surface receptor induces cell type specific mRNA accumulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 4319–4323, 1986
Oyama M, Blumberg DD: Changes during differentiation in requirements for cAMP for expression of cell type specific mRNAs in the cellular slime mold, Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol 117: 550–556, 1986
Oyama M, Blumberg DD: Cyclic AMP and NH3/NH4 + both regulate cell type specific mRNA accumulation in the cellular slime mold, Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol 117:557–566,1986
Haribabu B, Dottin R: Pharmacological characterization of cyclic AMP receptors mediating gene regulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol 6: 2402–2408, 1986
Sussman RR, Sussman M: Cultivation of Dictyostelium discoideum in axenic medium. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 29: 53–55, 1967
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J: Molecular Cloning, A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratories, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 1982, pp 109–112
Mehdy MC, Ratner D, Firtel RA: Induction and modulation of cell type specific gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell 32: 763–771, 1983
Dahmus ME: Purification and properties of calf thymus casein kinases I and II. J Biol Chem 256: 3319–3335, 1981
Schaap P, van Driel R: Induction of post aggregative differentiation in Dictyostelium discoideum by CAMP-evidence for involvement of the cell surface receptor. Exp Cell Res 159:388–399,1985
Mann SKO, Firtel RA: Cyclic AMP regulation of early gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum: mediation via the cell surface cyclic AMP receptor. Moll Cell Biol 7: 458–469,1987
Collins MKL, Rozengurt E: Binding of phorbol esters to high affinity sites on murine fibroblastic cells elicits a mitogenic response. J Cell Phys 112: 42–50, 1982
Loomis WF: The Development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Academic Press, New York, 1982, p 338
Okamoto K, Takemoto S, Kato K, Takeuchi I: Changes in activity of enzymes associated with prespore differentiation in suspension culture of Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Acta 716: 94–100, 1982
Gomer RH, Armstrong D, Leichtling BH, Firtel RA: cAMP inductions of prespore and prestalk gene expression in Diciyostelium is mediated by the cell-surface CAMP receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 8624–8628, 1986
Kay RR, Noce T, Tsang AS: Translocation of an unusual cAMP receptor to the nucleus during development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 2322–2326,1987
Behrens MM, Mazon MJ: Yeast cAMP dependent protein kinase can be associated to the plasma membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 151: 561–567,1988
Meier K, Klein C: An unusual protein kinase phosphorylates the chemotactic receptor of Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 2181–2185, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brickey, D.A., Naranan, V., Sucic, J.F. et al. Regulation of the two forms of glycogen phosphorylase by cAMP and its analogs in Dictyostelium discoideum . Mol Cell Biochem 97, 17–33 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231698
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231698